Lecture 1 - Upper Iowa University
advertisement

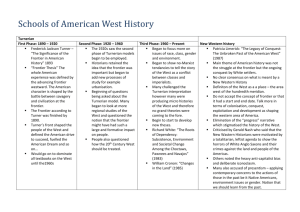
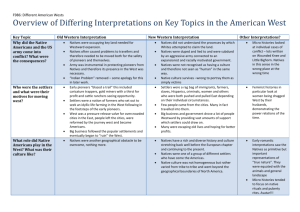
Hist 111 American Civilization II Instructor: Dr. Donald R. Shaffer Upper Iowa University Lecture 1 Westward Expansion: Significance of the Frontier The West exerted a powerful influence on the U.S. during the 19th century Manifest Destiny: the idea that Americans spreading from the Atlantic to the Pacific was divinely foreordained End of the Frontier 1890 Census found no frontier line, only pockets of unsettled land Announcement caused Americans to reassess the frontier’s meaning “Significance of the Frontier in American History” (1893) Prompted the Census Bureau’s 1890 report Frontier had acted as a social safety valve Frontier had promoted individualism, pragmatism, egalitarianism, equality, and democracy Frederick Jackson Turner Author of the “Significance of the Frontier in American History” Lecture 1 Westward Expansion: The New Western History Turner and his followers helped create a romantic view of the West that made its way into popular culture Epitomized by Hollywood western in which settlers and the U.S. army bring civilization to the wild West The New Western History refers to a group of scholars that reject Turner’s positive, rosy view of westward settlement They even rejects the concept of “frontier” itself since human societies had long existed in the American West Speak of “borderlands” where U.S. citizens encroached on and disrupted established societies, and wastefully exploited nature often causing serious environmental damage in the process Critics have charged this view is too negative and contend that the effect of American settlers on the West was on balance positive Although lacking a significant effect on popular culture, 1990’s Dances with Wolves is arguably a New Western History Hollywood Western – why? Lecture 1 Westward Expansion: The Mining Frontier Americans moved west to pursue economic opportunity Nowhere was this fact more dramatically illustrated than among the miners Nothing like a gold or silver strike could bring Anglo-Americans faster into a new area Characteristics of the Mining Frontier: Overwhelmingly male: mining was hard manual labor, which discouraged the presence of women Transient: miners only stayed in a location as long as it was producing Miners generally lacked concern about the natural environment Hence to obtain minerals they sometimes used environmentally disastrous practices like hydraulic mining Hydraulic Mining Utilized high powered water hoses, literally eroding hillsides to get at the minerals beneath Lecture 1 Westward Expansion: The Ranching Frontier Texas Cattle Frontier Appeared before the Civil War The Long Drive: longhorn cattle fattened on government rangeland and then driven to Kansas railheads Ranching highly profitable in its early decades: $5 calf raised and fattened on free government grass could sell for $25 or more As frontier moved west so did the center of the ranching frontier: from Texas to Colorado, into Wyoming, Montana and the western Dakotas Open-range ranching ended, causes: Overgrazing Winters of 1885-1887 Cowboys: Myths vs. Reality Became a historical icon Tough work for low wages Cowboys gathered around a chuck wagon out on the open range Lecture 1 Westward Expansion: The Farming Frontier “The Great American Desert”: before Civil War the far west was commonly considered unsuitable for agriculture New farming techniques opened up this region to American farmers Irrigation (not so new) “Dry Farming”: farming to maximize moisture conservation Homestead Act (1862) Helped spur agricultural settlement of the West Free land for small filing fee, fiveyears residence, and improvement of the property Railroads also spurred settlement by transporting settlers and packaging land for sale on affordable terms Lonely, isolated, often primitive life in early years Prairie sod house in North Dakota Why did early settlers build their houses from earth? Lecture 1 Westward Expansion: Native Americans U.S. expansion came at expense of Native Americans, who lost much of their land as well as their way of life Buffalo exterminated, Indians cleared from plains Indian Wars: 1865-1890 Battle of the Little Bighorn (1876): rare Indian victory What to do with the Native Americans of the plains? Even Indians’ friends believed they must be assimilated into larger American society Dawes Severalty Act (1887): encouraged assimilation by distributing tribal lands to individual Indian families Ghost Dance movement: evidence of Indian cultural trauma Wounded Knee (1890): U.S. army crushed the last armed Indian resistance in what amounted to a massacre “Before” and “After” pictures of a Navajo boy at the Carlisle Indian Industrial School, c. 1880s Boarding schools were tools of assimilating Indian children to Victorian American culture