Hardening Windows XP
advertisement

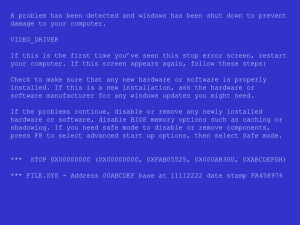
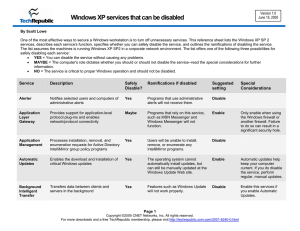
HARDENING WINDOWS XP: YOUR DEFINITIVE LOCKDOWN GUIDE 1 WHAT IS A SERVICE PATCH? This presentation will examine the following items and how to lock them down step by step. This will enable your XP system to be lean, mean and ready to do battle with attackers of all types. Windows XP Professional Configuration Checklist Details 1. Verify that all disk partitions are formatted with NTFS 2. Change Logging Settings 3. Disable Indexing Service 4. Protect file shares 5. Disable fast User Switching 6. Use software restriction policies 7. Disable unnecessary services 8. Keep up-to-date on the latest security updates 9. Use Security Baseline Analyzer 2 BEST PRACTICE #1: DISK PARTITIONS ARE FORMATTED WITH NTFS Many older XP workstations still use the older less secure FAT, FAT32, or FAT32x files systems. The enhanced NTFS file system offers greater access controls and protections that aren't available with the FAT, FAT32, or FAT32x file systems. Make sure that all partitions on your computer are formatted using NTFS. If necessary, use the “Convert Utility” to non-destructively convert your FAT partitions to NTFS. Before running this utility always make a backup of critical data, but that should go without saying! 3 BEST PRACTICE #2: CHANGE SYSTEM LOGGING SETTINGS By default the system logging does not provide for extensive logging activity. To change the system logging follow these steps: 1. Open Event Viewer 2. In the console tree, click the log you want to change. 3. On the Action menu, click Properties. 4. On the General tab, in Maximum log size, specify the new log size in kilobytes. Change log sizes 5. Application: 81920, overwrite as needed 6. Security: 81920, overwrite as needed 7. System: 81920, overwrite as needed 8. To put the new setting in effect, click Clear Log. 4 BEST PRACTICE #3: DISABLE INDEXING SERVICE Indexing Service is a base service for Microsoft Windows operating systems that extracts content from files and constructs an indexed catalog to facilitate efficient and rapid searching. Indexing Service can extract both text and property information from files on the local host and on remote, networked hosts. The files can be simply members of a selected file system or part of a virtual Web hosted by, for example, Internet Information Services (IIS). The index server has been a major vulnerability of the XP operating systems. It is recommended to turn off this service unless otherwise needed. To disable the indexing service performs the following steps: 1. In the "Start" menu, choose "Run." 2. Type "services.msc" and press Enter. 3. Scroll-down to "Indexing Service" and double-click it. 4. If the service status is "Running", then stop it by pressing the "Stop" button. 5. To make sure this service doesn't run again, under "Startup Type:", choose "Disabled." 6. Windows search will still work if you perform these steps, but it will work more slowly than if indexing was enabled. 5 BEST PRACTICE #3: DISABLE INDEXING SERVICE 6 BEST PRACTICE #4: PROTECT FILE SHARES By default, Windows XP Professional systems that are not connected to a domain use a network access model called "Simple File Sharing," where all attempts to log on to the computer from across the network will be forced to use the Guest account. This means that network access as well as Remote Procedure Calls (RPCS) will only be available to the Guest account. This can be a big vulnerability and has been exploited by some the most widely used attack tools targeting the Windows XP OS. 1. To change it, go to: Start => Programs => Accessories => Windows Explorer and drop down the Tools menu and select ‘Folder Options’. 7 BEST PRACTICE #5: DISABLE FAST-USER SWITCHING When multiple users share a computer, logging off and logging on to the computer in order to switch users can become tiresome. Fast User Switching, a feature that makes it possible for you to quickly switch between users without actually logging off from the computer. Multiple users can share a computer and use it simultaneously, switching back and forth without closing the programs they are running. However, if you are not sharing computers this feature should be disable. To disable fast-user switching: 1. Go to control panel > User Accounts 2. Select “change the way users log in and out” 3. Click “Off” the option for “Use Fast User Switching” 4. Apply Changes 8 BEST PRACTICE #5: DISABLE FAST-USER SWITCHING 9 BEST PRACTICE #6: USE SOFTWARE RESTRICTION POLICIES Software restriction policies provide administrators with a policy driven mechanism that identifies software running in their domain, and controls the ability of that software to run. Using a software restriction policy, an administrator can prevent unwanted programs from running; this includes viruses and Trojan horses, or other software that is known to cause conflicts when installed. Software restriction policies can be used on a standalone computer by configuring the local security policy. Software restriction policies also integrate with Group Policy and Active Directory. 