Rhetoric Terms PowerPoint
advertisement

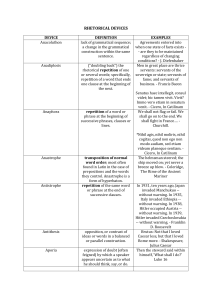
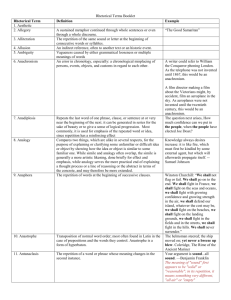
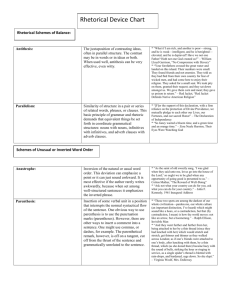
Scheme Scheme • An artful deviation from the ordinary arrangement of words Trope Trope • An artful deviation from the ordinary significance of a word Parallelism Parallelism • Similarity of structure in a pair or series of related words, phrases, or clauses [adds balance, rhythm and clarity] Climactic Parallelism Climactic Parallelism • The arrangement of w/p/c in an order of increasing importance, often in parallel structure. Isocolon Isocolon • A series of similarly structured elements having the same length, emphasizing similarity of elements. Antithesis Antithesis • Contrast of ideas or words in a balanced or parallel construction [useful for making distinctions or for clarifying differences which might be otherwise overlooked by a careless thinker or casual reader] Juxtaposition Juxtaposition • A device in which normally unassociated ideas, words, or phrases are placed next to one another, especially for comparison or contrast [often creates an effect of surprise and wit] Paradox Paradox • A self-contradictory statement that reveals a deeper truth Oxymoron Oxymoron • Placing two ordinarily opposing terms adjacent to one another Listing Listing • A series of items one after the other, designed to create a feeling of plenty Ellipsis Ellipsis • Omission of a word or shot phrase easily understood in context Asyndeton Asyndeton • Omission of conjunctions between coordinate phrases, clauses, or words, often resulting in a hurried rhythm or vehement effect. (the counterpart to polysyndeton) [often used for strong and direct climactic effect] Paralepsis Paralepsis • Emphasizing a point by seeming to pass over it [allows the speaker to make the listener assume a difficult point] Rhetorical Question Rhetorical Question • A question that does not need to be answered, because the answer is obvious, and is usually just yes or no [used to provoke the audience to your conclusion] Rhetorical Fragment Rhetorical Fragment • A sentence fragment [used deliberately for persuasive purpose] Repetition Repetition • A device in which words, sounds, and ideas are used more than once [used to enhance rhythm and to create emphasis] Synonymia Synonymia • The use of several synonyms together to amplify or explain a subject or term Anadiplosis Anadiplosis • Repetition of a word (or phrase) from the previous line, clause, or sentence at the beginning of the next. [next for emphasis of a main idea] Anaphora Anaphora • Repetition of a word, phrase, group of words at the beginning of successive clauses Epanalepsis Epanalepsis • Repetition at the end of a line, phrase, clause or sentence of the word that occurred at the beginning of the same line, phrase, clause, or sentence [calls special attention to a word] Epimone Epimone • Frequent repetition of a phrase or question; dwelling on a point Epistrophe Epistrophe • Repetition of a word or phrase at the end of successive clauses [adds emphasis to an important concept] Parenthesis Parenthesis • Insertion of some word or clause in a position that interrupts the normal syntactic flow of the sentence (asides are emphatic examples of this) [creates the effect of immediacy: you are relating some fact when suddenly something very important arises, or else you cannot resist an instant comment, so you just stop the sentence] Polysyndeton Polysyndeton • The repetition of conjunction in a series of coordinate words, phrases, or clauses, often slowing the tempo or rhythm [used to attempt to encompass something complex, highlight quantity or mass of detail or to create flowing, continuous sentence pattern] Chiasmus / Antimetabole Chiasmus / Antimetabole • A sentence strategy in which the arrangement of ideas in the second clause in a reversal of the first Stichomythia Stichomythia • Dialogue in which the endings and beginnings of each line echo each other, taking on a new meaning with each new line Zeugma Zeugma • The use of a verb that has two different meanings with objects that complement both meanings