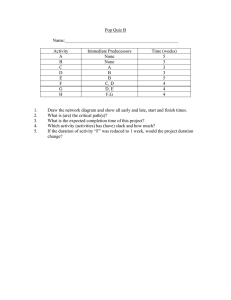
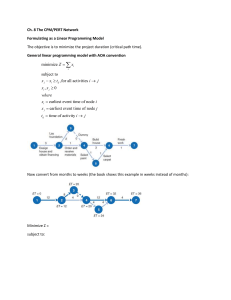
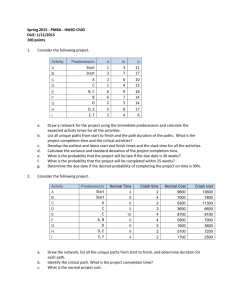
PROJECT SCHEDULING A step-by-step guide to Problem Solving, Network Construction, and the Critical Path Method (CPM) Algorithm. Problem Solving Core 1 Network Construction (AOA vs AON) 2 Simple Path Analysis 3 CPM Algorithm (Forward/Backward Pass) Network Construction Activity-on-Node (AON): The standard method. Activities are rectangles. Arrows show dependency. No dummy activities needed. Activity-on-Arrow (AOA): Older method. Activities are arrows. Nodes are events. The Dummy Activity: Essential in AOA when two activities share the same start and end nodes, or to preserve logic during merges. It has 0 duration. Sample Problem Data for Simple Path Analysis Activity Precedence Duration (Weeks) a — 5 b — 4 c a 6 d b 2 e b 5 f c, d 8 Simple Path Analysis Methodology Path Sequence Calculation Total Duration a → c → f → (End) 5+6+8 19 weeks b → d → f → (End) 4+2+8 14 weeks b → e → (End) 4+5 9 weeks For small networks, you don't need complex formulas. You can simply list every possible path from Start to End and sum their durations. Note: This method becomes inefficient for large, complex projects, which is why we use the Algorithm (Part 3). In this hypothetical adjustment, a-c-f is the longest. The CPM Algorithm The systematic approach to determining project duration and float for every single activity. The Four Key Values for CPM Algorithm ES (Early Start) EF (Early Finish) LS (Late Start) LF (Late Finish) The earliest possible The earliest an activity The latest an activity The latest an activity time an activity can can finish. Calculated can start without can finish without begin, assuming all as ES + Duration. delaying the entire delaying the project. predecessors are finished. project completion. Sample Problem Data for CPM Algorithm Activity Precedence Duration (Weeks) a — 4 b — 6 c a, b 5 d b 7 e c, d 2 f e 1 Step 1: The Forward Pass We move from Start to End to find ES and EF. The Merge Rule If an activity has multiple predecessors (a merge), its ES is the MAXIMUM EF of all predecessors. Why? Because you can't start until ALL previous steps are done. Step 2: The Backward Pass We move from End to Start to find LF and LS. Start Condition Set the LF of the last activity equal to the Project The Burst Rule Duration calculated in the Forward Pass. If an activity is a predecessor to multiple tasks (a burst), its LF is the MINIMUM LS of all successors. Why? Because you must finish in time for the earliest requirement of the next steps. LF (Final Node) = 19 Step 3: Slack & Critical Path Calculating Slack Activities with Zero Slack have no flexibility. Any delay in these tasks delays the whole project.