10 BEST PRACTICE #7: DISABLE UNNECESSARY SERVICES Hardening Windows XP included turning off any network services not required for normal operations. In particular, you should consider whether your computer needs any IIS Web services. By default, IIS is not installed as part of Windows XP and should only be installed if its services are specifically required. It is recommended that if you don’t need them, disable the following services ASAP: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Telnet Universal Plug and Play Device Host IIS (not installed by default) Netmeeting Remote Desktop Sharing Remote Desktop Help Session Manager Remote Registry Routing & Remote Access SSDP Discovery Service It is also recommend that the server service and computer browser be eliminated if you are on a stand-alone machine connected to the Internet. There is no practical use for them and leave you exposed. 11 BEST PRACTICE #7: DISABLE UNNECESSARY SERVICES 12 Best Practice #9: Keep up-to-date on the Latest Security Updates The Auto Update feature in Windows XP can automatically detect and download the latest security fixes from Microsoft. Auto Update can be configured to automatically download fixes in the background and then prompt the user to install them once the download is complete. To configure Auto Update, click System in Control Panel and select the Automatic Updates tab. Choose the first notification setting to download the updates automatically and receive notification when they are ready to be installed. 13 WHAT IS A PRODUCT FAMILY? A product family is a collection of products that have a related purpose. For instance, the Microsoft Windows® product family includes all Windows operating systems, such as Windows 3.11, Windows 95, and Windows 2000. A product is one member of a product family. For instance, Microsoft Windows NT® is a product in the Windows family. A version is an instance of a product. For instance, Windows NT 3.5, Windows NT 4.0, and Windows 2000 are different versions of the Windows NT product. 14 SERVICE PACK VERSUS PATCHES A service pack is a periodic update that corrects problems in one version of a product. For instance, there have been six service packs for Windows NT 4.0. Some Microsoft products use the term service release rather than service pack, but the terms mean the same thing. A patch is an update that occurs between service packs. A patch is sometimes also referred to as a hotfix. Note: Most patches are built to correct security vulnerabilities, but we also build patches to correct critical stability or performance issues. In this article, though, we'll only discuss security patches. http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc723502.aspx 15 WINDOWS UPDATE UTILITY WINDOWS 7 Click Start > Control Panel > Windows Update 16 VIEW UPDATE INFORMATION WINDOWS 7 From the Windows Update window, click on a link to view additional information on that update. The 1 important update was selected in this example,. 17 Review the Update History From the Windows Update Window, select View Update History 18 Frequently Asked Questions From the Windows Update window, select Updates: frequently asked questions to find out more information 19 Settings for Automatic Updates From the Windows Update window, select Change Settings 20 Running Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer Sample Scan 21 Additional System Information • Links provide more information for a particular issue • Report can be printed for documentation • Report can be copied to clipboard 22 Administrative Vulnerabilities Links are provided as to what was scanned, the result details, and instructions on how to correct an issue. 23
![[#OPENDS-2811] dsreplication disable doesn`t remove references](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007607046_2-08a65077c2c13d51befd2f9d7b501b32-300x300.png)