File - Mr. Gutierrez`s social studies website
advertisement

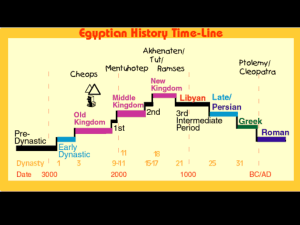
Life in Ancient Egypt Chapter 5, Lesson 2 Egypt's Early Rulers ► Around 2600 B.C., Egyptian Civilizations entered the period known as Old Kingdom. It lasted until about 2200 B.C. ► They had increased trade and a unified government. They prized unity and understood the importance of living under similar principles and beliefs. ► They developed a government lead by someone who controlled religious and political affairs. Theocracy – Government in which someone is both a political and religious leader. A Political Leader ► At first the Egyptian ruler was called a king but later was known as a pharaoh. Pharaoh originally meant “great house” and referred to the grand palace that the king and his family lived in. ► Egyptians were fiercely loyal to the pharaoh. They believed a strong ruler unified the kingdom. Held total power and commands had to be obeyed. They believed a pharaoh’s wisdom and leadership would help during disasters such as famines and wars. A Political Leader pharaoh appointed bureaucrats (government officials) to carry out his orders. ► The They supervised building/repair projects for dams, irrigation canals and brick granaries (place to store grain in case of an emergency.) What kind of emergencies? ► The pharaoh owned all the land in Egypt and could use it as he pleased. The pharaoh’s officials collected taxes of grain from farmers. The pharaoh also distributed land to officials, priests, and wealthy Egyptians whom he favored. A Religious Leader ► Egyptians believed the pharaoh was the son of Re (Ray), the Egyptian sun god. Believed he was a god on earth to protect Egypt. When the pharaoh appeared they would play music on flutes and cymbals and bowed their heads. ► The Pharaoh participated in many ceremonies to help the kingdom thrive. Riding a bull around Memphis produced fertile soil. First person to cut ripened grain at harvest time to produce abundant crops. Religion in Egypt ► Religion life. influenced most aspect of Egyptian They had many god like Mesopotamia but they believed theirs were more powerful and could control natural forces and human activities. Two of the most crucial were the Sun God Re (Ray) and the river god Hapi (HAH Pee) Osiris was an early pharaoh who taught his people to farming and made laws. Isis represented faithful Wife and mother. Both were gods who ruled over the world of the dead. Thoth was the god of learning. Egyptian Gods Sun God Re Nile God Hapi God of the Goddess of Dead Osiris Motherhood Magic, and Fertility God of Learning, Thoth The Afterlife ► Egyptians had a positive view of the afterlife. They believed it was even better than present life. ► Egyptians studied the book of the dead for its prayers and magic spells to prepare for the afterlife. ► It was believed Osiris greeted the recently deceased at the gate to the new world. If they knew the spells and had led a good life, they were granted eternal life. The Afterlife ► At first it was believed that only the pharaoh would enjoy the afterlife. ► They believed that the body held the soul and must be protected for the soul to make it safely to the afterlife. ► This lead to the process of embalming to protect the bodies. The Afterlife ► First, the priest would remove the bodies organs and stored in jars buried with the bodies. ► Next, the body was covered with a salt called Natron and stored for a few days which caused the body to dry up and shrink. ► Burial spices were then placed in the body and wrapped in long sheets of linen. ► The wrapped body was then known as a mummy which is sealed in a coffin and placed in a decorated tomb. The Afterlife ► Wealthy people had their mummies placed in coffins and buried in tombs. ► Poor people had their mummies buried in caves or the sand. ► Animals were viewed as sacred creatures so birds, cats, and other animals were also embalmed honoring their god and goddesses. Medical Skills ► Embalming lead to a greater understanding of medicine. ► The Egyptian doctors sewed up cuts, and set broken bones. First to use splints, bandages and compresses. ► They wrote down medical information on papyrus scrolls and would become the first medical books. Pyramid Tombs ► Egyptians ways. honored their pharaohs in special ► Pyramids were giant stone structures that were used to protect the pharaohs from flooding, wild animals, and