Ch. 3 PowerPoint Part I
advertisement

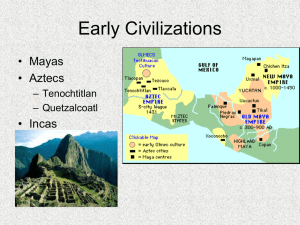
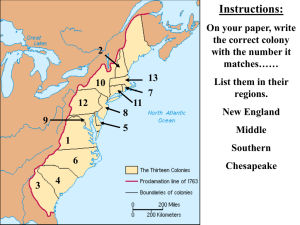
Unit 2: Colonial America Chapter 3: Founding the English Mainland Colonies 1585-1732 Why Migrate to America? England’s First Attempt at Colonization - Roanoke Sir Walter Raleigh Roanoke Island (1585, then 1587) off the coast of NC Settlement failed for unknown reasons Four Distinct Regions Settling the Chesapeake – VA & MD Joint-stock companies were used to finance trips to the New World Purpose - make money Plymouth Company - failed Virginia Company (London Company) Virginia Jamestown - The First Settlement Three ships set sail from England Dec. 1606 Settled at Jamestown (in honor of King James I) on May 24, 1607 Jamestown – The First Settlement Jamestown - The First Settlement Easy to defend but mosquito-infested & very unhealthy Settlers died by the dozens from disease, malnutrition, & starvation Spent time looking for gold instead of hunting or farming Jamestown – High Mortality Rates The “Starving Time” 1607: 104 colonists By spring, 1608: 38 survived 1609: 300 more immigrants By spring, 1610: 60 survived 1610 – 1624: 10,000 immigrants 1624 population: 1,200 Adult life expectancy: 40 years Death of children before age 5: 80% Jamestown - The First Settlement Captain John Smith took over the settlement in 1608 & helped make it successful “no work, no food” policy Discipline & order collapsed after he left in 1609 The Powhatan Confederacy Dominated small tribes in the James River area when the English arrived The Powhatan Confederacy Two groups cooperated at first, but the English exhibited a sense of superiority & entitlement that alienated the confederacy Relations grew worse - English raided Indian food supplies during the starving times War in the Chesapeake 1610-1614 - First Anglo-Powhatan War 1614-1622 - Peace 1622-1644 - Periodic attacks between Indians & settlers War in the Chesapeake Powhatan Uprising of 1622 Indians attacked the English, killing 347 1644-1646 - Second Anglo-Powhatan War Last effort of natives to defeat the English Indians defeated again War in the Chesapeake Peace Treaty of 1646 Removed the Powhatans from their original land Formally separated the Indian & English settlement areas English considered the Powhatan peoples extinct by 1685 Tobacco Tobacco saved the colony! Englishmen were a steady market for this “brown gold” Tobacco Young planter named John Rolfe transplanted a milder strain of West Indies tobacco to the colony (1612) Tobacco 1618 — Virginia produces 20,000 pounds of tobacco. 1622 — Despite losing nearly one-third of its colonists in an Indian attack, Virginia produces 60,000 pounds of tobacco. 1627 — Virginia produces 500,000 pounds of tobacco. 1629 — Virginia produces 1,500,000 pounds of tobacco. Tobacco Played a vital role to putting VA on firm, economic footing Lives revolved around tobacco Quickly exhausted the soil Growing tobacco required much land, thereby promoting the plantation system Increased demand for more land & cheap labor Indentured Servitude V.C. set up the head right system Granted each male colonist 50 acres of land for each settler he brought to VA Poor immigrants came to the New World & worked for several years Indentured Servitude Indenture Contract 4-7 years Promised “freedom dues” Forbidden to marry Life was short & brutal Frustrated Freemen - Bacon’s Rebellion Late 1600s - large number of young, poor, discontented men in the Chesapeake area Little access to land Few women to marry 1670 The Virginia Assembly disenfranchised most landless men Frustrated Freemen - Bacon’s Rebellion 1676 - 1,000 Virginians, led by planter Nathaniel Bacon, revolted Gov. of VA, William Berkeley, wouldn’t do anything about the Indian attacks on frontier settlements Berkeley monopolized the fur trade with the Indians Nathaniel Bacon Governor William Berkeley Frustrated Freemen - Bacon’s Rebellion Rebels attacked Indians, drove Berkeley from Jamestown, & burned the capital Bacon suddenly died of disease & Berkeley put down the rebellion Frustrated Freemen - Bacon’s Rebellion Results Exposed the unhappiness of landless former servants Pitted poor, backcountry frontiersmen against the plantation owners (gentry) Planters searched for laborers less likely to rebel - black slaves! House of Burgesses Small measure of self-govt. began in 1619 with the first meeting of the House of Burgesses Royal Governor appointed a council consisting of 6 leading planters 15 members were elected by the colony House of Burgesses 1624 James I revoked the charter of the bankrupt V.C. VA became a royal colony under the king’s direct control Powers of the H of B were restricted