Constellations-A
advertisement

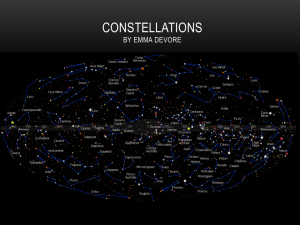
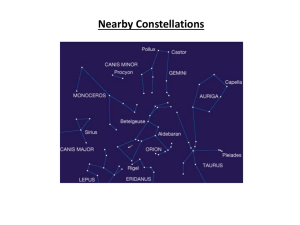
Constellations Astronomy The scientific study of the universe beyond the Earth Tells us about the origin, history and structure of our universe and solar system Uses telescopes and satellites Astrology The study that interprets how the positions of the stars, planets and moon effect your personality, fate, relationships etc ASTERISM A cluster of stars that is a subset of a constellation Ex : the Big Dipper is part of the constellation Ursa Major- the Great Bear An unofficial constellation CONSTELLATION A group of stars in the same region of the sky to which a name has been given Ex: Orion, Capricorn, Pegasus Any of the 88 groups of stars seen from Earth named by ancient Greeks after animals, objects or mythological figures CIRCUMPOLAR A group of 5 constellations that circle close to the North Star These constellations never fall below the horizon Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, Cassiopeia, Cepheus and Draco Ecliptic The part of the sky that is the plane of orbit of the sun, the moon and the planets The zodiac constellations fall in this great circle HOROSCOPE A prediction made based on the position of the sun, moon and planets A chart or diagram showing the positions of celestial bodies and interpreted for their influence over human events PRECESSION The slow cone shaped motion of the Earth’s axis of rotation The Earth wobbles as it rotates over a 25,800 year period This causes the zodiac constellations to line up differently with the sun over long periods of time Zodiac A band of constellations found along the ecliptic Originally contained 12 signs or “houses” The sun resides in each constellation for approximately one month Constellations There are only 88 official constellations 13 Zodiac Constellations 5 Circumpolar Constellations Several constellations are seen in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres In the past elaborate pictures were drawn to represent the story behind the constellation Orion the Hunter Orion the Hunter Ancient People in Europe and the Middle East saw a hunter brandishing a club when they looked at Orion In Australia, it is turned upside down To professional astronomers, Orion is an irregular part of the sky Orion the Hunter By the late 19th century, popular stargazing guides began to represent constellations as stick figures In 1952 H.A. Rey (author of Curious George) revolutionized the way we look at constellations by connecting the dots in new and clever ways. Orion 2 Orion 3 Which do you like better?