Uploaded by
A.B Iqbal
GCE O Level Chemistry Worksheet: Particulate Nature & Chemical Bonding
advertisement

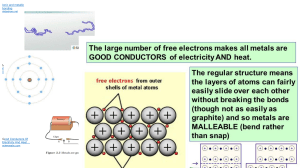
GCE O Level Chemistry Worksheet Topics: Particulate Nature of Matter & Chemical Bonding This worksheet mimics the structure and complexity of Paper 2 questions from the Cambridge GCE O Level Chemistry syllabus. Answer all questions in full sentences and show working where necessary. Part A: The Particulate Nature of Matter Question 1 The diagram below shows a model representing a sample of a substance at room temperature. (a) Identify the physical state of the substance and explain your reasoning using particle theory. (b) Describe the arrangement, movement, and energy of the particles in this state. (c) State what would happen to the particles if the substance were heated to become a gas. Explain your answer. (d) Sketch how the arrangement of particles would appear in the gaseous state. Question 2 Air is a mixture containing several gases. (a) Define the terms element, compound, and mixture. (b) Explain why air is considered a mixture rather than a compound. (c) Describe how the gases in air can be separated and give reasons why this method works. Question 3 Hydrogen and oxygen gases react to form water. The balanced equation is: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O (a) Explain what this equation tells you about the particles involved in the reaction. (b) Describe how the properties of hydrogen and oxygen gases differ from the compound they form. (c) Discuss how the particle model can be used to illustrate the conservation of mass during this reaction. Question 4 The following terms are commonly used in chemistry: atom, molecule, ion. (a) Define each term. (b) Give one example of each from either an element or compound. (c) Compare their relative sizes and charges. (d) Describe how each would be represented in a particle diagram. Part B: Chemical Bonding Question 5 Sodium reacts with chlorine to form sodium chloride. (a) Write the electronic configurations for sodium and chlorine atoms. (b) Draw a dot-and-cross diagram to show the formation of sodium chloride. (c) Explain how the transfer of electrons leads to the formation of ions. (d) Describe two physical properties of sodium chloride and relate them to its bonding and structure. Question 6 Ammonia (NH₃) is a covalent compound with a simple molecular structure. (a) Draw a dot-and-cross diagram to show the bonding in an ammonia molecule. (b) State the type of bonding in ammonia. (c) Explain why ammonia has a low melting and boiling point. (d) Predict whether ammonia conducts electricity and justify your answer. Question 7 Magnesium and oxygen react to form magnesium oxide. (a) Describe the type of bonding in magnesium oxide. (b) Write the electronic configurations of the ions formed. (c) Explain why magnesium oxide has a higher melting point than sodium chloride. (d) Compare the conductivity of solid and molten magnesium oxide, and explain the difference. Question 8 The diagram below shows a simplified model of metallic bonding in a metal. (a) Explain the term 'metallic bonding'. (b) Describe how this bonding allows metals to conduct electricity. (c) State why metals are malleable and ductile. (d) Compare metallic bonding to ionic and covalent bonding in terms of particle behavior and strength. Question 8 The diagram below shows a simplified model of metallic bonding in a metal. (a) Explain the term 'metallic bonding'. (b) Describe how this bonding allows metals to conduct electricity. (c) State why metals are malleable and ductile. (d) Compare metallic bonding to ionic and covalent bonding in terms of particle behavior and strength.