102 US Political Freedoms Prior to 1820
advertisement

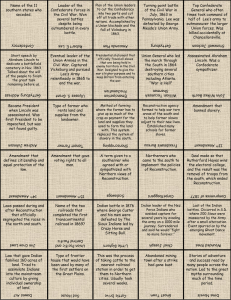
US Political Freedoms Prior to 1820 The Bill of Rights (1791) A series of Amendments to the Constitution designed to protect people and the states from the abuses of government Amendment I Freedom of Religion Freedom of Assembly Freedom of Petition Freedom of Press Freedom of Speech Remember RAPPS? Amendment II A well regulated Militia, being necessary to the security of a free State, the right of the people to keep and bear Arms, shall not be infringed. Amendment III No Soldier shall, in time of peace be quartered in any house, without the consent of the Owner, nor in time of war, but in a manner to be prescribed by law. Amendment IV No illegal search and seizures Searches may only take place under a warrant OR with reasonable suspicion Amendment V Indictment by a Grand Jury No Double Jeopardy No self-incrimination No person shall be deprived of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law Government may not take private property without fair compensation (eminent domain) Amendment VI Right to a speedy and public trial Right to trial by an impartial jury Right to be confronted with the witnesses against him Right to an attorney Amendment VII Provides for trial by jury in civil cases (lawsuits) Amendment VIII No excessive bail No excessive fines No cruel and unusual punishments Amendment IX The enumeration in the Constitution, of certain rights, shall not be construed to deny or disparage others retained by the people. Amendment X The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people Amendment XI (1795) Establishes “sovereign immunity” – citizens cannot sue a state in federal court for monetary damages, but may sue a state if the state is in violation of federal law Amendment XII (1804) Changes the rules for electing the president and vice-president Old rules – whoever got the most votes for president won, whoever got the second most votes became vicepresident! All men created equal? Originally, only WHITE, PROPERTY OWNING MEN were allowed to vote in the US! Role of Women Primary role was as wives, mothers, and homemakers Poor, single women might work outside the home as servants Had few property rights, could not vote Abigail Adams Wife of John Adams Pushed for women’s rights to education, own property, and have a voice in politicsvoting(suffrage) "...remember the ladies … Do not put such unlimited power into the hands of the Husbands … all Men would be tyrants if they could … [we] will not hold ourselves bound by any Laws in which we have no voice, or Representation.” Native American Relations As more white settlers pushed west, they came into increasing conflict with Native Americans Natives were NOT considered US citizens, and so had few rights US law protected settlers over native interests Tennessee & Kentucky become states First settled by whites in the 1750s and 1760s Led to conflicts with native groups Kentucky became the 15th state in 1792 Tennessee became the 16th state in 1796 Western Indian Confederacy Many Great Lakes area tribes worked together to present a united front against US expansion Badly defeated US troops in battles in 1790 and 1791 Battle of Fallen Timbers August 20, 1794, near Toledo, Ohio US troops under “Mad” Anthony Wayne defeated Indian Confederation under Blue Jacket Ended the Northwest Indian War Tecumseh Shawnee tribal leader Attempted to unite all Natives against US Opposed treaties with US government Allied himself with the British during the War of 1812 Killed during the war Treaty of Greenville August 2, 1795 Natives agreed to surrender most of Ohio and areas that are today Detroit and Chicago for $20,000 in goods and the creation of a permanent boundary between US and Indian territory Future settlers ignored the negotiated boundary Battle of Tippecanoe Nov. 7, 1811 US forces under Harrison attacked Tecumseh’s Indian alliance’s HQ in Indiana, shattering the new Indian confederacy Tecumseh fled to Canada and joined with the British British support of the Indians would be a contributing factor to the start of the War of 1812 William Henry Harrison Governor of the Indiana Territory Became a national hero due to his victories in both Tecumseh’s War and the War of 1812 Known as “Old Tippecanoe” Later elected President of the US Slavery: a “necessary evil” 3/5ths Compromise in Constitution only counted slaves as 3/5 of a person Slaves were NOT citizens and had no legal rights Some free blacks in the North did enjoy citizenship By 1800, close to 1 million slaves in US, or about 1/6 of the population Eli Whitney’s Cotton Gin Machine that separated usable cotton from its seeds Made cotton farming more profitable and led to the rise of “King Cotton”, the South’s dependency on the cotton trade Growth in the cotton trade led to further growth in slavery Beginnings of the Abolitionist movement Many people opposed slavery Most northern states passed laws ending slavery there Even though many Southerners questioned the morality of slavery, they considered it a “necessary evil” from which they could not escape.