MAJOR COMPARISONS/ANALYSES By - Course
advertisement

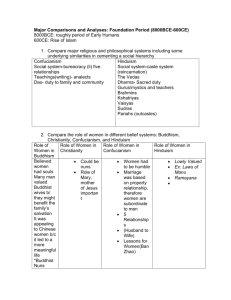
MAJOR COMPARISONS/ANA LYSES By: Deneshia W. and Kayla E. Compare Hinduism and Confucianism Hinduism Was a minor religion of classical India. Developed gradually over a period of many centuries. Monotheistic. Goal to attain nirvana. Popular in china. Confucianism Dealt with obedience and respect. Based on Chinese values. Elements were: polite, ritual, self control, etc. Sought elegant calligraphy in cultivation of scholar bureaucrats. Comparison Conficianism Hinduism •Spirituality •Religious •Social system •Worship more than one deities •Believe in reincarnation •Look into lifes meanings •Similar social hierarchy •Look for common good •Political and social philosophy •Family based •Peace •Tolerant •Respect family always •Patriarchal Compare the role of women in different belief systems: Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism R ol e s of w om e n i n Buddhism and C h r i st i ani t y Christianity Women were considered as property Subordinate to their husbands Take care of the family Women are to obey their husband They are to take care of their husband Buddhism Women were confined to household Didn’t restrict educational rights for women Could be in business Could be in trade Woman gained more rights Roles of women in Confucianism and Confucianism Hinduism Hinduism Patriarch families Women had to practice obedience Had to practice humility Had to practice devotion towards their husbands They were seen below men Patriarch society Expected to raise children Had to clean Tend to husband Had to cook for the family Women not allowed to remarry after death of husband No public authority Had to throw themselves in fire.(SATI) Collapse of the Roman Empire and the Han in China Collapse of Han Empire Heavy taxes levied on peasants. Decline in interests in Confucian intellectual goals. A decline in morality. Weak emperors and the increased influence of army generals. Social unrest, particularly by students. Emperors lost control Collapse of Roman Empire Decline in trade. • Plague Recruitment of non-Romans in the roman army. Invasions from Germanic tribes Social and moral decay in lack of interest in the elite classes. Decrease in money flow Epidemic diseases Roman dependence on Slave labor Comparison of Collapse of Roman and Han Empire Poor harvest Population decline from epidemic disease. A decline in trade Compare the caste system in India with slavery in the Roman Empire Caste System In India There was social mobility Priority to religious status Didn’t have a broad social group Introduced by Aryans Four classes(laborers, farmers, warriors, and brahma(priests)) Birth determined occupation Karma More religious Slavery in Roman Empire Democracy Citizens with rights Nobles Plebeians Aristocrats Comparison People into classes Had certain rights Compare Silk Road trade in the classical world with trade in the Mediterranean Sea Silk Road Trade Started in China There was a series of routes Started with Han dynasty China exported tea, silk, etc Imported spices from India Religions exchanged…. Mediterranean Sea Trade First sea used for trade Next to the coast Major link to East Linked Europe with goods from Asia Middle of Earth Comparison Both major trade routes Bothe made trading easier Both were successful trading routes Critical to development of western civilizations Compare the political and social structure of Mesopotamia and Egypt Social structure Political structure City-states Had social classes King had authority Had slaves Gov. provided court system Slaves could ear money Law code of Hammurabi King Priest Nobles Social structure Political structure Had a king/pharaoh Had social classes Taxation system Religion was important Theocracy government Had farmers Had laws on Farmers made up vast punishments majority of population Compare the role of women in the Middle East before and after the rise of Islam the role of women in the Middle East before the rise of Islam They could inherit property They could divorce their husband They could engage in businesses There was equality Dowries went straight to the bride Controlled sexual and social lives of women the role of women in the Middle East after the rise of Islam They couldnt inherit property They couldnt divorce their husband They couldnt engage in businesses There was no equality They still controlled sexual and social lives of women Analyze the interactions between Jews, Christians, and Muslims in this period They believed in the same God, but worshipped him in a different way. Black death, christians believed jews fault, so they burned jews to stop the disease. Crusades with jews and christians, lead to distrust between christians and muslims. They worked and lived together and made achievements in astronomy, art, poetry, etc. Compare Japanese and European feudalism Japenese Feudalism revamped tax system hired foriegn experts to facilitate economic development Meiji leaders goal was to to centralize power destroyed old social order new governors were appointed power lied with the emperor European Feudalism based on neat hierarchy of lords and vassels Took charge of politcal/military affairs Slaves and free peasants serfs Lords could execute