Sophocle’s Tragedy
Oedipus the King
The Greek Theatre
First performed on the stone threshing
floors, a circular “dancing place” or
orchestra in the country side of Greece.
Moved to the foot of a temple of the god
being honored. The temple served as a
background for early performances.
5th Century, completed design included its
early connections to the rural stone
threshing floors.
Greek Theatre’s Design
The builders positioned the orchestra at the
foot of a semi circular hillside into which
stone benches, the seeing place” or
theatron, were built.
Extending from the orchestra to each side of
the theatron were two broad aisles, the
parados, the term which identified the
entrance for the chorus in a tragedy.
Perpendicular to the orchestra was the
skene, a rectangular building with three
doors in the front, providing a backdrop for
the play as well as an area where the actors
could exit the scene.
Towards the end of the century, a small
platform, the proskenion, in the front of the
skene appeared to give the actor more
visibility and to separate them from the
chorus.
The Greek Actor
Participating in Greek drama was considered to be a citizen’s civic duty.
Women were not allowed to act. They were often excluded from the
audience or made to sit in the upper rows of the theatron.
The actor portraying a god, king, or legendary hero needed to appear larger
than life, so he donned a costume, which added size and distinction to his
role. (The actor wore a long, flowing robe, dyed in symbolic colors, called a
chiton, with a lot of padding.)
Platformed shoes, cothurni, were worn to add height.
Because of the distance of the audience, the actor used wide sweeping
gestures, which signified particular emotions, such as lowering the head to
indicate grief.
Properties, props, were carried to indicate roles. For example, a king would
carry a scepter, or a warrior would carry a spear.
A mask was worn to identify a specific character, yet generalized the
features enough to indicate the Everyman, helping the audience to glean
that personal message the Greeks intended to impart in their drama.
The Mask, the Persona
The mask served as a megaphone
with the large aperture for the
mouth, and as a symbol to
distinguish the role.
It also served to identify the age,
sex, mood, and rank of the
character.
The mask rested on the shoulders
and was constructed of bark, cork,
leather, or linen.
The most beautiful masks were
tragic; the most grotesque and
bizarre were reserved for comedy.
The flexibility of changing masks
allowed actors to change roles
easily.
The Dramatic Structure
Theorists believe that the dramatic structure of a Greek tragedy influenced the eventual
division of a play into acts and scenes.
The Greek tragedy is divided into five distinct sections:
1. The Prologue (Prologos): The opening portion of the play. Sets the scene and
contains the exposition.
2. The Parados: The entrance song of the chorus. The parados is named after the
broad aisles on either side of the theatron, along which the chorus entered or exited.
3. The Episodes (Scenes): Scene in the action of the drama. The episodes, performed
by the actors, are distinguished from the stasimons, performed by the chorus. The
episodes alternate with the stasimons.
4. The Stasimons (Odes): A choral passage, alternating with the episodes of the plot of
the drama. The ode is a type of lyric poem, using exalted, dignified diction, a poetic
form created for the choral passages. The chorus sang and danced the tragic odes,
accompanied by musical instruments. The tragic ode consisted of strophes and
antistrophes, essentially stanzas of the poems. Historians suggest that the chorus
sang the strophe, dancing in one direction around the orchestra, changing directions
with the antistrophe.
5. Exodus: The concluding section of the tragedy. The exodus ends with the chorus
singing their final lines as they exit.
For Oedipus the King the dramatic structure of the
play observes the following order:
Prologue (Prologus)
Parados
Scene 1 (Episode 1)
Ode 1 (Stasimon 1)
Scene 2 (Episode 2)
Ode 2 (Stasimon 2)
Scene 3 (Episode 3)
Ode 3 (Stasimon 3)
Scene 4 (Episode 4)
Ode 4 (Stasimon 4)
Exodus
After preparing the plot by way of the exposition, the conflict is introduced,
complicated by the rising action of the play to the point of climax, the crisis
or turning point of the play, the point at which the potential for that particular
action, born of the conflict, is realized. What remains is falling action, during
which the action simplifies or unravels. The play ends in resolution,
revealing the meaning of all that has proceeded it.
The Importance of Debate
Greek tragedy relies on the ear more than the eye to reach its audience.
Therefore, rhetoric is its chief component. The Ancient Greeks, a society
accustomed to listening, conducted their civic affairs in open, formal debate
and based their public choices on the persuasive effectiveness of orators.
Citizens accepted patterns of debate- established through open law court
practice, with speeches of equal length delivered by opposing sides, and
accusations, met by rebuttals- as appropriate rhetorical means of resolving
differences. The scientific method of observations and analysis had its
beginnings in Ancient Greece.
The Ancient Greeks sought balance, order, and symmetry, which is reflected
in their art and architecture, as well as literature.
Greek playwrights reflected the beliefs and practices of their society.
Therefore, Greek tragedies were complete with examples of long rhetorical
speeches, discussions between characters structured as debates, and
themes reflecting man’s struggle between the rational and irrational.
Playwrights developed a poetic device, called stichomythia (“line talk”), in
which single lines of verse dialogue alternate between two characters in a
ping-pong fashion. The device assisted the audience in distinguishing who
was speaking, and provided an appropriate form for the verbal parrying of
argumentation.
