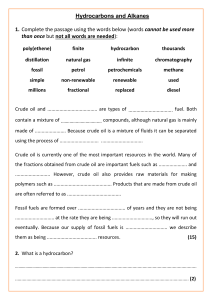
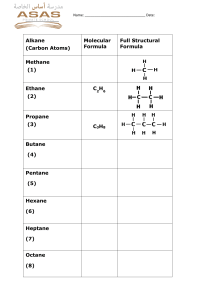
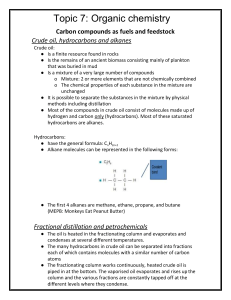
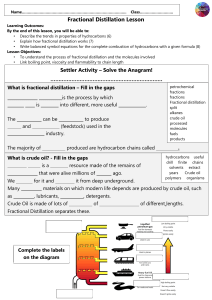
Fuels, alkanes and alkenes Do now : Why is it going to be such a problem when crude oil runs out in approximately 50 years? What do I need to know? Carbon Chemistry Carbon chemistry (“organic chemistry”) focuses on molecules made from carbon compounds: Carbon always forms 4 covalent bonds. Why? C Crude oil Crude oil is a finite resource found in rocks. DARK, SMELLY LIQUID - mixture of many different carbon compounds. Crude oil Crude oil straight from the ground has not much use. It has too many substances in it. All having different boiling points - must be separated into fractions by distillation. Remember - distillation separates liquids with different boiling points. Hydrocarbons and crude oil Crude oil is a mixture of HYDROCARBONS (compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen). Some examples: H C C H H H Ethane H H H H H C C C C H H H H Butane H Increasing length H H Shorter chain hydrocarbons are in greater demand because they have more uses and release more energy during burning. Alkanes Alkanes are SATURATED HYDROCARBONS. What does this mean? SATURATED means that all of these atoms are held together by single bonds, for example: H H H C C H H Ethane H H H H H H C C C C H H H H Butane Alkanes are very unreactive (but they do burn well). H Crude oil separation in the lab Long video. Skip between heating to him showing the fractions in the test tube and describing them. Then lighting them at the end. Explain the following terms Mark your answers in coloured pen Small molecules with few carbon atoms in short chains - most useful. Good fuels - ignite easily, burn well with less smoky flames than HC made up of larger molecules. FLAMMABLE! Fractional distillation Crude oil is separated into hydrocarbons with similar boiling points -fractions. Each hydrocarbon fraction contains molecules with similar number of carbon atoms. for heating and cooking for fuel in cars Learn these! You need to know the order, names, trends and uses (not temps) The gases move up the column and the hydrocarbons condense when they reach their boiling points. Burning hydrocarbons (propane gas) Write the word and symbol equation for this reaction. Hint: burning=combustion, what are the products of combustion? Remember: balance your equation so that the number of each element is balanced on both sides of the equation. Combustion is the reaction of a substance with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water. Burning propane gas Write the word and symbol equation for this reaction. Hint: burning=combustion, what are the products of combustion? Remember: balance your equation so that the number of each element is balanced on both sides of the equation. Propane + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water C3H8(l) + 5O2(g) → 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g) Complete combustion In your book state the products of complete combustion of a hydrocarbon. Describe and we can prove these are being formed using the apparatus below. Incomplete combustion What do you think it means? What are the products? What is the main issue with the products? Incomplete combustion If there is not enough oxygen: carbon monoxide is formed instead of carbon dioxide. Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas. It is colourless and odourless. Red blood cells permanently bind with this gas and carry it around in your blood instead of oxygen. Releases carbon monoxide Substitution reactions of alkanes with chlorine Halogen + alkane –(UV)-> halogenoalkane + hydrogen halide Must be in the presence of ultraviolet radiation (UV) e.g. sunlight UV light breaks the Cl-Cl bond in the halogen, creating a free radical, allowing it to react. Cracking This is a THERMAL DECOMPOSITION reaction, with clay used as a catalyst Cracking can be used (as well as fractional distillation) to extract petrol from crude oil. Cracking In the cracker long chain molecules are split apart or ‘cracked’. An example of such a reaction is: Octane hexane Heat pressure catalyst + Used as a fuel C8H18 → C6H14 + C2H4 ethene Ethene is used to make plastics Task Draw out displayed formulae of a pair of products formed by cracking decane H H H H H H H H H H H C C C C C C C C C C H H H H H H H H H H H Heat pressure H H H H H H H H H C C C C C C C C H H H H H H H H H octane decane catalyst + ethene Exam Question Exam Question Mark your work Exam Question Exam Question Mark your work Questions