File
advertisement

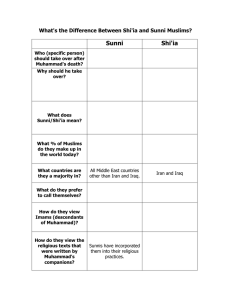
Shi’ite and Sunni Divisions within Islam The Dividing Issue • Sunni and Shi’ite Muslims share the same Islamic beliefs. • The division is political and revolves around the succession of Muhammad. • Should the successor be of “bloodline…or leaders most likely to follow the tenets of the faith,” is the question and conflict. Sunni • Sunnis believe that the first four caliphs Muhammad's successors - should be close advisors or companions of Muhammad. • “Sunnis chose Abu Bakr, the prophet’s adviser, to become the first successor to lead the Muslim state.” Shi’ite • Shia Muslims believe leadership should be based on bloodline and “passed directly to Muhammad’s cousin/sonin-law, Ali.” • “Ali and his successors are called imams,” and are considered to be descendants of Muhammad. • “Ali was martyred during Ramadan, the Islamic month of fasting.” How did the violence start? • “In 656, Ali’s supporters killed the third caliph. Soon after, the Sunnis killed Ali’s son Husain. • Fighting continued but Sunnis emerged victorious over the Shiites.” Populations and Spatial Distribution • Sunnis account for about 85 percent of the world's Muslims. • The Taliban are fundamentalist Sunni Muslims. • Shi’ites account for about 15 percent of the world's Muslims. • Shiites are dominant in Iran and are also the largest sect in Iraq. • Pockets of Shiite Islam also exist in Afghanistan, Pakistan and Tajikistan. Sources • http://hnn.us/articles/934.html • http://islam.about.com/cs/divisions/f/shia_s unni.htm • http://seattletimes.nwsource.com/art/news/ nation_world/sept_11/understandingthecri sis/islammap.pdf • http://www.google.com/imgres (Life Magazine: Unforgettable Photos