Chapter 30 war to end war
advertisement

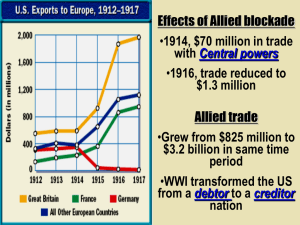
The War to End War 1917 - 1918 War by Act of Germany Jan 22, 1917 – futile attempt to mediate between the embattles belligerents – “peace without victory” Jan 31, 1917 – Germany announced unlimited submarine warfare – sink all ships, including America’s, in the war zone Wilson Responds Wilson broke diplomatic relations – War only if Germans took overt acts against American lives or property Wilson asked Congress for the authority to arm merchant ships – Filibuster to block measure – Reminder of the strength of American isolationism Zimmermann Note March 1, 1917 – note was intercepted & published – German foreign minister Arthur Zimmermann secretly proposed a German-Mexican Alliance – Promised recovery of Texas, New Mexico, & Arizona – Infuriated Americans, especially westerners Zimmermann Telegram Zimmermann Telegram Wilson Moves Toward War March 1917 - German U-boats sank 4 unarmed American merchant vessels Russian Revolution had overthrown the tsar – America could now fight for democracy April 2, 1917 – Wilson asked Congress for a declaration of war against Germany Wilsonian Idealism Enthroned 6 senators & 50 representatives voted against war – Jeannette Rankin – first congresswoman (Montana) Wilson goals for war: – “a war to end war” – Crusade “to make the world safe for democracy” Wilson’s Fourteen Points Jan 8, 1918 – Wilson delivered his 14 points to Congress 1st Five Points: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Abolish secret treaties Freedom of the seas Removal of all economic barriers Reduction of armament burdens Adjustment of colonial claims in the interest of both native peoples & the colonizers 14th Point – League of Nations International organization that would provide collective security Creel Manipulates Minds Committee on Public Information – headed by George Creel – Purpose: sell America on the war & sell the world on Wilsonian war aims – Employed 150,000 workers • Sent 75,000 “four-minute men” delivered countless speeches Varies forms: – Posters, leaflets, pamphlets, propaganda booklets, movies, & songs Propaganda Enforcing Loyalty & Stifling Dissent German-Americans numbered over 8 million – Dependable loyalty to the US Hatred of Germans & things Germanic swept the nation – Too bad for you Sauerkraut! I prefer liberty cabbage! Controlling Public Opinion – 1917 Espionage Act – stiff penalties for spying – 1918 Sabotage Act & Sedition Act – made it a crime to say, print, or write almost anything perceived as negative about the government 1,900 prosecutions under the laws – Mostly antiwar Socialists & members of the radical union Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) Eugene V. Debs sentenced to 10 years under the Espionage Act in 1918 (Socialists) – Later pardoned by President Harding in 1921 – William (Big Bill) Haywood (head of IWW) & 99 associations were also convicted Debs in Prison (Read Aloud) following quote from President Wilson regarding Eugene V. Deb’s release from prison. “I will never consent to the pardon of this man. While the flower of American youth was pouring out its blood…this man, Debs, stood behind the lines, sniping, attacking, and denouncing them. Before the war he had the perfect right to exercise his freedom of speech and to express his own opinion, but once the Congress of the United States declared war, silence on his part would have been the proper course to pursue… This man was a traitor to his country and he will never be pardoned during my administration.” Factories Go to War Wilson had done little to prepare for the possibility of war – 1915 – Council of National Defense – study problems of economic mobilization – Shipbuilding programs – Modest beefing-up of the army – 100,000 regulars 1918 – War Industries Board – Bernard Baruch – “Labor will win the war” The War & Workers 1918 – War Department’s “work or fight” rule – Threatened any unemployed male with being immediately drafted National War Labor Board – chaired by Taft – Head off labor disputes that might hamper the war effort • Helped workers receive higher wages & 8 hour days • Did not guarantee the right to organize into unions Samuel Gompers & AF of L – supported the war IWW (Wobblies) & other radical labor organizations – Engineered damaging industrial sabotage Strikes & The Strikebreakers 6000 strikes broke out during the war years 1919 – Steelworkers Strike – More than a quarter of a million workers walked off – Wanted right to organize & bargain collectively – did not get that right – Company refused to negotiate • Hired 30,000 African American strikebreakers – More than a dozen workers dead – Crippling setback for the union movement Great Migration African Americans moved North for war-industry employment Racial tensions resulted: – July 1917 – East St. Louis, MI • 9 whites & 40 blacks dead – July 1919 - Chicago Race Riot • Reign of terror lasted 2 weeks / 15 whites & 23 blacks dead Women & the War Thousands of female workers worked in factories & fields – took jobs vacated by men who went to war President Wilson – convinced to endorse woman suffrage as a “vitally necessary war measure” – 19th Amendment – women receive the right to vote 1920 Women’s Bureau emerged after the war – Protect women in the workplace Sheppard-Towner Maternity Act of 1921 – Provided federally financed instruction in maternal & infant health care Women’s Suffrage Forging a War Economy Food Administration – Headed by Hebert C. Hoover – already considered a hero because of the charitable drive to Belgium – Preferred voluntary compliance – Rejected ration cards – Propaganda campaign • Wheatless Wednesdays • Meatless Tuesdays • Victory Gardens 1919 – 18th Amendment – prohibited alcohol – Many brewers were German & used foodstuffs Voluntary Approach Fuel Administration – save fuel – Heatless Mondays – Lightless Nights – Gasless Sundays Treasury Department – Promoted sale of Liberty Loans – Victory loan campaign - 1919 – Taxes were eventually raised