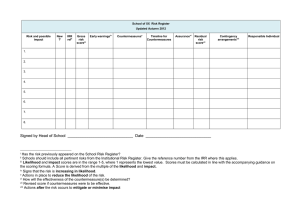
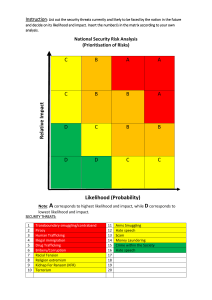
Risk Management Understanding risks Internal Risks: Arise from within the organization. External Risks: Arise from outside the organization. Multiparty Risks: Affect more than one organization. Intellectual property therft : poses a risk to knowleage-based organizations. Software license compliance: issues risk fines and legal action. Risk assessment Risk assessment identifies and triages risks. Threats: are external forces that jeopardize security. Vulnerabilities: are weaknesses in your security controls. Risks : are the combination of a threat and a vulnerability. Risks rank by Likelihood and Impact. Likelihood: is the probability a risk will occur. Impact: is the amount of damamge a risk will cause. we have two different categories of technique that we can use to assess the likelihood and Impact of a risk. 1. Qualitative Risk Assessment: Uses subjective ratings to evaluate risk likelihood and impact. ![[Qualitative Risk assessment.png]] 2. Quantitative Risk Assessment: Uses Objective numeric ratings to evaluate risk likelihood and impact. Risk treatment Risk treatment analyzes and implements possible responses to control risk. Risk Treatment Options 1. Risk avoidance Risk avoidance changes business practices to make a risk irrelevant. 2. Risk transference Risk treatment analyzes and implements possible responses to control risk. 3. Risk mitigation Risk mitigation reduces the likelihood or impact of a risk. 4. Risk acceptance Risk acceptance is the choice to continue operations in the face of a risk. Selecting security controls Security controls reduce the likelihood or impact of a risk and help identify issues. Two different ways of security controls 1. Control Purpose i. Preventive Preventive controls stop a security issue from occcurring. ii. Detective Detective controls identify security issues requiring investigation. iii. Corrective Recovery controls remediate security issues that have occurred. 2. Control Mechanism i. Technical use technology to achieve control objectives. ii. Administrative use processes to achieve control objectives. iii. Physical Impact the physical world. Configuration managment Tracks specific device settings Baselines: Provide a configuration snapshot. Versioning: Assigns numbers to each varsion. Diagrams serve as important configuration artifacts. Standardize Device Configurations Naming conventions IP adderessing schemes Change and management help ensure a stable operating environment.