robbers. Also housed the pharaoh’s personal possession they felt would bring happiness in the afterlife. How were pyramids built ► Thousands of workers over the course of years spent hard labor building pyramids. Farmers helped during the summer when the Nile flooded and they could not farm. ► Surveyors, engineers, carpenters, and stone cutters also helped. First great engineer was Imhotep, an official to the pharaoh. How were pyramids built ► Stones were found in the river valley or in Upper Egypt. ► When the stone was located skilled artisans used copper tools to cut it. ► Then they were tied with rope and pulled along logs. ► They were done pushed up ramps to the various levels where it was needed. How were pyramids built ► The challenges in building the pyramids lead to important discoveries. ► The pyramids entrance always faces North. This lead to Egyptians studying the sky and understanding astronomy. With this understanding, they made a calendar with 365 days, 12 months, and 3 seasons. This calendar would become the basis of our modern day calendar. How were pyramids built ► Also lead to the advancement of mathematics. Egyptians had to calculate how much stone was needed. They also needed to measure angles for the walls. ► They did these things by creating a number system based on 10. Also created fractions, which they then used alongside whole numbers to add, subtract, and divide. An Egyptian Wonder ► Around the mid 2000’s B.C., the Egyptians constructed the Great Pyramid for the pharaoh Khufu. ► It is one of the 3 pyramids still standing at Giza on the Nile’s west bank. ► 48 stories tall, shares an area of 9 football fields, and was constructed with more than 2 million stones each weighing around 2.5 tons. ► For more than 4,000 years it was the tallest structure in the world. Daily Life ► At its peak, Egypt’s population was 5 million. Roughly Colorado’s population. ► Most Egyptians lived in the fertile Nile valley delta (only about 3% of all of Egypt’s land). Even today it is still densely populated. Egypt’s Social Groups ► Top Tier – Pharaoh and his family. ► 2nd Tier – Small Upper class of army commanders, nobles, and priest. ► 3rd Tier – Middle class of traders, artisans, shopkeepers, and scribes. ► 4th Tier – Farmers and unskilled workers. ► Ambitious people could move up in social rank and improve their position. How People Lived ► Egypt’s upper class lived comfortably in homes of sun-dried bricks and wood along the Nile River. Also had pools with fish and gardens around the estate. ► Men and women dressed fashionably. White linen, dark eye makeup, and jewelry. ► They had servants complete tasks for them. How People Lived ► Middle class was made up of people who owned businesses and held skilled jobs Artisans made jewelry , clothing, pottery, and metal tools. ► They lived in smaller homes and dressed more simply than that of the upper class. How People Lived ► Largest Egyptian social class consisted of farmers, unskilled workers, and enslaved people. ► Most worked on land owned by nobles. ► Usually paid nobles with a portion of their crops. ► Homes were one room with palm leaves as the roof. ► They ate a simple diet of bread, vegetables, and fruit. Egyptian Families ► The family was the most important grouping in Egypt. Even the gods were arranged in families. ► The father was the head, and women had more rights than in most other civilizations at the time. Women could own property, buy and sell goods, and obtain divorces. Some were even Priestess. Women of higher standing were more likely to stay home while most others worked alongside their husbands. Egyptian Families ► Few Egyptian children attended school. Most children spent their time playing board games, spinning tops, leather balls, dolls, and other toys. ► As with most cultures, they had to respect their parents. Girls usually learned to sew, cook, and run households. Boys learned the trade of their fathers. Egyptian Families ► By the time children were teenagers they were expected to get married and start their own families. ► Most families were nuclear (consisting of a mother, father, and children). ► Extended families had older parents living with their married children. For farm families this provided extra hands to work. ► The oldest children were usually tasked with taking care of their parents in their old age which included making sure they received a proper burial after they died.