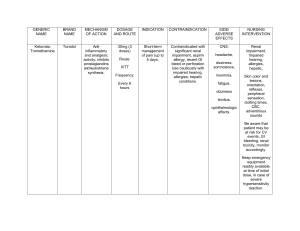
Aminoglycosides PHARMACOLOGY REVIEWER LONG EXAM 2 ANTIMICROBIAL GROUPS AND ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE Drug Mechanism PK Streptomycin Binds 30S → blocks initiation & causes misreading A: IM only (not absorbed orally). D: Extracellular; poor CSF. M: None. E: Renal (GF). Same A: IV/IM. D: Extracellular; poor CSF; accumulates in kidney/ear. M: None. E: Renal (GF). Tobramycin Same A: IV/IM, inhaled for CF. D: Extracellular, poor CSF. M: None. E: Renal. Amikacin Same; less enzyme inactivation A: IV/IM. D: Wide but poor CSF. M: None. E: Renal. Netilmicin Same A: IV/IM. D: Extracellular. M: None. E: Renal. Gentamicin PD Indications Spectrum Side/Adverse Toxicity Contraindications Dosage Rapid (parenteral) TB (2nd line), plague, tularemia, enterococcal endocarditis (with penicillin) Gram− bacilli, Mycobacterium, some Gram+ (with β-lactam) Vestibular dysfunction, rash, fever Ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity Pregnancy, renal failure 15 mg/kg/day IM Rapid IV/IM Severe G− infections (sepsis, pneumonia, UTI), enterococcal endocarditis (with βlactam/vancomycin) Broad Gram− rods, synergy vs Gram+ cocci Nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity Vestibular + renal toxicity Pregnancy, renal failure 3–5 mg/kg/day IV/IM Rapid Pseudomonas infections (esp. CF, pneumonia) Strong vs Pseudomonas Nephrotoxicity > gentamicin Nephro-, ototoxicity Same 3–5 mg/kg/day IV/IM; inhaled 300 mg bid Same Rapid Severe nosocomial infections, TB resistant to streptomycin Broad G− incl. Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter; some resistant TB Oto- + nephrotoxicity Auditory toxicity (irreversible) Same 15 mg/kg/day IV/IM Same Rapid Severe G− infections Similar to gentamicin Less nephrotoxic than gentamicin Ototoxicity Same 4–6 mg/kg/day IV/IM Conc.dependent bactericidal Conc.dependent, PAE Same Onset smsoriano PHARMACOLOGY REVIEWER LONG EXAM 2 Drug Mechanism PK Same (too toxic for systemic use) A: Oral (not absorbed), topical. D: GI lumen (oral use). M: None. E: Feces. Local bactericidal Kanamycin Same A: IM, oral (not absorbed). D: Extracellular. M: None. E: Renal. Paromomycin Same Plazomicin Newer aminoglycoside Aminoglycosides Neomycin Spectinomycin ANTIMICROBIAL GROUPS AND ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE Drug Spectinomycin Mechanism Binds 30S, inhibits translocation (similar to aminoglycosides but no misreading) Indications Spectrum Side/Adverse Toxicity Local Topical skin, oral for bowel sterilization, hepatic encephalopathy Gram− > Gram+, limited systemic GI upset, contact dermatitis Severe oto- & nephrotoxicity if systemic Systemic use Oral 1 g q6h (short course); topical Same Rapid TB (rarely used), bowel sterilization Broad G−, some mycobacteria High oto/nephrotoxicity Severe toxicity Same 15 mg/kg/day IM A: Oral (not absorbed). D: Stays in gut. M: None. E: Feces. Local Local Intestinal amebiasis, cryptosporidiosis Luminal parasites, some G− GI upset Rare systemic None Oral 25–35 mg/kg/day A: IV only. D: Extracellular. M: None. E: Renal. Same Rapid MDR Enterobacteriaceae MDR Gram− rods incl. CRE Similar to aminoglycosides Nephro/ototoxicity Renal impairment 15 mg/kg/day IV Toxicity Contraindications Dosage PK A: IM injection. D: Extracellular, not CNS. M: Minimal. E: Renal. PD PD Bacteriostatic Onset Onset Rapid IM Indications Gonorrhea (penicillin- or ciprofloxacinresistant strains) Spectrum N. gonorrhoeae only Side/Adverse Pain at injection site, fever, nausea Rare nephrotoxicity Contraindications Pregnancy (relative) Dosage 2 g IM single dose smsoriano PHARMACOLOGY REVIEWER LONG EXAM 2 Spectrum Common side/adverse Notable toxicity Contraindications Used only as fixed-dose combo with trimethoprim; see TMP-SMX below. Broad activity vs many gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria; some Nocardia, Chlamydia, several protozoa; Rickettsiae not susceptible; Pseudomonas intrinsically