America Enters WWI
advertisement

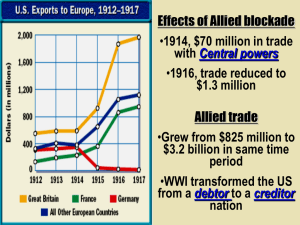
World War I “The Great War” APUSH By 1914… • Most European nations had divided themselves into alliances that led to war when a Bosnian nationalist shot & killed the heir to the Austrian throne – Central Powers: Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy, and Bulgaria – Triple Entente/Allied Powers: France, Russia, Great Britain • The US was NOT a member of an alliance & DID NOT have to join the war Why did the US avoid WWI? • Read Woodrow Wilson’s Speech from 1914 (Document A) & then discuss with your table partner & record your answer: 1. Why did Wilson think the US should NOT enter WWI? Provide evidence from the document to support your answer. • Read “Wilson and Mexico” on pp.774-775 in your textbook 2. Why was Wilson so reticent to enter WWI when recent American foreign policy (Manifest Destiny, War with Spain, etc.) had been so imperialistic? Why did the US choose this course of action? • It wasn’t our business – Which Europeans would the US support? – The US should push for peace • Problems with neutrality (a la GW) – Trade & connection to the British – Freedom of the Seas • Lusitania, 1915 • Arabic & Sussex pledges • US Prepares…for war or peace? – Army & Naval buildup – Negotiations… Why did the US join WWI? • Read Woodrow Wilson’s Speech from 1917 (Document B) • Discuss with your table partner & record your answers. Be sure to provide evidence to support your answers: 3. By 1917, why did Wilson think the US should enter WWI? Provide evidence from the document to support your answer. 4. What did Wilson accuse Germany of doing? 5. Do you think this is a good reason to go to war? Explain. 6. Re-read the last two paragraphs of the speech. Why do you think Wilson added these paragraphs? How do you think these words made Americans feel? • US Declaration of War… – Make the world safe for democracy – For the rights & liberties of small nations – A war to end all wars – Strengthen GB’s navy (a la Monroe Doctrine ) • Turning the Tide – War declared April 1917 – AEF arrives summer 1917 (American Expeditionary Force) • Americans were VERY ready by 1917 to go “Over There” Why the US Went to War Over There • In 1917, George M. Cohen, wrote the song, Over There. The 1942 movie Yankee Doodle Dandy used the song to help tell its story (Document C) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i5oWH6JWBJY – 7. How is the song useful as evidence of American life and attitudes during WWI? Explain. – 8. How is this movie clip useful as evidence of American life and attitudes during WWII? Explain. – 9. Which is more useful, the song for to explain attitudes during WWI or the video clip to explain American attitudes during during WWII? Explain • Why else did the US go to war? – Zimmerman Note – Return to Unrestricted Submarine warfare – GB broke – Chaos in Russia • Discuss with your table partner: 10. What do you think are the TWO biggest reasons why the US entered the war? 11. Based on the reasons in Wilson’s 1917 speech and those given above, do you think the US had good reasons for entering the war? Why or why not? Pulling the US into War A Little Bit about Historian Howard Zinn • Howard Zinn was a historian and activist who was best known for his 1980 book, A People’s History of the United States. His book tells American history from the perspective of minorities, women and poor people. He was very critical of the United States government. Were those really the reasons? • Read the excerpt from Zinn’s book, A People’s History (Document D) • Discuss with your table partner 12. Why did Zinn claim that Wilson made a “flimsy argument?” 13. What did Zinn suggest were the real reasons the US entered the war? 14. What evidence did Zinn provide to support his claims that the US was motivated by other reasons (besides German attacks of US ships)? 15. Do you find Zinn’s argument convincing? Why or why not? Primary Document Analysis (Documents E- N) • You will be given a set of primary documents to analyze that relates to the US home front during WWI: Set 1 (E & F), Set 2 (G & H), Set 3 (I), Set 4 (J), Set 5 (K & L), Set 6 (M & N). 16. Audience/Purpose: Why and for whom was the document produced, and how might this affect the reliability of the document? – 16. Main Idea: What was the document’s main idea or point that the author was trying to make? – 17. What does this document teach us about the US home front during WWI? – 18. In addition to analyzing your assigned documents, please do some additional research on the document’s main topic (listed after the document’s “letter”). Please take notes regarding the other documents. The Home Front… • Wilson’s Preparedness Program – “Mobilization of men, money, machines & minds” • Men (Docs E & F) – Selective Service Act, 1917 • Money (Docs G & H) – Liberty Bonds & Victory Loans • Machines – Ships, Guns, Jeeps… • Minds (Doc I) – Opposition to the war – Committee on Public Information Woodrow Wilson Fighting the War at Home • Conversion to Full Wartime Economy – War Industries Board (Doc J) – Council of Defense • Food Administration (Doc K) • Fuel Administration (Doc L) – The Labor Force • National War Labor Board • Attack on Civil Liberties WWI US Propaganda Poster • Espionage Act, 1917 • Trading with the Enemies Act, 1917 • Sedition Act, 1918 (Docs M & N) Woodrow Wilson’s 14 Points • Wilson’s Plan for World Peace (Doc O) • 9 Points – Self Determination – 19. What was said about the right of people to govern themselves? What people? How would territorial disputes be settled? • 4 Points – Causes of War – 20. What restrictions were put in place to make sure that war was avoided in the future? • 1 Point – League of Nations – 21. What was the purpose of this League? How would it “work”? The Surrender • German generals decide to surrender – Can’t win with US entry into the war – Hope the treaty will be based on the 14 Points – Kaiser abdicates • The cease fire goes into place at 11 AM on 11/11/1918 (Armistice Day) – Peace Conference set for January 1919 in Paris Paris Peace Conference & the Treaty of Versailles (Document P) • Wilson leads US delegation – Wants to “end all wars” • Treaty provisions – 22. What did members of the League of Nations commit themselves to? – 23. What kind of punishments did Germany receive? The “Big Four” (L to R) David Lloyd George – GB Couldn’t be trusted Georges Clemenceau – France Wanted revenge Vittorio Orlando – Italy Demanded new ports Woodrow Wilson – U.S. 1914: Before the Great War Great Empires: • Russia • AustriaHungary • Ottoman Empire (Turkey) After the Great War: by 1924 New Countries: • Finland • Estonia • Latvia • Lithuania • Poland • Czechoslovakia • Yugoslavia • Syria • Trans-Jordan • Iraq Fight Over the Treaty • Wilson returns to US (Docs Q & R) – 241. Why was Wilson so adamant that the Treaty be approved? • Senate has to approve treaty (Docs S & T) – 25. What was Lodge’s reason for rejecting the treaty? – 26. Do you agree or disagree with Lodge’s reservations? • No compromise: Wilson vs. Congress • League – set up in Geneva, Switzerland without the U.S. Reflection Questions • 27. What do you think was the biggest reason why Europe erupted into war? • 28. What provisions would you have put in the treaty of Versailles? What would you have excluded? • 29. What are two things that were new, interesting, or you know that you will (or should) remember a month from now?