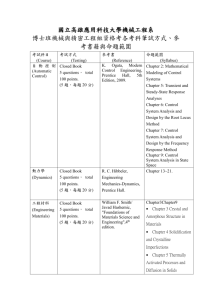
Study Set 8 – Manufacturing Processes 1. The figure below shows a machining setup where the arrows have been removed. a) In this setup, which component performs the rotational motion, and which performs the linear motion? b) What is the name of this machining process? c) What kind of part geometry is typically produced by this process? d) Suppose the roles of rotational and linear motion were reversed in an operation. Which machining process would the setup correspond to, and why? e) Finally, indicate which level of manufacturing process this operation belongs to (primary, secondary, or tertiary). 2. Compare sand casting, die casting, and investment casting in terms of finished geometry complexity, surface quality, material, size range. 3. Consider the three manufacturing processes: Casting, Forging, and Machining. Evaluate each process according to the following criteria: 1. Surface Finish Quality 2. Ability to Produce Complex Shapes 3. Dimensional Precision (Accuracy) 4. Material Waste Amount Based on these criteria, which process would most likely: i. Produce the best surface finish? ii. Produce the most complex shape? iii. Achieve the highest dimensional precision? iv. Be most suitable for high-volume production? Several metal components are provided below. For each component, the material, approximate size, production quantity, and requirements are listed under the corresponding image. Apply these to each part: 1. Identify the most appropriate manufacturing process (e.g., casting, forging, extrusion, machining, sheet metal forming, etc.) 2. Provide technical reasons explaining why the selected process is suitable (consider: material compatibility, geometry (complexity, size, weight), wall thickness, surface quality, dimensional tolerance, production quantity etc.) 3. If the component requires an additional process (machining, drilling, milling etc.) to achieve final geometry or surface requirements, name the secondary process and explain in one sentence why it is necessary. 4. Material: Steel Size: 150 mm x 135 mm x 40 mm Thickness = 2 mm Weight : 550 g Quantity : 500 pcs 5. Material: Aluminum Size: Ø70 x 40 mm Weight : 120 g Quantity : 800 pcs 6. Material: Stainless Steel Size: 150 mm x 100 mm x 50 mm Weight: 1.5 kg Quantity: 750 pcs 7. Material : Iron Size: Ø 3100 mm x 250 mm Weight : 25 tonnes Quantity : 4 pcs 8. Material: Steel Size: 300 mm x 150 mm x 100 mm Quantity: 5 – 10 pcs Weight: 32 kg Precision and Surface Quality: High 9. Material: Aluminum Size: 430 mm x 210 mm x 450 mm Thickness: 1 mm Quantity: High Volume Batch Production 10. Material: Aluminum Size: Ø 400 mm – thickness : 3 mm Weight: 750 gram Quantity: 12 000 pcs