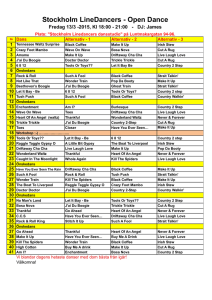
Viennese Waltz - fhs performing arts
advertisement

“Oom Cha Cha”!!!! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NBmM7F XyGbQ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=baBUyPJ-2w http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O1AkeBp yDsY&feature=fvwrel The Waltz first became popular in and around Vienna in the 1790’s NO electricity, therefore...NO lights, NO TV, NO iPod! They had to make their own amusement...Music, Dance, Drama, Reading and Conversation. Dance music. Fast triple meter-usually ¾ About 70 beats a minute. =70 Gives a feel of one beat in a bar, instead of 3. Slow harmonic pace. The same chord is generally used throughout an entire bar, often 2 bars and sometimes up to 4 bars. Simple harmonies (usually using the primary chords) made a bit more interesting by including gently dissonant appoggiaturas and chromatic notes. HOMOPHONIC. Simple melody lines with supportive accompaniment The accompaniment is often described as “Oom Cha Cha”. The bass note of the chord is played on the first beat followed by the second and third. Waltzes were seen as very risqué for the time as partners had to hold each other close. Before the Waltz, partners, if touching at all, were held at arms length. Critics thought the Waltz to be immoral. Early Waltzes were simple, in a Binary formAABB but changed to become more complex Popularity of the Waltz helped develop it. 1825, became very popular due to Orchestras getting larger and more sophisticated melody and harmony. An introduction became popular, this gave people time to get into position before the music started properly. Four or Five Waltzes would be played together in related keys and ending in a coda. Waltzes became much more substantial and where given names to make them more memorable. An important feature of a Waltz is the use of rubato. This means the second beat of the bar (the first ‘Cha’) is played slightly early. The effect it has in a waltz is to make it move on and sound even more lively. Viennese Waltzes were played by large orchestras. Johann and Johann II Strauss!!!!!!! Waltzes became so popular during the 19th century, they started to be written into other types of music... people liked to play them at home on their pianos. Shubert, Schumann, Weber, Chopin and Brahms all composed Waltzes for the Piano Waltzes were also incorporated into large orchestral works. Berlioz, Ravel and Tchaikovsky all did this. Tchaikovsky and Delibes included waltzes in ballets Waltzes have been used in musicals into the 20th century Johann Strauss II, The voices of spring time Chopin Waltz Op. 64 No. 1 aka Minute Waltz. Tchaikovsky Swan Lake-Waltz. Describe the rhythm of a Waltz What does tempo rubato mean? Where did the Waltz rise to fame? What does Homophonic mean? What instrument did people play the Waltz on in their own home? How would you describe the harmonic rhythm of a waltz? Describe two ways you would expect a Waltz to sound different from a Galliard?