Forceful Approach 1917 – Gov’t took over the nation’s railroads Gov’t seized merchant vessels in American harbors – Started campaign to build more ships// a few ships vessels were launched – Faith Making Plowboys into Doughboys Early American involvement – Used navy to uphold freedom of the seas – Shipped war materials to the Allies & supplied them with loans April & May 1917 – Allies confessed the need for American troops – More troops or the whole western front would collapse The Draft Wilson disliked draft but eventually supported conscription – Draft bill was criticized by Congress – Passed 6 weeks after US had declared war Required registration of all males 18 – 45 – No one could purchase an exemption or hire a substitute – Worked effectively – Army grew to 4 million Women & African Americans – Women admitted to navy & marines – African Americans – segregated units usually under white officers Fighting in France Bolsheviks withdrew Russia from war early in 1918 – Released Germans from the eastern front in Russia & moved them to western front in France Spring of 1918 before the US reached France to fight – Mainly used as replacements with the British & French Small detachments were also sent to Belgium, Italy, & Russia Spring of 1918 Allied nations united under French Marshal Foch in order to fight the Germans May 1918 – Germans came within 40 miles of Paris US troops sent to Château-Thierry; right into the German advance – 1st significant engagement of troops in European war July 1918 – Second Battle of the Marne – Beginning of the German withdrawal American War Continues Americans were demanding a separate army – General (Black Jack) Pershing was assigned a front Last mighty Allied assault – Sept 26 – Nov 11, 1918 - Pershing’s army undertook the Meuse-Argonne offensive • Goal was to cut the German railroad lines • Lasted 47 days & included 1.2 million American troops – Germans were ready to surrender Fourteen Points Disarm Germany October 1918 – Wilson demanded that the Kaiser be overthrown before an armistice could be reached – Kaiser was forced to flee to Holland Germany surrendered Nov. 11, 1918 US’s main contributions: – Foodstuffs, munitions, credits, oil, & manpower Woodrow Wilson Very popular Personally appealed for a Democratic victory in the congressional elections of 1918 – Republicans won a majority to Congress Decided to go to Paris for the peace conference – Infuriated Republicans Peace Treaty - snubbed the Senate & neglected to include a single Republican – Should have included Henry Cabot Lodge – chairman of the Senate Committee on Foreign Relations Idealists Battles the Imperialists The Big Four: – Woodrow Wilson – US – Vittorio Orlando – Italy – David Lloyd George – Britain – Georges Clemenceau – France Wilson’s goal- League of Nations – Victors would not take conquered territory outright – Receive territory as trustees of the League of Nations • Syria – France /// Iraq – Britain Feb. 1919 – League was included in peace treaty Hammering Out the Treaty League of Nations was not popular in US – William Borah & Hiram Johnson Republican senators refused to approve the League in its imperfect form France – Demand: the Rhineland & the Saar Valley – Compromise: Saar Bain would remain under the League for 15 years & then a popular vote & Britain and US would aid in defense from German invasion Italy – Demand: Fiume but Wilson insisted that the seaport go to Yugoslavia – Turned against Wilson Japan – Demand: China’s Shantung peninsula & German islands in the Pacific – Compromise: Japan kept Shantung & pledged to return it to China at a later date Treaty of Versailles June 1919 – Germans were forced to sign – – – – Take full responsibility for the war Disarmament Pay 33 billion in reparations Give up colonial holdings Wilson was forced to compromise in order to save the League of Nations – Liberation of millions of minority peoples Wilson was no longer popular in Europe US did not support any part of “entangling alliances” Wilson’s Tour Majority of Americans did support the treaty July 1919 – Lodge wanted to “Americanize,” “Republicanize,” or “senatorialize” it – Republicans wanted to take credit Summer 1919 - Wilson began speechmaking tour – Appeal directly to the people for their support – Midwest received Wilson lukewarmly – Rocky Mountain region & Pacific Coast – welcomed Wilson – Borah & Johnson spoke out against Wilson Wilson’s Collapse Breaking Point: – September 25, 1919 – Wilson pleaded for the League of Nations in Colorado – Collapsed & later had a stroke that paralyzed one side of his body – Did not meet with his cabinet for 7½ months Wilson Rejects the Lodge Reservations Senator Lodge proposed 14 formal reservations to the 14th Points – Rejected by Wilson with the strong support of the Democrats – Republicans disliked it because it morally bound the US to aid members – Article X Wilson sent word to all Democrats to vote no Nov 19, 1919 – treaty was rejected Defeat Through Deadlock Majority of Congress could not agree March 1920 – Treaty was brought up for a vote again – Wilson sent word to the Democrats to vote down the treaty with the Lodge reservations – March 19, 1920 – treaty was rejected again Who defeated the treaty? – Lodge-Wilson personal feud, traditionalism, isolationism, disillusionment, & partisanship – -Ultimately it was Wilson who defeated the treaty due to his inability to compromise!~ Election of 1920 Wilson proposed to settle the treaty in the election – Appealed to the people for a “solemn referendum” Republicans – Platform appealed to the Pro-League & Anti-Leaguers – Warren G. Harding – presidential candidate • Selected by Senate bosses meeting in the “smoke-filled” Room 404 of the Hotel Blackstone – Calvin Coolidge – vice presidential candidate Democrats – James M. Cox & Franklin Roosevelt Harding wins Election Results – First Presidential election for franchised female voters – Death sentence for the League Eugene V. Debs – received the largest vote ever for the Socialist Party – While he was in prison