CHOP1_KB_K1[1] - WordPress.com
advertisement
![CHOP1_KB_K1[1] - WordPress.com](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005237567_1-dcb6361dc70ee5d459b7122e117d70a1-768x994.png)
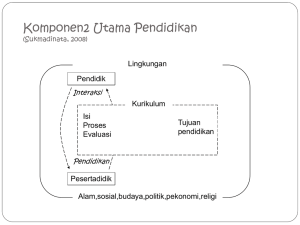
Medical Education Unit Dr. Isti Ilmiati Fujiati, MSc.CM-FM, MPd.Ked. INTRODUCTION Challenges in the 21st Century: - Health Problem: Disease influence by environment, Quality service - Globalization: Competition Era, Information Era - Ethics and Human Rights Study Skills Life long learning - Rapid changes in medical science & technology (biomolecular approach) - Medical education development THE CONTINUUM OF LEARNING Learning is continuous, with new learning built on what has already been learned Medical education is a continuum which starts at entry to medical school and ends with cessation of professional practice The content of what is learnt and the process of learning make a significant impact on the remaining phases of the continuum COMPONEN STUDY SKILLS Self directed learning Learning with understanding (deep learning), leading to long term retention Seeking and retrieving information from an increasing variety of sources Critically reviewing what is read Integrating new learning with existing knowledge by seeking links between them Assessing oneself on learning STUDY PLAN Readiness for learning depends on intrinsic motivation, as well as the acquisition of prerequisite learning on which new learning is built. In developing a study plan, the student must: - Identify the focus of study - Determine the depth to which study of a particular topic is to be undertaken - Understand the interrelationships of topics The student must learn to develop a study plan in which bring these relationships to the fore, even if it may not correspond to the school’s formal timetable CLASS CURRICULUM Semester-1 Semester-2 BUKU RANCANGAN PENGAJARAN Menggunakan modifikasi Instructional Design (Kemp) dalam menyusun Buku Rancangan Pengajaran (BRP) BRP terdiri dari 7 komponen KURIKULUM KELAS BUKU RANCANGAN PENGAJARAN … Komponen: 1. Pendahuluan: - Pentingnya Blok dan “tempat” blok - State of the art - Magnitude of the problem - Tujuan Umum BUKU RANCANGAN PENGAJARAN … 2. Pra syarat mahasiswa: Penting untuk menyusun suatu blok. Apakah satu blok merupakan prasyarat untuk blok lainnya. 3. Objektif: - Objektif mahasiswa – sasaran pembelajaran - Objektif blok BUKU RANCANGAN PENGAJARAN … 4. Lingkup bahasan Dirujuk dari Buku Standar Kompetensi Pendidikan Dokter 5. Metoda - Instruksional: kuliah, demonstrasi - Interaktif: diskusi kelompok - Independent: assignment The Learning Pyramid Average Retention Rate Lecture 5% Reading Audiovisual 10% Demonstration 30% Discussion group Practice by doing 50% Teach others 80% 20% 75% National Training Laboratories, Bethel, Maine, USA BUKU RANCANGAN PENGAJARAN … 6. Sarana Prasarana: Sumber Daya Manusia: - Narasumber - Fasilitator (PBL – Tutorial) - Instruktur klinik (Basic clinical skills) - Waktu: matriks kegiatan Sumber belajar: - Buku Rujukan (sebagai indikator) - Laboratorium – Slide, dll - Internet - Ruang kuliah besar - Ruang tutorial - Ruang praktikum - Ruang skills lab Waktu – Matriks kegiatan BUKU RANCANGAN PENGAJARAN … 7. Evaluasi Evaluasi hasil pembelajaran: - Evaluasi materi - Evaluasi proses Evaluasi program: - Efektifitas - Efisiensi Jenis – formatif, sumatif Bentuk – MCQ, OSCE, MDE, dll Jadwal – Shifting of ME Paradigm Teacher-centered Information gathering Discipline-based Hospital-based Standard program Opportunistic Student-centered Problem-based Integrated Community-oriented Early clinical exposure Systematic STRUKTUR KURIKULUM 1. KURIKULUM NASIONAL – 80% KIPDI III = KBK Standar Kompetensi Dokter (KKI) 2. KURIKULUM FAKULTAS – 20% Visi – Misi Universitas/ FK Rencana Strategik 3. KURIKULUM KELAS – BUKU RANCANGAN PENGAJARAN KURIKULUM NASIONAL KURIKULUM UNIVERSITAS/ FAKULTAS - University for Industry (U for I) - Tropical medicine 7 Area Kompetensi (Kompetensi Utama) dalam KIPDI 3 1. 2. 3. Keterampilan komunikasi efektif Keterampilan klinik dasar Keterampilan menerapkan dasar-dasar ilmu biomedik, ilmu klinik, ilmu perilaku, dan epidemiologi dalam praktek kedokteran keluarga 4. Keterampilan pengelolaan masalah kesehatan pada individu, keluarga, ataupun masyarakat dgn cara yg komprehensif, holistik, bersinambung, terkoordinir, dan bekerjasama dlm konteks Pelayanan Kesehatan Primer 5. Memanfaatkan, menilai secara kritis dan mengelola informasi 6. Mawas diri dan pengembangan diri/ belajar sepanjang hayat 7. Etika, moral dan profesionalisme dalam praktik Educational Principles tudent-centered roblem-based integrated ommunity-oriented arly clinical exposures ystematic SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2 Basic Biology of Cell (2.5/2.5) Basic Biomedical Sciences-2 Metabolic System Basic Biomedical Sciences-1 (8) SEMESTER 3 Reproductive System (4.5/4) SEMESTER 4 SEMESTER 5 SEMESTER 6 SEMESTER 7 Dermato musculo Skeletal System Genitourinary System (3/3) Brain and Mind System Tropical Medicine (3/2) Cardiovascular System Gastro Intestinal System (3/3) Hematology& Immunology System Growth and Development System (4/3) Respiratory System Special Senses System (2/3) Clinical Skills Program-1 Clinical Skills Program-2 (1) Clinical Skills Program-3 Clinical Skills Program-4 (2) CHOP-2 (1) CHOP-3 CHOP-1 (2.5) Family Medicine (3/2) Emergency Medicine Clinical Skills Program-5 Oncology (3) Clinical Skills Program-6 (1) CHOP-4 CRP-1 (1.5) CRP-2 CRP-3 (1) CRP-4 CRP-5 (2) CRP-6 CRP-7 (2) BHP-1 (3) BHP-2 BHP-3 (3) BHP-4 BHP-5 (2) BHP-6 BHP-7 (1) TOTAL 144 SKS ANGKATAN 2011 KURIKULUM FAKULTAS BLOK MODUL PEMICU PEMICU BLOK MODUL PEMICU BLOK BLOK MODUL PEMICU PEMICU PEMICU