A P PHYSICS 1 TABLE OF INFORMATION =
advertisement
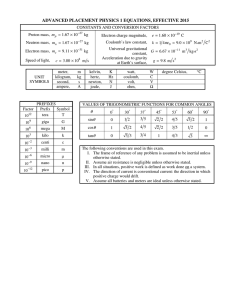
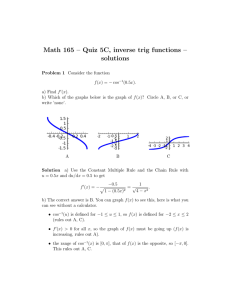
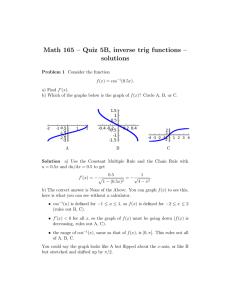
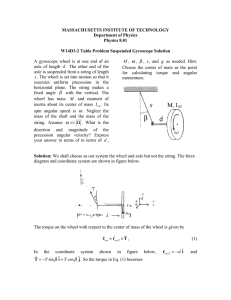
® AP PHYSICS 1 TABLE OF INFORMATION CONSTANTS AND CONVERSION FACTORS Proton mass, m p = 1.67 ¥ 10 -27 kg Electron charge magnitude, Neutron mass, mn = 1.67 ¥ 10 -27 kg Coulomb’s law constant, UNIT SYMBOLS Factor 1012 c = 3.00 ¥ 108 m s meter, kilogram, second, ampere, PREFIXES Prefix Symbol tera T m kg s A k = 1 4 pe0 = 9.0 ¥ 10 9 N i m 2 C2 Universal gravitational -11 m 3 kgis2 constant, G = 6.67 ¥ 10 Acceleration due to gravity 2 at Earth’s surface, g = 9.8 m s Electron mass, me = 9.11 ¥ 10 -31 kg Speed of light, e = 1.60 ¥ 10 -19 C kelvin, hertz, newton, joule, K Hz N J W C V W watt, coulomb, volt, ohm, ∞C degree Celsius, VALUES OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS FOR COMMON ANGLES q 0 30 37 45 53 60 sinq 0 12 35 2 2 45 3 2 1 90 10 9 giga G 10 6 mega M cos q 1 3 2 45 2 2 35 12 0 10 3 kilo k tanq 0 33 34 1 43 3 • 10 -2 centi c 10 -3 milli m 10 -6 micro m -9 nano n 10 -12 pico p 10 The following conventions are used in this exam. I. The frame of reference of any problem is assumed to be inertial unless otherwise stated. II. Assume air resistance is negligible unless otherwise stated. III. In all situations, positive work is defined as work done on a system. IV. The direction of current is conventional current: the direction in which positive charge would drift. V. Assume all batteries and meters are ideal unless otherwise stated. ® AP PHYSICS 1 EQUATIONS MECHANICS Ãx = Ãx 0 + a x t 1 x = x 0 + Ãx 0 t + a x t 2 2 Ãx2 = Ãx20 + 2 a x ( x - x0 ) a= Â F = Fnet m m Ff £ m Fn Ã2 r ac = p = mv Dp = F Dt 1 2 mv 2 K = DE = W = F d = Fd cos q DE Dt P= q = q0 + w0 t + 1 2 at 2 w = w0 + at x = A cos (2p ft ) Â t = t net a = I I t = r^ F = rF sin q L = Iw a d E f F h I K k L m P p r T t U V v W x a m q r t w = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = ELECTRICITY acceleration distance energy frequency force height rotational inertia kinetic energy spring constant angular momentum length mass power momentum radius or separation period time potential energy volume speed work done on a system position angular acceleration coefficient of friction angle density torque angular speed DUg = mg Dy 2p 1 T = = w f m k Ts = 2 p DL = t Dt 1 2 Iw 2 K = Fs = k x Us = r= 1 2 kx 2 m V Tp = 2 p Fg = G g m1m2 r 2 I = Dq Dt R= r A I = DV R 2 r P = I DV Rs = Â Ri 1 = Rp i 1 Â Ri i WAVES l= f = frequency v = speed l = wavelength v f GEOMETRY AND TRIGONOMETRY Rectangle A = bh Triangle 1 A = bh 2 Circle A = pr 2 C = 2 pr Rectangular solid V = wh Cylinder V = pr 2 S = 2 pr + 2 pr 2 V = Gm1m2 r A = area F = force I = current = length P = power q = charge R = resistance r = separation t = time V = electric potential r = resistivity q1q2 Sphere Fg g= m UG = - FE = k 4 3 pr 3 S = 4 pr 2 A= C= V= S = b = h = = w= r = area circumference volume surface area base height length width radius Right triangle c 2 = a 2 + b2 a sin q = c b cos q = c a tan q = b c a 90° q b