Uploaded by
ajsmininglight
AP Physics C Electricity & Magnetism Constants & Formulas Reference
advertisement

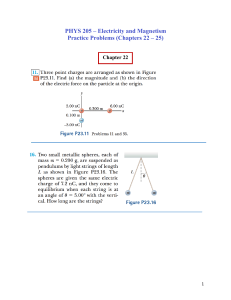
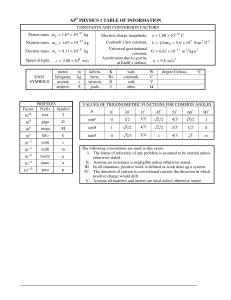
ADVANCED PLACEMENT PHYSICS ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM TABLE OF INFORMATION CONSTANTS AND CONVERSION FACTORS UNIT SYMBOLS ampere, A coulomb, C electron volt, eV farad, F henry, H hertz, Hz joule, J kilogram, kg meter, m newton, N ohm, Ω second, s tesla, T volt, V watt, W Coulomb constant, − Vacuum permittivity, 0 Vacuum permeability, 0 − Proton mass, mp = 1.67 × 10−27 kg Neutron mass, mn = 1.67 × 10−27 kg Electron mass, me = 9.11 × 10−31 kg Elementary charge, e = 1.60 × 10−19 C 1 electron volt, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10−19 J Speed of light, c = 3.00 × 108 m s 1 unified atomic mass unit, 1 u = 1.66 × 10−27 kg = 931 MeV c 2 Mp Mnsme Universal gravitational constant, G = 6.67 × 10 11 Magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity at Earth’s surface, g = 9.8 m s 2 Magnitude of the gravitational field strength at Earth’s surface, g = 9.8 N kg PREFIXES Factor Prefix Symbol tera T 1012 9 giga G 10 mega M 106 kilo k 103 centi c 10−2 −3 milli m 10 −6 micro µ 10 10−9 10−12 nano pico n p VALUES OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS FOR COMMON ANGLES 0° 30° 37° 45° 53° 60° 90° sin 0 12 35 2 2 45 3 2 1 cos 1 3 2 45 2 2 35 12 0 tan 0 3 3 34 1 4 3 3 The following conventions are used in this exam: • The frame of reference of any problem is assumed to be inertial unless otherwise stated. • Air resistance is assumed to be negligible unless otherwise stated. • Springs and strings are assumed to be ideal unless otherwise stated. • The electric potential is zero at an infinite distance from an isolated point charge. • The direction of current is the direction in which positive charges would drift. • All batteries, wires, and meters are assumed to be ideal unless otherwise stated. AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Course and Exam Description 1 Appendix V.1 | 184 Return to Table of Contents © 2024 College Board ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM q1q2 r2 0 dq r̂ r2 qenc enc ( r ) dV q1q2 r V dr k q1q2 r2 A = area C = capacitance d = distance E = electric field F = force I = current J = current density ℓ = length P = power q = charge Q = charge r = radius, distance, or position R = resistance t = time U = potential energy V = electric potential or volume = electric permittivity ρ = resistivity or charge density k = dielectric constant = ux A = area B = magnetic field C = capacitance F = force I = current ℓ = length L = inductance n = number of loops per unit length N = number of loops q = charge r = radius, distance, or position R = resistance t = time U = potential energy v = velocity or speed = emf = magnetic permeability = time constant = ux = angular frequency v fide Edr V AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Course and Exam Description 2 Appendix V.1 | 185 Return to Table of Contents © 2024 College Board a = acceleration E = energy f = frequency F = force h = height J = impulse k = spring constant K = kinetic energy ℓ = length m = mass M = mass p = momentum P = power r = radius, distance, or position t = time T = period U = potential energy v = velocity or speed W = work x = position or distance y = height l = linear mass density m = coefficient of friction 0 a = acceleration d = distance f = frequency F = force I = rotational inertia k = spring constant K = kinetic energy ℓ = length L = angular momentum m = mass M = mass p = momentum r = radius, distance, or position t = time T = period v = velocity or speed W = work x = position or distance a = angular acceleration q = angle t = torque f = phase angle w = angular frequency or angular speed i 2 AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Course and Exam Description Appendix V.1 | 186 Return to Table of Contents © 2024 College Board GEOMETRY AND TRIGONOMETRY Rectangle A = bh V = ℓwh Triangle 1 A = bh 2 Cylinder V = r 2ℓ Circle A = r2 C=2 r Sphere 4 3 V= r 3 S = 4 r2 s=r A = area b = base C = circumference h = height ℓ = length r = radius s = arc length S = surface area V = volume w = width q = angle Rectangular Solid s r S = 2 rℓ + 2 r 2 Right Triangle a 2 + b2 = c 2 a sin = c b cos = c a tan = b c a 90° b VECTORS CALCULUS IDENTITIES ( df df du = dx du dx log a bx ) log a + x log b sin 2 + cos 2 = 1 d n x = nx n−1 dx ( ) sin ( 2 ) = 2sin cos d ax e = ae ax dx ( ) sin = tan cos d 1 ln ax ) = ( dx x d sin(ax = a os( ax ) dx d cos( dx ax) ax) 4 AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Course and Exam Description Appendix V.1 | 187 Return to Table of Contents © 2024 College Board