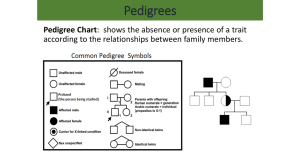
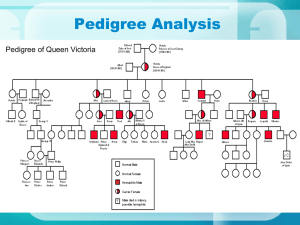
Genetics and Society Section 17.3 Breeding Plants Maize (Corn) • Humans selected and breed the plants that produce the largest grains and most clusters of grain. Canola (Rapeseed) • Two chemicals found in rapeseed are toxic • Banned from human consumption • 1970’s – selective breeding resulted in a variety with very low levels of the toxins • New variety is called Canola Breeding Animals • • • http://www.farmsanctuary.org/learn/factory-farming/turkeys-used-for-meat/ Selection for cattle that will produce offspring that produce: ➢ Leaner meat ➢ Higher milk yield Some turkeys have been selectively bred to the point where they can no longer reproduce naturally Human desire for larger turkey breasts means the males cannot mount the females to breed Human Genetics To study human genetics, we use a pedigree instead of crossing certain males and females Pedigree ➔ A flowchart using symbols to show the patterns of relationships and traits in a family over many generations Analyzing a Human Pedigree Pedigrees can be used to determine the pattern of inheritance of traits Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Autosomal Inheritance Traits (dominant and recessive) that are coded for by genes on autosomes Example: Polydactyly Autosomal dominant condition Results in the occurrence of extra fingers and toes Polydactyly What do you notice about both parents in the first generation? What about their children? Polydactyly Whenever a recessive phenotype occurs in a child of parents who exhibit the dominant trait, the parents must be heterozygous for that trait. How do you know that individual II 2 is heterozygous? Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Huntington’s Disease • Brain deteriorates over a period of 15 years • Fatal • Symptoms usually appear after age 35 • Irritability and memory loss • Involuntary muscle movements • Eventually leads to dementia and loss of muscle control Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Marfan Syndrome • Connective tissue disorder • Unusually long bones ➔ Abnormal curvature of the spine • Glaucoma and increased risk of retinal detachment • Heart and respiratory problems • Becomes worse over time Autosomal Recessive Inheritance Phenylketonuria (PKU) • Affects development of the nervous system • Enzyme that converts Phenylalanine ➔ Tyrosine is defective or absent • Phenylalanine ➔ Phenylpyruvic acid (toxic) • Newborns with PKU appear healthy at birth but can be affected within a few months What do you notice about the parents? Phenylketonuria How do you know that individual III 1 is heterozygous? Autosomal Recessive Inheritance Cystic Fibrosis • Build up of thick mucus in lungs and digestive system • Increased risk of pneumonia and respiratory failure, difficulty digesting food • 1 in 2500 Canadian children are born with cystic fibrosis Sex-Linked Traits Hemophilia • Affects the body’s ability to produce proteins involved in blood clotting • Simple cut can lead to severe blood loss • Which gender is more affected in the Royal family? • X-linked recessive trait Other examples? X-Linked Recessive Traits Duchene muscular dystrophy • Can not manufacture the muscle protein dystrophin • Muscle tissues weaken and degenerate • Life expectancy of only 20 years Assignment and Readings • • • • Read pages 610 to 616 in textbook Section 17.3 Review page 617 Pedigree Worksheet Multiple Alleles Worksheet