Past Modals
advertisement

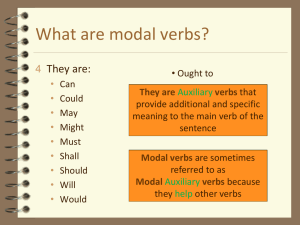
I – MODALS II - PAST MODALS MODALS - I Must Mustn't Obligation? Necessity? prohibition? Have to Don't have to Ought to Lack of obligation? Lack of necessity Should Shoudn't Need to Needn't Advice? recommendation? Must: obligation Mustn't: prohibition Have to: obligation Don't have to: lack of necessity Ought to: advice/recommendation Should: advice/recommendation Shoudn't: advice/recommendation Need to: necessity Needn't: lack of necessity How strong is the obligation? ● You must ● You have to ● You need to ● You ought to ● You should ● You can/could ● You may ● Which one means a good idea/advice? A possibility?an obligation? NEED – Is it necessary? ● ● ● ● You need to check all the information on your CV. You needn't translate it into English. The Italian version is enough. Need: to express necessity Needn't: No necessity – lack of obligation (you don’t need to) Modals of likelihood Probability? Certainty? Possibility? Match the level of likelihood to modal verb. ● Certain Might, May, Could ● Possibility Should, Ought to, Would ● Probable To be going to, Will (using the future) Match the level of likelihood to modal verb. Key ● Certain To be going to, Will (using the future) ● Possibility Might, May, Could ● Probable Should, Ought to, Would ● ● ● ● Certain: To be going to, Will (using the future) The company will pay for the extra costs. It has enough financial resourses. Possibility: Might, May, Could The parcel may arrive late I only sent it yesterday by ordinary post. ● Probable: Should, Ought to, Would ● eg: It ought to/should work, I repaired it this morning. ● eg: Tighter laws would protect the rainforest. Can – May Both 'can' and 'may' are used in question form to ask permission. Asking Permission: Eg: Can I come with you? Eg: May I come with you? (May is more polite than can) Can - To Be Allowed To ● 'can' is used to express permission. ● we use 'can' as a polite form to request something. When 'can' expresses permission to do something specific. In this case, 'to be allowed to do something' can also be used. 'To be allowed to' is more formal and is commonly used for rules and regulations. Examples of request: Can I come with you? Can I make a telephone call? Examples of Asking Permission Eg:Can I go to the party? => Am I allowed to go to the Can - To Be Able To 'Can' is also used to express ability. Another form that can be used to express ability is 'to be able to'. Usually, either of these two forms can be used. Examples: I can play the piano. => I'm able to play the piano. She can speak Spanish. => She's able to speak Spanish. There is no future or perfect form of 'can'. Use 'to be able to' in both future and perfect tenses. Examples: Jack's been able to golf for three years. I'll be able to speak Spanish when I finish the course. Can - To Be Able To Special Case of the Past Positive Form When speaking about a specific (non-general) event in the past only 'to be able to' is used in the positive form. However, both 'can' and 'to be able to' are used in the past negative. Examples: Positive: I was able to get tickets for the concert. NOT I could get tickets for the concert. Negative I couldn't come last night. OR I wasn't able to come last night. Must Must and Have to 'Must' is used for strong personal obligation. When something is very important to us at a particular moment we use 'must'. Examples: Oh, I really must go. My tooth is killing me. I must see a dentist. Have to Use 'have to' for daily routines, laws and responsibilities. Examples: He has to get up early every day. You have to pay higher transport costs. Do they have to travel a lot for their jobs? Mustn't vs Don't have to Remember that . 'Don't have to' expresses something that is not required/necessary You can do it if you want, but there is no rule. (the person may choose to do so if he or she pleases). Eg:You don't have to put a stamp on that letter. Postage is free. Eg:Children mustn't play with medicine. Eg:I don't have to go to work on Fridays. However Mustn't is different! Mustn't is used about something which is wrong to do. Eg: You mustn't smoke in the workshop. Should – ought to – had better 'Should' is used to ask for or give advice. Eg: Should I see a doctor? He should leave soon if he wants to catch the train. Should, Ought to, Had Better Both express the same idea as 'should'. They can usually be used in place of 'should'. Examples: Eg: You should see a dentist. => You'd better see a dentist. They should join a team. => They ought to join a team. NOTE: 'had better' is a more urgent form. Which modal verb is used when...? Choose the correct number ● ● ● ● ● ● An action is necessary (an obligation) 1) You have to pay higher labour costs in this country. An action is a good idea (advice) 2) You may get a better discount. An action is not a good idea (advice not to do something) 3) You don't have to wait a long time for delivery. A situation is possible. 4)You should always use the same supplier. That way, you build up a good relationship with them. An action is not necessary (there is no obligation) An action is not possible for you to do (because it is against the rules or for another person) 5) No, you shouldn't depend on one supplier. You should use several so that if one can't supply your needs you can use another. KEY -Which modal verb is used when...? ● ● ● ● ● ● An action is necessary (an obligation) 1) You have to pay higher labour costs in this country. An action is a good idea (advice) 2) You may get a better discount. An action is not a good idea (advice not to do something) 3) You don't have to wait a long time for delivery. A situation is possible. 