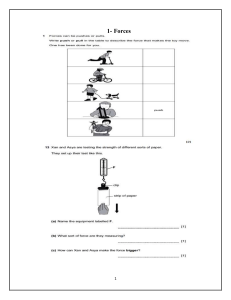
Electricity Revision Notes (Years 4–8) 1. Introduction to Electricity (Year 4–5) � What is Electricity? - A form of energy caused by the movement of electrons. - Powers things like lights, computers, and TVs. ⚡ Types of Electricity - Static Electricity – caused by rubbing (e.g., rubbing a balloon on your hair). - Current Electricity – flows in wires and powers devices. � Electrical Sources - Cells (Batteries): Portable sources of electricity. - Mains Electricity: Comes from power stations, used in homes and schools. � Basic Components - Cell – provides energy. - Wires – conduct electricity. - Bulb – lights up when electricity flows. - Switch – opens or closes a circuit. Topical Questions: 1. What’s the difference between static and current electricity? 2. Draw a simple circuit with a cell, bulb, and a switch. 3. What happens when you open a switch in a circuit? 2. Simple Circuits (Year 5–6) � Complete Circuits - Electricity only flows in a complete (closed) circuit. - Open circuit: Switch is off – no flow. - Closed circuit: Switch is on – flow occurs. � Series Circuit - All components are in one loop. - If one bulb goes out, all others go out too. � Parallel Circuit - Components are on separate branches. - If one bulb goes out, others stay on. � Conductors vs Insulators - Conductors: Allow electricity (e.g., metals). - Insulators: Don’t allow electricity (e.g., plastic, rubber). Topical Questions: 1. What is a series circuit? Give an example. 2. Name two conductors and two insulators. 3. Why does a bulb go off in a series circuit if another one breaks? 3. Electrical Safety (Year 6) ⚠️ Key Safety Rules: - Never touch plugs or wires with wet hands. - Don’t overload sockets. - Keep water away from electrical devices. ⚠️ Fuses and Circuit Breakers - Protect you from too much current. - A fuse breaks the circuit if current is too high. Topical Questions: 1. Why is water dangerous near electricity? 2. What is the purpose of a fuse? 3. Give two rules for staying safe with electricity. 4. Measuring Electricity (Year 7–8) ⚠️ Electrical Quantities - Voltage (V) – Push of electricity (measured in volts). - Current (I) – Flow of electricity (measured in amperes or amps). - Resistance (R) – Opposition to flow (measured in ohms). ⚠️ Ohm’s Law -V=I×R � Measuring Instruments - Voltmeter – measures voltage. - Ammeter – measures current. � Series vs Parallel (Advanced) - Series: Current is the same; voltage is shared. - Parallel: Voltage is the same; current is shared. Topical Questions: 1. State Ohm’s Law. 2. In a series circuit, what happens to the current? 3. What instrument is used to measure voltage? 5. Practical Applications (Year 8) � Everyday Devices - Appliances convert electrical energy to other forms (light, sound, heat). � Energy Efficiency - Energy-saving bulbs use less electricity. - Look for energy ratings on devices. � Renewable vs Non-Renewable Sources - Renewable: Solar, wind, hydro. - Non-Renewable: Coal, oil, gas. Topical Questions: 1. Give two renewable sources of electricity. 2. How does a kettle use electricity? 3. Why are energy-efficient devices better? Circuit Diagrams Series Circuit: Parallel Circuit: Basic Components of a Circuit: - Cell: Provides energy (symbol: |‾|). - Wire: Connects components (symbol: ——). - Bulb: Converts electrical energy to light (symbol: ⊗). - Switch: Opens/closes circuit (symbol: •/ ◦ ). Electricity Practice Worksheets Worksheet 1: Circuit Symbols and Components Match the circuit symbols with their correct names: 1. ⊗ a) Switch 2. |‾| b) Cell 3. —— c) Wire 4. •/◦ d) Bulb Answers: 1. __ 2. __ 3. __ 4. __ Worksheet 2: Series and Parallel Circuits 1. In a series circuit, what happens if one bulb breaks? 2. In a parallel circuit, why do other bulbs stay on if one breaks? 3. Draw a simple series circuit with a battery, two bulbs, and a switch. 4. Draw a simple parallel circuit with two bulbs and a battery. Worksheet 3: Electricity in Daily Life 1. List five devices at home that use electricity. 2. Which of them convert electricity into: - Light: __________ - Heat: __________ - Sound: __________ 3. Name two safety rules when handling electrical appliances. Worksheet 4: Electrical Calculations (Year 7–8) Use the formula: V = I × R 1. A current of 2 A flows through a resistor of 5 ohms. What is the voltage? 2. A circuit has a voltage of 12 V and resistance of 6 ohms. What is the current? 3. A current of 3 A flows when the voltage is 9 V. What is the resistance? 4. Which instrument would you use to measure current? __________ 5. Which instrument would you use to measure voltage? __________