resistant. Rash, fever, photosensitivity; GU “crystalluria/urinary disturbances” (class). Kernicterus risk (class); see class AEs. Avoid when sulfonamide is contraindicated; (chapter emphasizes neonatal/pregnancy risk at class level). Bacteriostatic With pyrimethamine for toxoplasmosis As above As above As above As above Bacteriostatic With pyrimethamine for malaria (historical/where used); resistance & severe reactions limit use As above Severe cutaneous reactions cited historically; see text. Severe skin reactions (noted); Use restricted; see text. Same (acts in gut; prodrug split in colon) A: poorly absorbed (designed for local action). D: local in bowel. M/E: metabolized to sulfapyridine + 5-ASA in colon; systemic exposure less emphasized. Local effect Inflammatory bowel disease Local GI pathogens/inflammation context (not used as systemic antibacterial). GI intolerance possible (class). — — Sodium sulfacetamide (topical/ophthalmic) Same A: topical ocular. D: local. M/E: not emphasized. Local Bacterial conjunctivitis (2nd-line) Ocular surface bacteria Local irritation possible — — Silver sulfadiazine (topical) Same; silver adds broad topical activity A/D: topical local. M/E: not emphasized. Local Burns (prevention/treatment of infection) Broad topical coverage Local reactions — — Mafenide acetate (topical) Same; also inhibits carbonic anhydrase A/D: topical; systemic absorption can occur. Broad topical Pain on application; metabolic acidosis (due to CA inhibition) Metabolic acidosis risk — Drug MOA PK Sulfamethoxazole (oral absorbable; used mainly in combo) PABA analog; competitively inhibits dihydropteroate synthase → blocks folate synthesis A: well absorbed from small intestine. D: widely distributed incl. CSF; variable protein binding. M: hepatic acetylation/glucuronidation. E: urinary excretion; t½ ↑ in renal failure. Bacteriostatic alone Sulfadiazine (oral absorbable) Same as above As above for oral absorbable sulfonamides. Same Long half-life (class note longacting); otherwise as above. Sulfasalazine (oral non-absorbable) Sulfadoxine (oral absorbable; longacting) Sulfonamides ANTIMICROBIAL GROUPS AND ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE PD Local Indications Burns (alternative) smsoriano Trimethoprim (TMP), Pyrimethamine, and TMP–SMX PHARMACOLOGY REVIEWER LONG EXAM 2 ANTIMICROBIAL GROUPS AND ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE Drug / Combo MOA PK Trimethoprim (TMP) Selectively inhibits bacterial dihydrofolate reductase → blocks tetrahydrofolate formation (downstream of sulfonamides). A: oral; concentrates in acidic prostatic & vaginal fluids. D: distributes to body fluids/CSF. M: minimal. E: renal. Pyrimethamine TMP–SMX (cotrimoxazole) Inhibits protozoal DHFR Oral Sequential blockade of folate synthesis (DHPS + DHFR) → synergy; bactericidal vs many organisms compared with sulfonamide alone. A: oral and IV; oral tablets include singlestrength (80/400 mg) & double-strength (160/800 mg); IV formulations described. D: wide tissue distribution. M: limited. E: renal. PD Indications Bacteriostati c alone UTIs, prostatitis, respiratory pathogens—most often combined with SMX; TMP alone discussed mechanistically. — With sulfadiazine for toxoplasmosis; also with sulfadoxine for malaria (resistance/toxicity limit use) Bactericidal (combo) UTIs, prostatitis, Shigella/Salmonella (selected situations), Nocardia, S. aureus (many community strains susceptible), respiratory pathogens (H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis), and Pneumocystis jirovecii (treatment/prophylaxis). Spectrum Common side/adverse Notable toxicity Nausea, vomiting, rash (when in combo noted); megaloblastic anemia/leukopenia/granulocy topenia (folate-related). — Protozoa (Toxoplasma; Plasmodium with sulfadoxine) — Bone-marrow suppression risk noted when combined; leucovorin often cogiven (described in text). Broad across listed organisms Nausea, vomiting, rash; folaterelated cytopenias; hyperkalemia reported. Severe