gerunds
advertisement
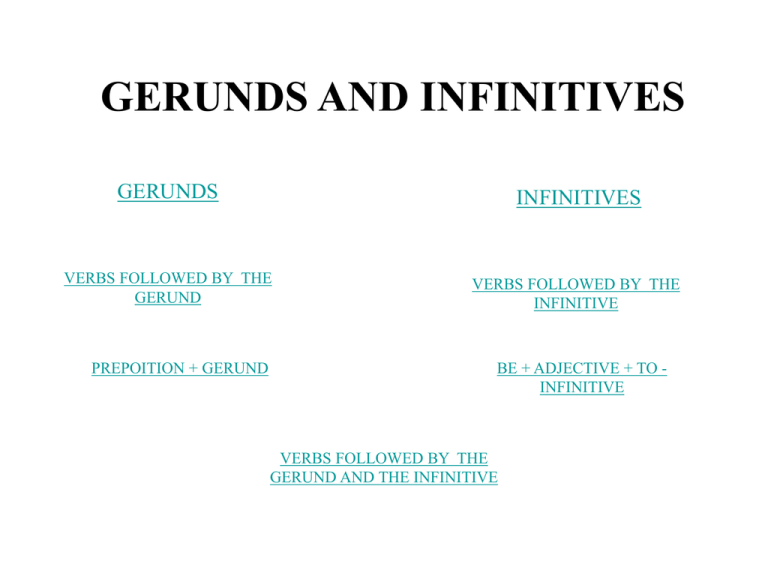
GERUNDS AND INFINITIVES GERUNDS INFINITIVES VERBS FOLLOWED BY THE GERUND VERBS FOLLOWED BY THE INFINITIVE PREPOITION + GERUND BE + ADJECTIVE + TO INFINITIVE VERBS FOLLOWED BY THE GERUND AND THE INFINITIVE GERUNDS The gerund describes an activity. It does not indicate a time sequence. Example We enjoyed seeing you last weekend. VERBS FOLLOWED BY THE GERUND The verbs enjoy, detest, hate, love, stop, advise, don’t mind, imagine, feel like, sugest, practice, miss and can’t stand are followed by a gerund. Examples I advise finding a good lawyer. I hope they stop making so much noise so I can get some sleep. I hate studying I hate studying. I enjoy listening to music. PREPOSITIONS + GERUNDS Prepositions such as aggre with, after, admit to, believe in, complain about, confess to, talk about, forget about, worry about are followed by the gerund. Example I agree with playing darts. INFINITIVES Infinitives are the "to" form of the verb. The to-infinitive after a verb often describes a future event, and event following the main verb. For example, after hope, expect, promise, want, the event in the to-infinitive comes after the activity or thought in the main verb. Example I hope to watch “scream” next week. (future event) VERBS FOLLOWED BY THE INFINITIVES The verbs, agree, hope, promise, ask, learn, expect, decide, afford, offer, choose, and want are followed by a verb in the infinitive form. Examples I promise to buy a house. I decided to eat a sandwich. They offered to buy the clothes. BE + ADJECTIVE + TO - INFINITIVE The verb in the infinitive often refers to an event in the future. Examples Wer’e sure to have a good time They are willing to lend us the money We can use adjective of feeling, adjectives describing personal characteristics + ofperson, adjectives describingthe activity before the to-infinitive. Examples I’m pleased to see you. This book is very difficult to read. It’s good of you to come. My friend is very amusing to talk to. It was selfish of me to ignore you. VERBS FOLLOWED BY THE GERUND AND THE INFINITIVE The verbs, love, like, hate, prefer, begin, start, be, remember, forget, stop, go on, begin, continue, advise, allow, encourage, forbid, recommend are followed by either and infinitive or a gerund. NO DIFFERENCE IN MEANING. Examples I started to shout = I started shouting I love to read = I love reading. I hate to wait I hate to wait = I hate waiting