for serious misconduct Comparison Both european and japanese feudalsim had political structure Social structure Honor code based on culture Do a SPRITE chart for the Sudanic States (Mali, Ghana, Songhai) Mali Had centralized government Extended across senegal Mali took over after ghana Controlled trade Muslim kingdom Ghana Ghana thrives Had a large army Was principal state Converted to islam Trade improved Songhai Muslim kingdom Built up after Mali empire Important trade center with Mali Weakened by internal problems Had central government Was a fishing community Well trained army Believed in many gods Analyze the Chinese civil service exam system, the rise of cities, and technological and economic innovations of the Tang/Song dynasties Civil service exam used mainly to grade officials Rates were very small Were in a small cubicle Watched over closely Lived in the cubicle the rise of cities, and technological and economic innovations Rise of regional military Development of woodblock printing Market quarters grew larger saw Analyze the growth and spread of Indian Ocean trade during this time period —include monsoon winds, dhows, et Was an important trade area Extended from East Asia through India to the east coast of Africa Trade winds half of the year blew northeast (December to March) and the other half of the year they blew southwest (April to August) Trade winds were a primary factor of merchants movements The Junks sailed on the Indian Ocean Had to wait for monsoon winds Islam and buddhism were spread through trade Spread the Black Death Dhow boat helped move more flexible and easier 1450CE-1750CE C o l o n i a l a d m i n i s t rat i on o f t h e Spanish and the British Spanish Gained control over most of the new world Extended control over American empire The kings representatives were the viceroys Settle could not make there own laws Colonial business were control by spanish royals British Had control over colonies affairs Maintain there own assemblies Chose there own governors British ruled People finance the expeditions to America Had privateinvestors Coercive labor systems Couldnt own land Worked with no pay Had to pay land lords Sold to other coutries Got little pay Were beated Chain together Boarded on ships Traded slaves for goods Were chained on ships Worked on planatations No pay Exchanged slaves for goods Introduced to new diseases Worked on planatation and mines No pay Russia’s Interaction Ottoman Empire Instabul becomes the capital Wheat and rice were major crops Had long distant trade Behind in Technology Constaniople is conquered Osman Bey was the founder China Mongols taught them to fight Trade parnters Gun power empires Both control by the mongols Advanced weapons Western Europe Russia wanted there land Traded with each other Wanted trade dominance Wanted protection Eastern Europe Russia wanted there land Traded with each other Wanted trade dominance Wanted protection over there nationalism Development of Empires Asia Africa Asia Urbanized Bureaucracy Merchants increased Centralized government No foreign influences Rejected Christianity Isolated from the world Africa Bureaucracy Prospered from help from European nations Slave trade increased Imperial System Eupropean Seaborne Land based Asian Empire New crops were introduced Population increase at a rapid rate Westernized Foreigners were forced off the land and nationals were kept in Aztec/Inca Aztecs Trade and markets were more developed Spoke Nahuatl Human Sacrifice Forced to pay tribute Inca Temple of the sun Spoke Quechua Pachacuti was the ruler Split inheritance Holy shrines mountains, stones rivers caves etc. Hatian and French Revolution Hatitian Revolution Based on sugar Divided among slave workers Declared independence in1804 Toussaint L’Overture French Revolution Began in 1789 King Louis XIV Increased of enlightenment ideas 1750CE-1914CE Industrial Revoltion Western Europe Wanted power and resources Wood was a main source of fuel but they were using a lot of tree Use coal for stream power Agriculture efficiency improved Less people needed to work the lands More people moved to the cities to get jobs in the factories Japan Meiji Restoration Wanted to compete with industrialized nations and avoid foreign influences Upset because of unequal treaties from other nations Transportation and communication was improved Introduced to railroads , stream boats and telegraphs New banking system Ottoman Empire Did not accept foreign influence from Jews and Christians Didnt except advanced weapons Not worthy of their culture Cause the decline of there Empire China Shut themselves out from the world Were behind in new technologies British were selling new technologies to china British fought the chinese because the selling these new technologuies was tearing apart communities India British took control of India Wanted to take over because of wealth from trade The Sepoy’s Rellibion India was changed schools were built, Sati could not be practiced Indians could voice there opinion Southeast Asia Dutch Ruled Dutch wanted to control the spice market Japan British, French, and U.S came to establish relations with the japenese Sailors were rude and had poor hygiene Unequal treaties Took the governments control over the tariffs and