Stichomythic Dialogue
Stichomythia was used by the Greek and Roman tragedians as a
technique for providing contrast to lengthy speeches and choral
speeches, of which their plays are principally composed. Ordinarily,
the passages of stichomythia occur at moments of high tension or
conflict between the characters.
Stichomythia may be used to present thesis and counter thesis,
question and answer, or argument and refutation. In its best form,
the structure of the lines is nearly parallel, and cue words lead the
thought from one speech to the next. A variation of the technique is
antilabe, in which a single verse line is broken up between alternate
speakers. This creates an intense dramatic effect.
Ancient playwrights used stichomythia to distinguish for the
audience one masked actor from another, to separate the long ,
rhetorical speeches, and to provide appropriate form for
argumentation, thus heightening audience emotion.
What are the characteristics of
stichomythia in this example.
Creon: Now listen to me. You have talked; let me talk too.
You can not judge unless you know the facts.
Oedipus: You speak well; there is one fact: but I find it hard
to learn from the deadliest enemy I have.
Creon: That above all I must dispute with you.
Oedipus: That above all I will not hear you deny.
Creon: If you think there is anything good in being stubborn
against all reason, then I say you are wrong.
Oedipus: If you think a man can sin against his own kind
and not be punished for it, I say you are mad.
The Role of the Chorus
Provides a link from audience to actors that responds to the play in a
manner the playwright hoped- the ideal spectator.
Provides tension release.
Reflects upon what has happened: ponders what might happen, asks
questions.
Advises the central character.
Is the conscience of the people.
Establishes mood and heightens dramatic moments.
Adds theatrically to the performance.
Helps to establish important pacing of the play , pointing out moments for
the audience to reflect upon.
Can be in the play, as a participant (Choragos), or outside as an observer.
Separates scenes of action from one another.
Usually through a leader or spokesperson (Choragos), could interact with
the central characters
Characteristics of the Greek
Chorus
Group of approximately 15 men
Sang lyric poetry and danced
Were unpaid
Drawn from the citizenry at large, a civic
duty
Were trained and costumed
Wore the dress of the people they
represented and wore light masks
Archetype
1.
2.
A basic model from which copies are made: therefore
a prototype.
In general terms, the abstract idea of a class of things
which represent the most typical and essential
characteristics shared by a class.
The fundamental facts of human existence are archetypal:
birth, growing up, love, family and tribal life, dying,
death, the struggle between parents and children, and
fraternal rivalry etc.
Certain character or personality types are archetypal: the
rebel, the Don Juan, the hero, the villain, the traitor, the
snob, the siren, the social climber etc.
Animals, things, and themes can also be archetypal: the
lion, the eagle, the rose, and the quest or journey.
Characteristics of the
Archetypal Hero
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Born the son of a distinguished fatherA “dream” showed child as a danger to the fatherUsually surrendered to the water to kill the childSaved by animals or lowly people such as shepherdsAs an adult, found his natural parentsTook revenge on his father and was rightful heir to the
throneAchieved rank and honor-
Themes
1. The quest2. The King as the sacrificial scapegoat-
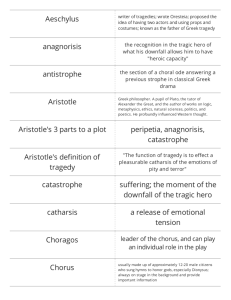
The Classical Definition of Tragedy
Aristotle beginsTragedy, then, is an imitation of an action that is
serious, complete, and of a certain magnitude:
in language embellished with each kind of
artistic ornament, the several kinds being
found in separate parts of the play: in the form
of action, not of narrative; through pity and fear
effecting the proper purgation for these
emotions.
The following are facets of
Aristotle’s definition:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
The writer of tragedy imitates a serious and complete action, of a
certain magnitude, represented by what is said and done on
stage.
The “action” taken is the rational purpose of the play.
The elements of pathos, a scene of suffering, is essential to the
whole.
Plot is the arrangement of carefully selected, carefully sequenced,
tragic incidents to represent one complete action.
The plot consists of parts or types of incidents in the beginning,
middle, and end of the play such as prologos, episodes, pathos,
and tragic recognition.
Plots may be simple, complex, ethical or pathetic. Complex plots
include peripeteia and tragic recognition.
The story must be probable.
Plot is divided into two main parts: complication and denouement.
9. The play is unified by a single action and single catastrophe.
10. The central action of the play springs from character and thought,
manifested in the dialogue.
11. The chorus represents the action of the play.
12. Characters contrast sharply with one another and reflect the central
action of the play in the development of the character.
13. The tragic hero should be a ruler or leader, whose character is good
and whose misfortune is brought about by some error or frailty.
14. Language should be elevated in the form of today’s blank verse and
should reflect persuasion in the Episodes and Choric Odes.
15.The special quality of man’s pleasure in tragedy comes from the
purgation of the passions of fear and pity felt by the audience as
they watch the fate of the tragic hero unfold, recognizing in it the
universal human lot.
The End