Egypt & Mesopotamia Notes
advertisement
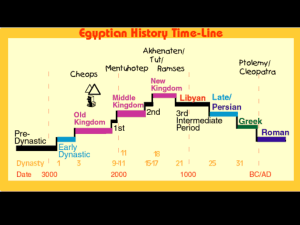
MESOPOTAMIA SWBAT Identify primary and secondary sources Use AP PARTS to analyze a primary source & describe how this primary source helps us understand Sumerian society Civilization Bell Work 9/4 What does it mean to be called civilized? What does it mean to be called a savage? 7 Features of Civilization What do you think makes a civilization? 1. Organized Government 2. Complex Religion 3. Job Specialization 4.Social Classes 5.Arts & Architecture 6.Public Works 7.Writing Famous example of sedentary society Çatul Hüyük, 6700-5700 B.C It was a walled Neolithic community sustained by food surpluses enabling Religion, specialization of labor, government, writing, etc… Today Take out your civilization chart, compare your answers with your neighbor and finish up anything that you haven’t completed By the end of today you should be able to Distinguish between secondary and primary sources Explain the purpose & implications of Hammurabi's code Notes – Mesopotamia & AP PARTS – 9/5/14 Copy the following into your notebook Primary Source- A primary source is a document or physical object which was written or created during the time under study. These sources were present during an experience or time period and offer an inside view of a particular event Secondary Source - A secondary source interprets and analyzes primary sources. These sources are one or more steps removed from the event. Secondary sources may have pictures, quotes or graphics of primary sources in them IDENTIFY THAT SOURCE! APParts – How to Break down Documents in AP AUTHOR: Who created the source? What do you know about the author? What is the author’s point of view? PLACE AND TIME : Where and when was the source produced? How might this affect the meaning of the source? PRIOR KNOWLEDGE : Beyond information about the author and the context of its creation, what do you know that would help you further understand the primary source? For example, do you recognize any symbols and recall what they represent? AUDIENCE: For whom was the source created and how might this affect the reliability of the source? REASON : Why was this source created at the time it was produced? THE MAIN IDEA: What point is the source trying to convey? SIGNIFICANCE Why is this source important? What inferences can you draw from this document? Ask yourself, “So what?” in relation to the question asked. AP PARTS Practice – Code of Hammurabi Read the primary source on page 11 in your book and work through the AP PARTS sheet Once you’ve finished compare notes with the person next to you Bell Work 9/9 Mesopotamia WH You are the king of Mesopotamia sent by the god Shamash to rule its people. You live in the capital city of Babylon which is located right between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. After decades of bountiful harvests the population of the city has skyrocketed. The people have been hardworking; many have left the farms due to the surplus of crops to start new businesses. The city now has merchants, artists, blacksmiths, scribes, warriors and even street entertainers who dance, tell jokes or do magic for passersby. Unfortunately though this years harvest was ruined by a devastating flood. People who were once peaceful and joyous towards their neighbors have turned on one another and the city has been engulfed in a wave of crime. Your city officials have come to you for answers, what would you do? Bell Work 9/9 AC How do you think your environment affects you as a person? Think about it, how do you think people from wealthier areas grow up compared to people from poorer areas? How do people from urban areas (big cities) grow up differently than people in rural areas (farming towns) Mesopotamian Environment - Located in the Middle East in modern day Iraq between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers - Unpredictable floods - No natural borders – people had to build walls to defend from invaders - Had to use irrigation to bring water to dry land - Not many natural resources Question: How could Mesopotamia's environment have influenced the civilization? Kingdoms of Mesopotamia A kingdom occurs during a period of stability, with strong rulers and cultural growth – called dynasties Sumerians – the 1st Civilization 3300 BC- 2300 BC 1. Made up of several independent city -states 2. Each city state responsible for their own walls, irrigation, tax collection City State City State City State Regional Problems City State City State City State City State City State Kings Ruled by DIVINE RIGHT “You in your judgment, you are the son of Anu; your commands, like the word of god cannot be reversed; your words like rain pouring down from the heavens are without number Society was structured in a Hierarchy City State Kings Priests & Nobles Merchants & Artisans Farmers Ziggurats 1. Built to keep gods happy. 2. Used for social events – animal sacrifices ,religious ceremonies & for defense against in coming armies Bell Work 9/10 Take out the worksheet from yesterday and compare answers with your neighbor Based on the graph, explain in detail what occurred around 10,000 years ago Why do you think the first evidence of recorded laws are from about 4,000 years ago? Ancient Civilization 9/10 - QUIZ You have a quiz, you have 5 minutes to look over your vocabulary. It will then be collected. Once you finish come place your quiz in the tray on the front table and grab a marker. In the mean time I have posted what will need to be in your notebooks below. Things you should have in your notebook include: Moon landing Bell Work Origin Story Notes 8/27 Near East Homework #1 (1.1 FOR WORLD HISTORY) Bell Work & Notes - Neolithic Revolution 9/2/14 (cartoon as well) Bell Work 9/3/14 – Zombie Apocalypse Civilization Bell Work 9/4 (Civilized vs. Savage) Bell Work 9/9 Mesopotamia & Notes Near East #2 ( 1.3 FOR WORLD HISTOTRY) Empires come and Go Akkadian Empire 2300-1800 BC Started by Sargon when