4)You should always use the same supplier. That way, you build up a good relationship with them. An action is not necessary (there is no obligation) An action is not possible for you to do (because it is against the rules) 5) No, you shouldn't depend on one supplier. You should use several so that if one can't supply your needs you can use another. Modal + Various Verb Forms Modal verbs are generally followed by the base form of the verb. Eg: She should come with us to the party. They must finish their homework before dinner. I might play tennis after work. In this case we are referring to a present or future moment. However, modal verbs can also be used with other forms of verbs. The most common of these forms is the use of the modal + a perfect form to refer to a past time. Eg: She must have bought that house. Jane could have thought he was late. Tim can't have believed her story. Other forms used include the modal + the progressive form to refer to what may / should / could be happening at the present moment of time. Eg: He may be studying for his math exam. Eg: He must be thinking about the future. Eg: Tom can't be driving that truck, he's sick today. Answer with a,b or c ● “Delivery is free. There is no charge for postage and packing.” a) you mustn't pay delivery charges. b) You don't have to pay delivery charges. c) you can't pay delivery charges. ● “Please do not disturb! Meeting in progress.” a) you mustn't interrupt the meeting. b) you don't have to interrupt the meeting. c) you should interrupt the meeting. ● “Cheques without a banker's card definitely not accepted”. a) We can't accept cheques without a banker's card. b) We don't have to accept cheques without a banker's card. c) We may accept cheques without a banker's card. Key - Answer with a,b or c ● “Delivery is free. There is no charge for postage and packing.” a) you mustn't pay delivery charges. b) You don't have to pay delivery charges. c) you can't pay delivery charges. ● “Please do not disturb! Meeting in progress.” a) you mustn't interrupt the meeting. b) you don't have to interrupt the meeting. c) you should interrupt the meeting. ● “Cheques without a banker's card definitely not accepted”. a) We can't accept cheques without a banker's card. b) We don't have to accept cheques without a banker's card. c) We may accept cheques without a banker's card. II - Past Modals ● ● ● We use past modals to make past deductions and and speculations: When you think of a decision you made in the past which may not have been the best one in the circumstances. You then say what happened and how you should/could have acted instead. Past modals are formed with: Modal verb + have + past participle. Past modals ● When we talk about the past we often refer to hypothetical events and situations: - to talk about alternative possibilities in the past: eg: With more time and money we could have improved the design. - to give advice after events have happened: eg: We should have patented the product immediately. - to talk about likelihood in the past: eg: I may have made a mistake in the calculations. Use may/might/can’t/couldn’t + have + past participle to make deductions or speculate about past actions: ● Use must have when you are almost sure something happened or was true. ● The opposite of must have is can’t have! Not mustn’t have. ● Use might/may/could + have when something was possible. ● ● Use can’t/ couldn’t have when you are almost sure something didn’t happen or that it was impossible. Use should have/ought to to say somebody didn’t do the right thing. Eg: We should have/ought to have invested more in research. “Failed innovation” complete the statements with appropriate past modal forms with verbs Verbs: research – design – waste - stop – know – charge – miscalculate – spend - conduct ● They …....the technology more thoroughly. ● They …....money developing their own systems. ● They …....the system was going to be too expensive. ● They …....the project before it was too late. ● They …....lighter handsets. ● They …....less for calls. ● They …....a more successful marketing campaign. ● They …....so much time and energy. ● They …....the size of the potential market. “Failed innovation” KEY: complete the statements with an appropriate past modal forms with verbs Verbs: research – design – waste - stop – know – charge – miscalculate – spend – conduct ● They could/should have researched the technology more thoroughly. ● They could/should have spent money developing their own systems. ● They could/should have kown the system was going to be too expensive. ● They could/should have stopped the project before it was too late. ● They could/should have designed lighter handsets.(mobile phones) ● They could/should have charged less for calls. ● They could/should have conducted a more successful marketing campaign. ● They shouldn't have wasted so much time and energy. ● They shouldn't have miscalculated the size of the potential market. Find the mistake ● ● I think I may had made a mistake in the calculations. We waited too long. We should have patent our new product immediately. ● With more time and money, we could won the competition. ● You shouldn't spent have so much time on the particular idea. ● If they' d had more support, it might had been easier for them. ● What could I have did to improve my design? Key - Find the mistake ● ● I think I may have made a mistake in the calculations. We waited too long. We should have patented our new product immediately. ● With more time and money, we could have won the competition. ● You shouldn't have spent so much time on the particular idea. ● If they had more support, it might have been easier for them. ● What could I have done to improve my design? ● Practice in dispensa ● Modals: See grammar pages: 198 – 199 -200 ● Past modals: See grammar Practice page: 223