cutaneous reactions are discussed with sulfonamide component in class notes. Active vs many UTI/resp pathogens when combined smsoriano Trimethoprim (TMP), Pyrimethamine, and TMP–SMX PHARMACOLOGY REVIEWER LONG EXAM 2 ANTIMICROBIAL GROUPS AND ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE Drug / Combo MOA PK Trimethoprim (TMP) Selectively inhibits bacterial dihydrofolate reductase → blocks tetrahydrofolate formation (downstream of sulfonamides). A: oral; concentrates in acidic prostatic & vaginal fluids. D: distributes to body fluids/CSF. M: minimal. E: renal. Pyrimethamine TMP–SMX (cotrimoxazole) Inhibits protozoal DHFR Oral Sequential blockade of folate synthesis (DHPS + DHFR) → synergy; bactericidal vs many organisms compared with sulfonamide alone. A: oral and IV; oral tablets include singlestrength (80/400 mg) & double-strength (160/800 mg); IV formulations described. D: wide tissue distribution. M: limited. E: renal. PD Indications Bacteriostati c alone UTIs, prostatitis, respiratory pathogens—most often combined with SMX; TMP alone discussed mechanistically. — With sulfadiazine for toxoplasmosis; also with sulfadoxine for malaria (resistance/toxicity limit use) Bactericidal (combo) UTIs, prostatitis, Shigella/Salmonella (selected situations), Nocardia, S. aureus (many community strains susceptible), respiratory pathogens (H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis), and Pneumocystis jirovecii (treatment/prophylaxis). Spectrum Active vs many UTI/resp pathogens when combined Protozoa (Toxoplasma; Plasmodium with sulfadoxine) Broad across listed organisms Common side/adverse Notable toxicity Nausea, vomiting, rash (when in combo noted); megaloblastic anemia/leukopenia/granulocy topenia (folate-related). — — Bone-marrow suppression risk noted when combined; leucovorin often cogiven (described in text). Nausea, vomiting, rash; folaterelated cytopenias; hyperkalemia reported. Severe cutaneous reactions are discussed with sulfonamide component in class notes. smsoriano PHARMACOLOGY REVIEWER LONG EXAM 2 Drug MOA ANTIMICROBIAL GROUPS AND ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE PK Common side/adverse Notable toxicity CI Strong vs gram-neg rods; less pneumococcal activity (per class narrative) QT risk (class), tendons (class) Avoid in pregnancy/children (class cautions) t½: ~8 h; F: ~58%; Cmax: ~7.5; Oral: 450 mg bid; Excretion: renal Bactericidal Activity vs gram-positive & gram-negative; newer agent described Broad incl. MRSA/gram-neg per class discussion — Class cautions t½: ~8 h; F: ~70%; Cmax: ~1.6; Oral: 320 mg qd; Excretion: renal & nonrenal Bactericidal “Respiratory” FQ (chapter) Enhanced pneumococcal activity QT risk noted among class Class cautions Bactericidal “Respiratory” FQ; community pathogens Broad incl. pneumococcus; gram-neg QT risk (class) Class cautions Bactericidal Respiratory/anaerobic coverage mentioned in narrative Good gram-positive/anaerobe activity; not renal route QT prolongation emphasized among class Avoid where QT risk high; not relied upon for UTIs (non-renal excretion) Delafloxacin Gemifloxacin Moxifloxacin Spectrum Bactericidal Ciprofloxacin Levofloxacin Indications UTIs; broad gram-negative infections incl. Pseudomonas; GI pathogens mentioned in chapter narrative t½: ~3–5 h; F: ~70%; Cmax: ~2.4 mg/L; Oral dose: 500 mg bid; Excretion: renal Inhibit DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II) and topoisomerase IV, blocking DNA synthesis; bactericidal. PD t½: ~7–10 h; F: ~0.99 (≈100%); Cmax: ~3.1; Oral: 500–750 mg qd; Excretion: renal t½: ~10 h; F: ~0.86; Cmax: ~3.1; Oral: 400 mg qd; Excretion: non-renal (hepatic) Norfloxacin t½: ~3–5 h; F: ~0.35–0.70 (35–70%); Cmax: ~1.1; Oral: 400 mg bid; Excretion: renal Bactericidal UTIs (narrower use) Urinary pathogens — Class cautions Ofloxacin t½: ~5–7 h; F: ~0.95; Cmax: ~3.0; Oral: 400 mg bid; Excretion: renal Bactericidal UTIs and systemic gram-neg infections Broad gram-neg — Class cautions smsoriano