foreigners extraterritorial rights Nationalism China/ japan Traded with other countries Self involved society Didn’t accept foreign influence Didn’t trade with others countries 1853 open for trade Tried to become a democratic govenment Italy Napolean invading Italy was the main cause Haven’t been a united country Austria was dominant power Nationalist ideas were ignored Pan Africanism Spoke for all Africans Had no political power Edward Blyden (didnt like mixed marriages) Had no equal rights Indian Congress Movement Led by Mahanadi Ghandi Believed in non-violence No equal rights Could not be in high positions Boycotted british goods British seperated Bengal India had to fight Germany Western Intervention Latin America Haiti’s population was made up of 90% slaves Main goods were coffee, sugar,cocoa, and indigo Pierre Toussaint L'Ouverture formed a slave revolt In 1804 Haiti became a free republic Argentina Jose De San Martin took control of the Army Boilvar established a national congress Brazil Porgual was invaded by Napolean Pedro declared brazil independent Africa Established colonial rule Egypt had levied there own taxes Egypt had Dominant trade South Africa discovered diamonds and gold South African abolished slavery in1833 South East Asia Wanted to bring buddism to reduce western influence (Young Man’s Buddhist Association) Sareket Isalm bring all Muslims together Malayas were brought to the civil service Indonesia National Party was by indonesians in Dutch school WOMEN Women in Latin America Take care of the house Cant own a business Don’t get Proper health care Discrimination in the work force No Abortion Men ran the house hold Women in Europe Had to look good for men Rape wasnt a crime Low rates of births Married early No education Took care of the house Nationalism Europe They had The French Revolution They divided Italy (was no equal) Form a group called Young Italy(Guisseppe Mazzini) to unify Foreign Intervention WARS Foregin intervention Wanted power More equal Colonial areas Independence Movements India 1857 The Indian Independence movement Lead by Mahatams Ghani in India, This movement was caused by rascism towards them and the british forcing them to swith relgions. He practiced non violence and encourged Indians not to purchase British goods. Africa Africa Fought against the French for there independence and did many protests against un equal rights Effects of Western Consumer Society Positive Effects Less expensive Newer technology Better relationship with other countries Increases the growth of the economy Negative Effects Human rights are abused More Poverty Hurts the environment Corperations are dominanting Warfares Trench Faliure of the Schlieffen Plan Wanted to invade France through Beligum For soliders protection Formed in ZIG ZAG Troops slept in ltitle hole dug in the trenches Planks and sandbags were used to support the roofs of the trenches Terrorism When you go back in fourth against one side . They shot guns, throw grandes and other weapons against others Guerilla Means little war Smaller armies goes against bigger armies and the bigger armies , The smaller armies usually strikes and rans back to there side of the war line Nucleaur Is when power weapon forces are thrown at the enemy side such as missles, bombs Economic Growth Nafta Began in 1994 Removed Barriers and trade investments among USA, Canada , and Mexico Free trade with Mexcio EU Helped stop violence Protecting citizens Enhance the government *Compare patterns and results of decolonization in Africa and India Africa Nationalism was promoted Political instability Economical disaster forced to industrialize(kenya) India More tension between hindus and muslims War between india and pakistan after gandhi death Gandhi killed because of tryng to reunite muslims and hindus Motivated to gain independence because of lack of natives in gov. positions Comparison Tired of being controlled by europeans Great depression lowered incomes Developed sense of nationalism *Pick two revolutions (Russian, Chinese, Cuban, and Iranian and compare their effects on the roles of women Chinese Foot binding Granted women and men were equal Divorce legal One child policy Loyalty to state Loyalty to family Equal rights in labor systems Russian Full abortion rights Women given more job opportunities Increase change in education Fought prostitution Women had more freedom in marriage, family, and guardianship More political chances Japanese Used war as an excuse for imperialism Captured german colonies Declared war on china Helped retain power in pacific and asia Defeated by soviet union united states became main supplier Europe couldn’t export to japan Japan attacked pearl harbor Japanese pursued expansion *Compare legacies of colonialism and patterns of economic development in two of three areas (Africa, Asia, Latin America Africa Faced large foreign debts Controlled by European Couldn’t develop because of WWI Great Depression cause problems for Africa High unemployment rights Wars for independece occured *Compare the effects of WWI and WWII on areas outside of Europe Asia Expanded authority to parts of Ceylon Built extensive railway systems Cleared forests Constructed new canals Reconstructed landholdings Asia affected by Great Depression