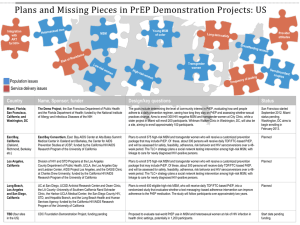
HIV/AIDS 101
Ground Rules
• Use “I” Statements when expressing your thoughts/concerns.
• We are all equal in this room and here to learn.
• Confidentiality – any personal information shared in this room, will
stay in the room
• There is no such thing as a stupid question!!!
Definitions
What Does HIV
Stand For?
What Does AIDS Stand
For?
H Human
A Acquired
I Immuno-deficiency
I Immune
V Virus
D Deficiency
S Syndrome
Transmission Information
HIV Can be Transmitted Via:
HIV Can NOT Be Transmitted Via:
Infectious "bodily fluids“
Non- infectious "bodily fluids"
•
Blood (including menstrual blood)
•
Saliva
•
Semen
•
Tears
•
Pre-seminal fluid (pre-cum)
•
Sweat
•
Cervical and vaginal mucous
•
Feces
•
Breast milk
•
Urine
•
Anal fluids
Transmission Cont’d.
Three primary ways in which HIV can be transmitted:
1.
Unprotected vaginal and/or anal contact with someone who has the virus
2.
Direct blood contact through sharing needles
3.
Mother to child contact during birth or through breastfeeding
HIV can NOT be transmitted by:
1. Insect bites
2. Sharing dishes, eating utensils, or food
3. Casual, day to day contact (including using restrooms)
4. Donating blood
5. Using hot tubs and/or swimming pools
6. Using the same toilet seat as someone living with HIV
How Does HIV/AIDS Work?
• HIV/AIDS infects our white blood
cells and slowly breaks down our
body’s ability to fight off infections
and diseases.
• When a person is infected with
HIV, the body produces
antibodies. If HIV antibodies are
detected, it means that the
individual is now living with HIV
– HIV antibodies can usually be
detected in a “window period”
6-12 weeks after infection,
and in some rare cases up to 6
months.
Testing Information
Anonymous
HIV test where a specialized code
is used instead of a name or
initials. The results will never
appear on your health record
and only the person getting
tested knows the code.
Nominal/name
based Testing
Your actual name is used on the
test, and if the result is
positive, public health needs
to be notified.
Non-nominal Testing
Identical to nominal/name based
testing except your name
does not appear on the test.
Either a code or initials are
used.
**Both last options are confidential, but the test and the results goes on your health records, and you need
an Ontario Health Card – offered at most health services in Ontario. If you test positive you are reported to
the Medical Officer of Health and the information stays confidential with that organization
Testing Locations: York Region
7 Sexual Health Clinics:
Markham
4261 Highway 7
Phone: 905-940-1787 Ext. 4211
Richmond Hill
50 High Tech, 2nd floor
Phone: 905-762-1282 Ext. 4811
Newmarket
22 Prospect Street
Phone: 905-895-4512 Ext. 4311
Woodbridge
(Woodbridge College Students only)
Woodbridge College, Guidance Department
71 Bruce Street
1-800-361-5653
Keswick
(Keswick High School Students only )
Keswick High School, 100 Biscayne Boulevard
Phone: 1-800-361-5653
King City
Seneca College, King Campus, 13990 Dufferin Street
Phone: 1-800-361-5653
Sutton
Sutton High School, 20798 Dalton Road
Phone: 1-800-361-5653
*Rapid and Anonymous Testing Available at all sexual health clinics
**Must call to make an appointment for testing, clinic hours may vary by location and date
HIV and Other STIs
For persons with an STI infection:
– The risk of HIV transmission is increased
3-50 fold
For persons with an HIV infection:
– HIV genital shedding in men and women
increases in the presence of STIs and can
accelerate the depression of the immune
system
Global HIV/AIDS Statistics
• Globally – 33.2 million people are
living with HIV
• In recent years, the UN has reported
a 70% global reduction in the
number of new reported infections
• Most of the reduction is explained
by decreases in new reported
HIV/AIDS cases in India as well as
several sub-Saharan African
countries including: Nigeria,
Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Kenya
and Angola.
UNAIDS 2007
Canadian HIV/AIDS
Statistics
•
•
In Canada, approx. 65,000 people
are living with HIV (as of the end of
2008)
Men who have sex with Men
(MSM) account for 48% of reported
cases.
VS.
Ontario HIV/AIDS
Statistics
•Ontario has had the highest number of
HIV+ results since 1985: 26,461.
•Men who have Sex with Men (MSM)
account for 50.4% of reported cases
•Women account for 23%
•
Heterosexual contact accounts for
31%
•Injection Drug Users (IDU) account for
9.5%
•
Injection Drug Users account for
17%
•Heterosexual contact accounts for 16.9%
•
Aboriginal people account for
approximately 12.5% of new
infections
Public Health Agency of CanadaGovernment of Canada
•People from countries where HIV is
endemic count for 19.4%
University of Toronto
Toronto HIV/AIDS
Statistics
VS.
York Region
HIV/AIDS Statistics
•Toronto accounts for the largest
number of individuals testing
positive for HIV in Ontario –
16,458.
•Approximately 230 People have been
diagnosed between 1998 and 2007
•Men who have sex with men
(MSM) 73.9% of reported cases
•20-25 cases are investigated each
year.
•Women 12%
•Injection drug users (IDU) 4.3%
•Heterosexual contact 7.8%
•People from countries where HIV
is endemic 7.9%
University of Toronto
•In 2007 alone, 17 new cases were
reported
HIV/AIDS and Stigma
•
•
Stigma can be found in societal, organizational and religious policies, cultural norms and in the
way we relate to each other and ourselves.
HIV stigma is rooted in a lack of knowledge about sexual health, our own fear, and our prejudices
about certain communities
• The effect of being stigmatized is great in that it can result in:
•Social isolation
•Loss of self-esteem
•Fear of disclosure
•Depression, anxiety and stress
•Depressed immune system
•Despair and hopelessness
•Increased risk of not engaging in safer sex practices, not getting tested and being
unable to properly care for one’s health
HIV does not discriminate based on what neighbourhood you live in, gender,
race or sexual orientation. It is an equal opportunity infection and you can NOT
tell if someone is living with HIV/AIDS by simply looking at them.
What Can You Do if You Think You may
Have Been Exposed?
• Go to the ER or your doctor immediately!
• They will go through a “risk assessment” with
you to determine the likelihood of
transmission
• If appropriate, you and your doctor will decide
TOGETHER whether a small dosage of the HIV
cocktail should be administered
• After the window period an HIV test will be
conducted
Questions, Comment or Concerns?
Additional Information and Resources
•
AIDS Committee of York Region
www.acyr.org
– Provides links to a variety of other York Region community resources
•
York Region Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual Youth Support at
www.rainbowyouthyork.com
•
Public Health Agency of Canada
http://www.phac-aspc.gc.ca/index-eng.php
•
UNAIDS
http://www.unaids.org/en/
•
ACT (AIDS Committee of Toronto)
www.actoronto.org
•
HIV/AIDS Bureau
http://www.hrsa.gov/about/organization/bureaus/hab/index.html