Non-Linear Plot Notes
advertisement

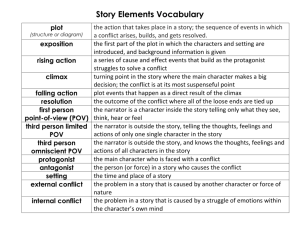
Non-Linear Plot Non Linear Plot Nonlinear narrative is a technique sometimes used in literature wherein events are portrayed out of chronological order. It is often used to mimic the structure and recall of human memory. Examples: •The Notebook •Forrest Gump Non- Linear Techniques • • • • Foreshadowing Flashback Sub-plot Parallel plot structure Foreshadowing • To show or indicate beforehand • Reveal an upcoming event Example: •In the opening of The Wizard of Oz, set in Kansas, the transformation of Miss Gulch into a witch on a broomstick foreshadows her reappearance as Dorothy's enemy in Oz. Flashbacks • A transition (in literary or theatrical works or films) to an earlier event or scene that interrupts the normal chronological development of the story • An unexpected but vivid recurrence of a past experience Example: Forrest Gump reminisces about past experiences in his life while he waits for a bus. Subplots • A secondary story in a narrative. A subplot may serve as a motivating or complicating force for the main plot of the work, or it may provide emphasis for, or relief from, the main plot. Example: In Possession two plots unfold. 1. That with the present day characters. 2. Plot taking place in the past. Parallel Structure Definition: Two or more major plots that occur within a story and usually intersect. Example: Pulp Fiction has multiple story lines that frequently intersect: • Vincent Vega (John Travolta) and Marsellus Wallace’s wife (Uma Thurman) • Butch Coolidge (Bruce Willis), Marsellus Wallace (Ving Rhames) and his gold watch • Vincent Vega (John Travolta) and Jules Winnfield’s (Samuel L. Jackson) escapades as hitmen Point of View (POV) POV Definition: Determines who is telling the story—the perspective, or vantage point from which an author presents a story. First Person POV Definition: In first person point of view, the story is told by one of the characters. Example: As I placed a carefully wrapped package on the park bench, I looked up and saw Molly walking across the street. I hoped that she hadn’t seen me. Third Person POV Definition: In the third-person point of view the story is told by a narrator who is not a character in the story. Types: Limited Omniscient Narrator relates the thoughts and feelings of just one character Omniscient Narrator knows the thoughts and feelings of all the characters Examples Limited Omniscient Narrator As George placed the carefully wrapped package on the park bench, he looked up and saw Molly walking across the street. Omniscient Narrator George anxiously hoping that no one was watching him, placed a carefully wrapped package on an empty park bench. But Molly, who was walking home, saw him and couldn’t help thinking that he was acting strangely. Food For Thought… You must be able to do more than simply identify the point of view: 1.How does the point of view affect your responses to the characters? 2. How is your response influenced by how much the narrator knows and how objective he or she is? 3. First person narrators are not always trust worthy. How will you determine what is the truth and what is not? Imagery the use of language to create mental images and sensory impressions. Imagery can be used for emotional effect and to intensify the impact on the reader.