he conquered all of the surrounding Sumerian city states Babylonian Empire 1790- 1400 BC Hammurabi establishes a code of law “Eye for an Eye” “if a house collapsed because of poor construction the houses builder could be put to death” What would it be like if we had laws like that today? Hittites 1400 – 1200 BC Develop iron working – Iron swords are stronger than bronze Why do you think so many empires came and fell in Mesopotamia? Mesopotamian Religion 1. Pessimistic - saw the gods as cruel & angry 2. Polytheistic – believed in many gods and goddesses 3. Afterlife- Everyone lived in a grim underworld from which there was no release “The place where they live on dust, their food is mud, blackness.” and they see no light living in 4. Divination – arose to discover the purposes/desires of the gods & took a variety of forms, from animal sacrifices to analyzing smoke patterns from incense Open Book Quiz – 2/6/14 you have 15 minutes to answer the following – in complete sentences. 1. Describe the "Miracle of the Nile." 2. What were the 3 periods of Egyptian history characterized by? (in essence, what did they have in common that made them worthy of being called the Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms) 3. Explain the role of the vizier. 4. How was the role of the pharaoh different during the Middle Kingdom? 5. Describe how the story of Osiris symbolically represented the flooding of the Nile. Bell Work 9/11 World History TAKE OUT YOUR HOMEWORK SO I CAN CHECK IT IN! Describe the social classes of MacArthur High School, who do you believe to be at the top of the social pyramid? Who is at the bottom? Also, Write your name in Hieroglyphs! Mesopotamian Social Patterns 1. Social Classes/ Hierarchy Most people were farmers 2. Cuneiform wedge writing 3. Women had some rights but were not equal with men 4. Created the wheel, plow & were the first to use bronze & Iron - also 1st to come up with TAXES! Kings Priests & Nobles Merchants & Artisans Farmers Note Book Check! – Ancient Civilizations & World History Things you should have in your notebook include: Moon landing Bell Work Origin Story Notes 8/27 Near East Homework #1 (1.1 FOR WORLD HISTORY) Bell Work & Notes - Neolithic Revolution 9/2/14 (cartoon as well) Bell Work 9/3/14 – Zombie Apocalypse Civilization Bell Work 9/4 (Civilized vs. Savage) Bell Work 9/9 Mesopotamia & Notes Near East #2 ( 1.3 FOR WORLD HISTOTRY) Egypt’s Environment - Located in Africa - Civilization grew up along the Nile River - The Sahara Desert is a natural barrier to the west - The Red Sea is a natural barrier to the east - The Mediterranean Sea is a natural barrier to the north Mediterranean Sea HOW COULD THOSE LANDFORMS HAVE INFLUENCED THE CIVILIZATION? Kingdoms of Egypt - Periods of Stability, strong pharaohs and cultural growth – called dynasties - Old Kingdom (2686-2125 BC) Pharaoh - 1. Egyptian kings called Pharaohs organize a strong central state - 2. Pharaohs were thought of as gods in the flesh - 3. They used a bureaucracy to control their kingdoms - Vizier Vizier Viziers = Managers (think adviser) - 4. Great Construction Projects - the Pyramids - The Middle Kingdom 2055-1650 - New Kingdom 1567-1100 Irrigation Tax Collection Farming Construction Trade Pyramids - 1. Built to be the eternal resting place of the Pharaoh's -They would be buried with everything they needed -Mummification Egyptian Religion 1. Optimistic- saw the gods as kind & helpful 2. Polytheistic – believed in many gods and goddesses 3. Afterlife- Gods promised eternal life after death so long as a person could prove themselves to Osiris Mummification They would remove all of the organs and save them in jars, except the brain which they pulled out through nose and tossed in the garbage. Then the wrap the body. the Egyptian Social Patterns 1. Social Classes/ Hierarchy Most people were farmers 2. Hieroglyphs- Egyptian picture writing 3. Used Geometry & developed a Calendar 4. Medical- could fix broken bones, take heart rate & had some surgeries 5. Women had the same rights as men Bell Work 9/16 Egyptian Odds & Ends AC Imagine that when Barack Obama was elected president he outlawed all religions and tried to force everyone to treat him as the son of a new god. What would your reaction be? Bell Work 9/16 Compare & contrast Egypt and Mesopotamia W.C. What is one similarity and one difference between the two Empires of Egypt and Mesopotamia? Also take one from the folder and one Venn Diagram. The Three Kingdoms of Egypt Old Kingdom – Ended with a series of droughts that caused people to lose faith in the Pharaoh which caused devolution or the decline of central authority Intermediate Period- kings of individual cities compete for power Middle Kingdom Begins with the rule of Mentuhotep Pharaoh becomes a “shepherd of the people” Religion becomes more important, the people worship Re – the son god Osiris – God of the dead and judgment Isis – the wife of Osiris Ends when the Hyksos, a Semitic speaking people invade Egypt The Three Kingdoms of Egypt The Hyksos bring new military tech. that the Egyptians use to throw off Hyksos domination New tech = horse drawn chariot, heavier swords and compound bows. Pharaoh Ahmose expels the Hyksos & begins the New Kingdom Hatshepsut- Egypt’s most famous female pharaoh goes on to expand the borders of Egypt into new territory in search of gold and slaves Amhenotep III (Ahmose’s great – great – great Grandson) faces a military challenge from the Hittites in the north The New Kingdom – When Egypt Got Weird Ahmenhotep IV introduces the worship of Aten, god of the Sun-disk & changes his name to Aten Moves capitol from Thebes to a new city called Akhetaten Dies mysteriously & is replaced by the boy king Tutankhamun who returns the government to Thebes and restores the old gods. The empire declines from there and is eventually conquered by a group of IndoEuropeans from the Caucus region north of the black sea who were the first to use Iron weapons. Aten and the Hebrew Bible Page 25