Anecdotal & Stacked Evidence: Logical Fallacies Explained
advertisement

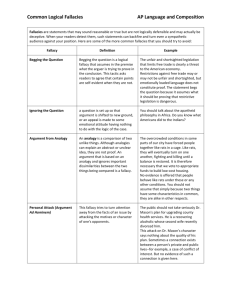
Logical Fallacy: Anecdotal and Stacked Evidence Cameron Knight Definition • Anecdotal Evidence: Supporting your argument with a personal story. • Stacked Evidence (Card Stacking): When your argument is one sided and doesn’t address a counter argument. You only use evidence that is helpful to your point. (Like how most of us write!) Examples Anecdotal Evidence Yeah, I've read the health warnings on those cigarette packs and I know about all that health research, but my brother smokes, and he says he's never been sick a day in his life, so I know smoking can't really hurt you. Stacked Evidence Richard Nixon was a family man, an experienced politician, and world-known. Let's build him the national monument he deserves! Reflection on example Anecdotal Evidence - Says smoking can’t hurt because his brother smokes and he's never been sick from it. Used a personal story to prove his point. Stacked Evidence Praises the good aspects of Richard Nixon and ignores the bad. Citation • Acker, Christine. “Rhetorical Fallacies.” Undergraduate Writing Center Handouts. July 2006. Texas University. http://projects.uwc.utexas.edu/handouts/? q=node/30 • Dowden, Bradley. “Fallacies.” Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 2009. California State University, Sacramento. http://www.iep.utm.edu/f/fallacy.htm#Anec dotal%20Evidence