New England Colonies
advertisement

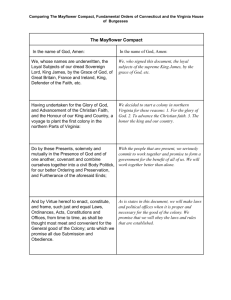
New England Colonies The Beginning of the 13 Colonies Vocabulary (Religion) Dissenter you disagree with the Church of England Persecuted Mistreated those who rejected the Church Tolerance Those who accepted different opinions Pilgrim Those who travelled to gain religious freedoms Vocabulary (Religion) Puritans Wanted to purify or reform the Church of England Protestants Can serve God by faith alone, rather than by good works. Also states that the Bible is the final source of authority for all Christians Est. by Martin Luther (Reformation) Huguenot Protestant from France Quakers Protestant dissenters. Believed that God could be known through an inner light. Believed that church services got in the way of the direct experience of God. Practiced that women were equals. Vocabulary (Mercantilism) Subsistence farming Produced just enough for themselves and a little for trade Navigation Acts All goods had to be carried on English ships or ships made in the colonies Tobacco, wood, and sugar could only be sold to England or the colonies Imports to the colonies had to pass through English ports All colonial goods not shipped to England were taxed Vocabulary (Mercantilism) Triangular Trade Game Dissenter Persecuted Huguenot Tolerance Puritan Pilgrim Protestant Quaker Subsistence Farming New England Massachusetts Rhode Island Connecticut New Hampshire Massachusetts Joint Stock Company Massachusetts Bay Company (1629) Royal Charter created a royal colony Issued by the monarchy for a colony to rule its self by appointed or elected officials Founder John Winthrop 1st Governor of Massachusetts Bay “We must be knit together in this Work…We must delight in each other, make others’ conditions our own and rejoice together, mourn together, labor and suffer together…For we must consider that we shall be as a City upon a Hill; the eyes of the people are on us.” Mayflower Compact Established the practice of self government and majority rule The Compact says Virginia because they were to settle in Virginia and missed their mark Can still be seen today in Washington DC Rhode Island Founder Roger Williams Left the Puritans as a dissenter and formed the colony of Rhode Island Shocked Puritans by stating the following: The colonists have no right to take the Native Americans land by force No one should be force to attend church Puritans should not impose their religious beliefs on others Church and state should be kept separate Anne Hutchinson Another dissenter from Massachusetts Bay She believed that many of the clergy were not among the “elite”– those chosen by God Connecticut Founder Thomas Hooker was a prominent Puritan religious and colonial leader, who founded the Colony of Connecticut after dissenting with Puritan leaders in Massachusetts The Fundamentals Orders of Connecticut o o Thought to be the 1st written Constitution in America The Orders extended voting rights to non-church members. This expanded representative government Charter Oak Connecticut's constitutional charter had been hidden within the hollow of the tree to thwart royal-ordered confiscation by English authority. This document is what earned Connecticut its nickname as the Constitution State, and the Charter Oak is Commemorated on the Connecticut State Quarter. Game Roger Williams Thomas Hooker John Winthrop Fundamental Orders of Connecticut Mayflower Compact Anne Hutchinson Massachusetts Bay Company Game Roger Williams Thomas Hooker John Winthrop Fundamental Orders of Connecticut Mayflower Compact Anne Hutchinson Dissenter Huguenot Puritan Massachusetts Bay Company Persecuted Tolerance Quaker Pilgrim Protestant Subsistence Farming Homework Read pg. 68 and 74 of the text book and write a summary of the Mayflower voyage and Mayflower Compact. Describe the reasons for their voyage Next read pg. 75 of the textbook and write a summary of the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut Finally compare or contrast The Mayflower Compact and the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut. What do they have in common or disagree on. Due Friday September 30!