Battle of Galicia
advertisement
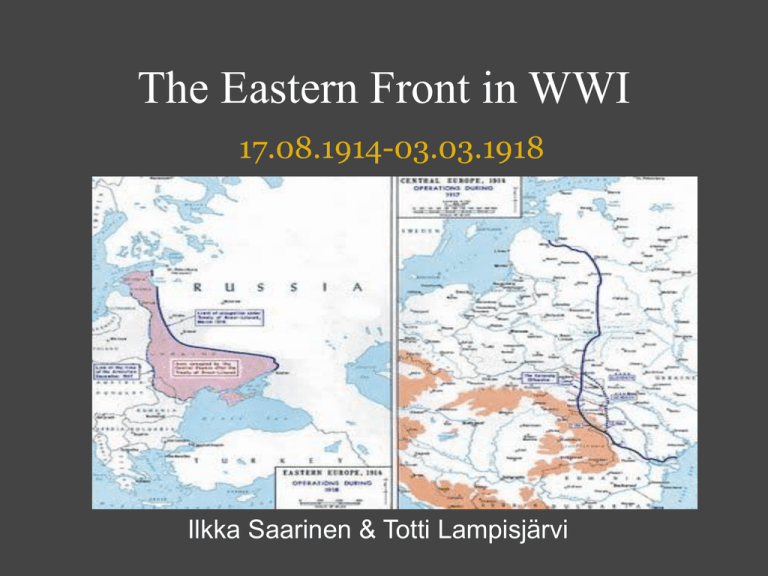
The Eastern Front in WWI 17.08.1914-03.03.1918 Ilkka Saarinen & Totti Lampisjärvi Belligerents: • The Russian Empire (later the Russian Republic, Russian SFSR) and Romania (1916) versus • The German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire and Bulgaria. Introduction • Eastern Front around 1600km long, stretching from Saint Petersburg and the Baltic in the North to the Black Sea in the south. • Different warfare compared to the Western Front. • Opening battle the Battle of Stallupönen. • 1914-1918 Battles There were numerous battles going on on the Eastern Front from 1914-1916. These include: • Battle of Stallupönen (first battle) • Battle of Tannenberg (significant) • Battle of Galicia • • • • • Battle of Gumbinnen First and Second Battle of the Masurian Lakes Battle of Bolimov Battle of Lake Naroch Battle of Lutsk VS. Battle of Stallupönen (Present day Nesterov) • This is a significant battle because this was the first military action that was seen on the Eastern Front. • The battle was between Paul von Rennenkampf's men (Russia - 200,000 troops) and Hermann von Francais' men (Germany - 40,000 troops). • This battle ended in a minor victory for Germany and did not affect Russia as a strength significantly (yet). CHECK THAT MUSTACHE! The Battle of Tannenberg 1914 • 23-30.08.1914 • Complete defeat and demoralization of the Russians(~78,000 killed or wounded, whereas only 5,000 Germans killed). • Early phases 23-26.08. • Main battle 26-30.08. • Demoralised the Russian armies completely. • http://www.youtube.com/wa tch?v=y7qbZaf_olY The Battle of Galicia (1914) • Russia invaded the AustroHungarian province of Galicia. • They won, and ruled Galicia for almost a year. • Contributed to the decision made by the Central Powers to concentrate on the Eastern Front starting in 1915. 1915: The Central Powers Attack • The Central Powers launched a major offensive in 1915 against the Russians. • Russians retreated, more due to lack of sufficient weapons than lack of knowledge or numbers. • Russians pushed back hundreds of kilometers from Ger/Aus-Hun borders, advance was stopped as the threat from Russia was gone. • Front stayed more or less the same until 1917. 1916: Limited Russian Success • The Russians, having received more and newer weaponry, attacked. • Larger military concentration/population than Germany • June 1916: General Brusilov started an offensive that went 5070km into Austria-Hungary, capturing hundreds of thousands of prisoners, and weaponry. • Ended in September due to reinforcements coming in from the west. • Romanians successful at first, but then overthrown by superior weaponry and lack of support from Russians. The Eastern Front (Provisional Govt) • Following the February Revolution, the government of Alexander Kerensky needed a victory to raise support for the war. • The Kerensky offensive in July 1917. • Early successes, complete failure later due to lack of discipline and morale. • Complete halt by July 16th, followed by retreat. The Eastern Front (Communist) • Despite wanting to end the war, Lenin did not want to accept the harsh German peace terms. • The Germans started marching across Ukraine more or less with impunity. • Lenin was in essence forced to agree to the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk. • The war on the Eastern Front was over (3 March 1918 - signing of BrestLitovsk). Main Sources BBC - History: World War One http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/worldwars/wwone/ First World War.com - The Eastern Front http://www.firstworldwar.com/battles/ef.htm The War Times Journal - The Eastern Front 1914-1917 http://www.richthofen.com/ww1sum2/