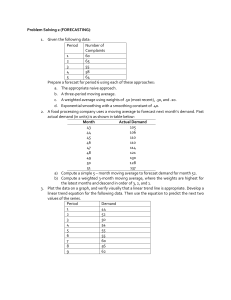
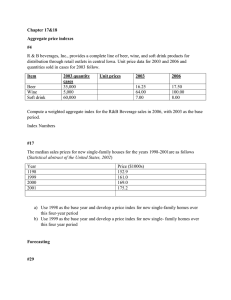
Operations Management Midterm Study Guide Chapter 4: Forecasting Key Topics: - Exponential Smoothing: Calculation with given demand, forecast, and alpha value. - Weighted Moving Average: Forecast calculation using different weights for previous periods. - Trend Projection: Understanding slope interpretation in trend projections. - Forecasting Time Horizons: Short, medium, and long-range forecasts for different planning needs. - Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD), Mean Squared Error (MSE), Mean Absolute Percent Error (MAPE): Calculations and applications for measuring forecast accuracy. - Tracking Signal: Used to monitor forecasting errors and detect bias in predictions. Formula for Exponential Smoothing: Ft = Ft-1 + α(At-1 - Ft-1) Where Ft = new forecast, Ft-1 = previous forecast, α = smoothing constant, At-1 = previous actual demand Practice Questions from Chapter 4: 1. Given an actual demand this period of 103, a forecast value for this period of 99, and an alpha of .6, what is the exponential smoothing forecast for next period? 2. John's House of Pancakes uses a weighted moving average method to forecast pancake sales... 3. A trend projection equation with a slope of 0.78 means that there is a 0.78 unit rise in Y per period. 4. Forecasts used for new product planning, capital expenditures, facility location or expansion, and R&D typically utilize a: Chapter 5: Product Design Key Topics: - Product Life Cycle (PLC): Introduction, Growth, Maturity, and Decline stages with associated strategy focuses. - Product Strategy Elements: Selection, definition, and design as core components of product decision. - Factors Influencing Product Opportunities: Economic and sociological changes, technology, etc. - Product Design Documentation: Engineering drawings, Bill of Materials (BOM), Assembly Charts, and Route Sheets. - Sustainability in Product Design: Concepts like Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) for sustainable design. Example Product Life Cycle Diagram (Introduction, Growth, Maturity, Decline) Practice Questions from Chapter 5: 5. In which stage of the product life cycle should product strategy focus on process modifications as the product is being 'fine-tuned' for the market? 6. When should product strategy focus on forecasting capacity requirements? 7. The three major elements of the product decision are: 8. Which of the following would likely cause a change in market opportunities based upon levels of income and wealth? Chapter 11: Supply Chain Management Key Topics: - Supply Chain Strategies: Matching inventory strategies with corporate strategies (e.g., low cost, differentiation). - Supply Chain Risks and Mitigation Tactics: Supplier failures, logistics delays, and related mitigation strategies. - Bullwhip Effect: Causes and methods for mitigation to improve supply chain stability. - Logistics and Distribution Management: Ensuring effective flow of goods from origin to destination. - Make-or-Buy Decision: Determining whether to produce goods in-house or outsource. Practice Questions from Chapter 11: 9. Operations managers must be able to anticipate changes in which of the following? 10. For which corporate strategy(ies) should supply chain inventory be minimized?