Diner
advertisement

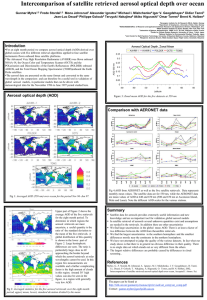
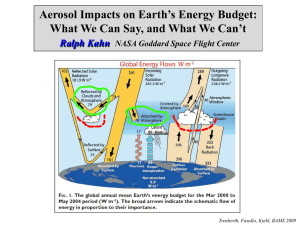
CalWater-2, MISR, and AirMSPI CalWater 2015 Planning Workship La Jolla, CA 23 April 2014 D.J. Diner, M.G. Tosca, M.J. Garay, O.V. Kalashnikova, and F. Xu Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology © 2014 California Institute of Technology. Government sponsorship acknowledged. Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) Airborne Multiangle SpectroPolarimetric Imager (AirMSPI) 446, 558, 672, 866 nm 355, 380, 445, 470*,555, 660*, 865*, 935 nm (*polarimetric) Flying on Terra since 1999 705 km flight altitude Multiangle viewing between ±70º Spatial resolution: 275 m Flying on NASA ER-2 since 2010 20 km flight altitude Multiangle viewing between ±67º 1 Spatial resolution: 10 m Dust source characterization - 1 Transport models such as NAAPS predict dust trajectories, but need reliable source locations and emission strengths Plume height 3 km 2 km 1 km 0 km ASIA: MISR 9-angle animation and stereo retrieval of dust plume height in Gobi Desert, 30 March 2007 MIDDLE EAST: Increasing prevalence of sandstorms 2 Dust source characterization - 2 AFRICA 0.02 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 0.01 Aerosol Optical Depth (558 nm) AOD retrieval over bright land areas 0.12 0.24 0.36 0.48 Nonspherical Aerosol Optical Depth Fraction Particle shape discrimination 0.60 0.1 0.6 1.3 1.9 2.6 >3.2 Frequency of Wind Speeds Greater Than 20 m/s Cloud- and plume-tracked wind retrievals MISR CAPABILITY 3 MISR aerosol observations over CA Central Valley Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Map of Central California from 20 January 2013 showing MISR retrievals of AOD at 4.4 km resolution. Diamonds are ground-based AERONET DRAGON sites colored by AOD. Regression plot is also shown. 4 Example AirMSPI aerosol retrieval during SEAC4RS Southern Arkansas, 23 Aug 2013, 1617 UTC Elevated, transported smoke present in scene 29.1º view zenith angle Radiance 445, 555, 660 nm Degree of linear polarization 470, 660, 865 nm Spatially Averaged 4STAR (30 min average) vs. AirMSPI (spatial average) AOD 0.998 0.6 4STAR AOD AirMSPI AOD scattering Single albedo Single Scattering Albedo (Imag) depth Aerosol optical AOD 0.5 4STAR sunphotometer on DC-8: Mean and stdev over 30 min window 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 200 AirMSPI: Spatial mean and stdev Aerosol over entire scene retrievals run at JPL using Univ. of Lille GRASP code, courtesy O. Dubovik 0.996 0.994 0.992 0.99 0.988 0.986 400 600 800 1000 Wavelength 1200 Wavelength (nm) 1400 1600 0.984 300 400 500 600 700 Wavelegnth (nm) Wavelength (nm) 800 900 5 Polarimetric sensitivity to aerosol particle size Monomodal aerosol model Median particle radius 0.06 mm Both models are consistent with MISR radiance-only data. AirMSPI polarimetry distinguishes them model observations Bimodal aerosol model 40% fine mode, median particle radius = 0.03 mm 60% coarse mode, median particle radius = 1.00 mm Aerosol bow due to larger particles in model—not seen in degree of linear polarization (DOLP MISR image off the California coast, 19 July 2012 6 AR cloud height and wind retrievals from MISR m/s 21 Dec 2010 mid-level clouds SSMI Water Vapor Imagery (yellows, reds = high vapor content) MISR heightresolved wind vectors show details of the flow within landfalling atmospheric rivers low clouds high clouds height (m) 7 Cloud height and wind retrievals from AirMSPI AirMSPI flight transects across atmospheric rivers will allow simultaneous retrieval of cloud height and wind speed at high spatial resolution (~100 m) As with MISR, stereo retrievals are purely geometric no dependence on atmospheric temperature profile accurate height assignments of winds 26.5º forward: 19:44 UTC Nadir: 19:45 UTC 26.5º backward: 19:46 UTC 8 AirMSPI cloud-top drop size retrieval over warm clouds glory primary cloudbow supernumerary bows 6 August 2013 1859 UTC The cloudbow, glory, and supernumerary bows indicate spherical drops 0.80 0.60 Offset peaks cause colored fringes 0.40 P12 0.20 An effective droplet radius of 12 mm fits the data well 0.00 -0.20 -0.40 470 nm data 660 nm data (+0.3) 865 nm data (+0.6) -0.60 470 nm model 660 nm model (+0.3) 865 nm model (+0.6) -0.80 135 140 145 150 155 Scattering angle (deg) 160 165 170 9 Identification of ice clouds in polarized light from AirMSPI scattering angle of subsun 1 February 2013 2111 UTC Absence of glory or cloudbows indicates nonspherical particles. Subsun implies horizontally-oriented ice crystal plates. Polarized radiance vs. scattering angle optical depth and crystal habit (Chepfer et al., 1998; van Diedenhoven et al., 2012, Cole et al., 2013) Cloud Physics Lidar (CPL) data show a high-altitude cloud layer above lower cloud credit: J. Yorks, W. Hart 10 Conclusions MISR multiangle radiance and AirMSPI multiangle radiance/polarization observations provide contextual aerosol and cloud microphysics, height, and wind data to complement other CalWater measurements • These data provide environmental constraints on factors governing precipitation rates • The combination of MISR, AirMSPI, and CALIPSO could be used to improve optical models of transported Pacific dust A second-generation instrument, AirMSPI-2, is being readied for initial flights in fall 2014. AirMSPI-2 adds O2 A-band and shortwave infrared (SWIR) channels • Multiangle O2 A-band observations are sensitive to cloud geometric thickness • SWIR channels enable MODIS-like joint retrievals of cloud optical depth and particle size 11