Irene Sheridan - Higher Education Authority

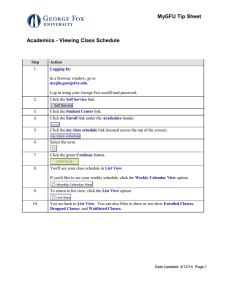
• What is meant by the term ‘engagement’?
• What does an engaged higher education institution look like?...from the outside?
• Can we… should we… move engagement from the periphery to the core?
• How can we structure our institutions… collect and use business intelligence?
Regional Engagement and Knowledge Transfer
Universities as ‘engines of the knowledge economy’ (Vorley and Nelles
2008)
OECD ..’regional engagement …create the conditions in which innovation thrives’
European Commission…
R&D collaboration and commercialisation
Mobility of academics and students
Curriculum development and delivery
Lifelong learning
Entrepreneurship
Governance
Knowledge transfer – exchange – co-creation
National
Economic and social value – employment, skills needs, enterprise development, cultural interactions
Institutional
Academic – relevancy and currency of learning
Knowledge creation and application
Diversity of missions
National Strategy for Higher Education to 2030 calls for:
..higher education institutions to ‘engage with the communities they serve in a more connected manner—identifying community, regional and enterprise needs and proactively responding to them’
What does an engaged HEI look
Enhancement of employability
like?
skills
Career fairs and company visits
Course design and delivery
Professional
External examiners
Bodies
Workplacement
Volunteering
Customised
Learning
CPD
Placement and projects
Work-based learning
Service Learning
RPL
Guest lectureships
Alumni Relations
Supporting
Entrepreneurship
Spin-outs and spin-ins
Innovation
Partnerships
Strategic
Partnerships and Research
Solutions Patents and licences
Applied research
Commercialisation
Long-term relationship planning
Education in Employment project – workplace as a valuable learning location and the employer as a partner
REAP – development of partnership continuum and exploration of good practice models for engagement interactions
Relationships, resources and realistic expectations
Engagement has to be an institution wide commitment, not confined to individual academics or projects.
It has to embrace teaching as well as research, students as well as academics, and the full range of support services.
All universities need to develop strategies to guide their engagement with wider society, to manage themselves accordingly and to work with external partners to gauge their success
.
Goddard, J. (2009) Reinventing the Civic University,
8
Key elements
Stimulus to generate the ‘pull’
Exemplars of activity
Point of contact
Informed view of capabilities, experience and expertise
Guidelines for good practice
Professional approach to case management
Collate expertise and experience from our separate
(competing?) units
Develop an informed, strategic view of past, present and future engagement interactions
Articulate clearly what makes engagement work (for both partners)
▪ Structures
▪ Expectations,
▪ Timeframes
▪ Cultures
▪ Climate…
Quantify: Connections made – leads generated – interactions progressed
Measurable
Relationship mapping and progression:
Work placement
?
Customised learning
Research
Social and economic value generation?
Dr Irene Sheridan www.reap.ie
www.cit.ie/extendedcampus