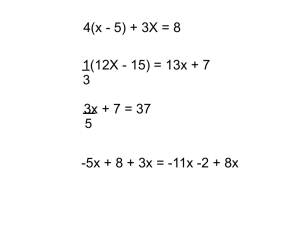WARM UP ACTIVITY: recall how to multiply a monomial by a polynomial. a. 4(3x − 2) 4(3x − 2) 12x -8 Answer b. x(5x + 3) x(5x + 3) 2 5xAnswer +3x 2 c. 3x(x − 3x − 1) 2 3x(x – 3x - 1) Answer 2 3 3x -9x -3x 2 d. 4x (3x − 5) 2 4x ( 3x - 5) 3 2 Answer 12x -20x 3 3 e. x (x − 2x + 4) 3 3 x (x – 2x + 4) 6 3 4 Answer x -2x +4x OPERATION ON FUNCTIONS We can multiply and divide functions! The result is a new function. Lesson 2 Multiplication and Division of Functions MULTIPLICATION • Product – the product of two functions and is denoted by (f●g)(x) ; • this product is defined as (𝑓 ●𝑔)(𝑥) = 𝑓(𝑥) ● 𝑔(𝑥). Example: Find the product of the functions f(x)=4x+1 and g(x) = x² - 3x + 2. Solution: (f⋅g)(x) = f(x)· g(x) (f⋅g)(x) = (4x+1)(x² - 3x+2) (f⋅g)(x) = 4x³-12x²+8x + x² - 3x+2 2 (f⋅g)(x) = 4x³-11x +5x+2 Example Let f(x)=4x-1 and g(x) = x² -3x-2. Find (f ●g)(x). Multiply the two given expressions for f(x) and g(x). (𝑓 ●𝑔)(𝑥) = 𝑓(𝑥) ● 𝑔(𝑥). 1. Substitute the given functions. (f●g)(x) = f(x) ● g(x) (f●g)(x) = (4x-1)(x²-3x-2) 2. Multiply the expressions (f●g)(x) = (4x-1)(x²-3x-2) (f●g)(x) = 4x³- 12x² - 8x - x²+3x+2 3. Group similar terms together. (f●g)(x) = 4x³-12x²-8x-x² + 3x + 2 (f●g)(x) = (4x³) + (-12x² - x²)+(-8x+3x) + (2) 4. Combine similar terms. (f●g)(x) = (4x³) + (−12x² − x²) + (−8x + 3x) + (2) (f●g)(x) = 4x3 - 13x2 -5x+2 Thus, (f●g)(x) = 4x³- 13x²-5x+2. Example Let f(x)=4x-1 and g(x) = x² -3x-2. Find (f●g)(0). Multiply the two given expressions for f(x) and g(x). (𝑓 ●𝑔)(𝑥) = 𝑓(𝑥) ● 𝑔(𝑥). 1. Substitute the given functions. (f●g)(x) = f(x) ● g(x) (f●g)(x) = (4x-1)(x²-3x-2) 2. Multiply the expressions (f●g)(x) = (4x-1)(x²-3x-2) (f●g)(x) = 4x³- 12x² - 8x - x²+3x+2 3. Group similar terms together. (f●g)(x) = 4x³-12x²-8x-x² + 3x + 2 (f●g)(x) = (4x³) + (-12x² - x²)+(-8x+3x) + (2) or (f●g)(x) = 4x³ -12x² - x² -8x + 3x + 2 4. Combine similar terms. (f●g)(x) = (4x³) + (−12x² − x²) + (−8x + 3x) + (2) or (f●g)(x) = 4x³ -12x² - x² -8x + 3x + 2 3 2 (f●g)(x) = 4x - 13x - 5x + 2 Thus, (f●g)(x) = 4x³- 13x²-5x+2. 5. Substitute x = 0 to the resulting function. 2 (f●g)(x) = 4x³- 13x -5x +2 3 2 (f●g)(0) = 4(0) – 13(0) -5(0) + 2 (f●g)(0) = 0 – 0 - 0 + 2 (f●g)(0) = 2 WARM UP recall how to divide polynomial The polynomial we divide with is called The Dividend The polynomial we divide by is called The Divisor The answer is called The Quotient How to fill in as to start? First, write the dividend inside. Next, write the divisor outside. Then, divide and the Quotient will be up. Quotient Divisor Dividend DIVISION • Division – the quotient of two functions and is denoted by ; (f/g)(x). • this quotient is defined as Example: Let f(x) = x - 1 and g(x) = x² - 3x + 2. Find(f/g)(x). Solution: Divide the two given expressions for f(x) and g(x). Example 1: Let f(x) = x - 1 and g(x) = x² - 3x + 2. Find(f/g)(x). 1. Substitute the given functions. (f/g)(x) = f(x) / g(x) 2 (f/g)(x) = x – 1 / x – 3x + 2 Example: Let f(x) = x - 1 and g(x) = x² - 3x + 2. Find(f/g)(x). 2. Factor the denominator (f/g)(x) = __x – 1___ x2 – 3x + 2 (f/g)(x) = ___x – 1___ (x -1 )(x-2) Example: Let f(x) = x - 1 and g(x) = x² - 3x + 2. Find(f/g)(x). 3. Cancel out common factors to simplify. (f/g)(x) = __x – 1___ x2 – 3x + 2 Thus, (f/g)(x) = (f/g)(x) = ___x – 1___ (x -1 )(x-2) 1____ x-2 Example 2: Let f(x) = x3 + 6x2 + 11x + 6 and g(x) = x + 2. Find(f/g)(x). Solution: Divide the two given expressions for f(x) and g(x). Example 2: Let f(x) = x3 + 6x2 + 11x + 6 and g(x) = x + 2. Find(f/g)(x). 1. Substitute the given functions. (f/g)(x) = f(x) / g(x) 3 2 (f/g)(x) = x + 6x + 11x + 6 x+2 Example 2: Let f(x) = x3 + 6x2 + 11x + 6 and g(x) = x + 2. Find(f/g)(x). 2. Divide the two expressions We can divide the expressions either factoring or by synthetic division. Example 2: Let f(x) = x3 + 6x2 + 11x + 6 and g(x) = x + 2. Find(f/g)(x). -2_| Multiply 1 1 6 6 -2 11 -8 -6 4 3 0 Since the remainder is 0, the quotient of the two given functions x2 + 4x + 3 Example 3: Let f(x) = x - 2 and g(x) = 3x2 -5x - 2. Find(f/g)(3). Solution: Divide the two given expressions for f(x) and g(x). Example 3: Let f(x) = x - 2 and g(x) = 3x2 -5x - 2. Find(f/g)(3). 1. Substitute the given functions. (f/g)(x) = f(x) / g(x) (f/g)(x) = __ x – 2___ 2 3x -5x - 2 Example 3: Let f(x) = x - 2 and g(x) = 3x2 -5x - 2. Find(f/g)(3). 2. Factor the denominator (f/g)(x) = __ x – 2___ 2 3x -5x – 2 (f/g)(x) = __ x – 2___ (x – 2)(3x + 1 ) Example 3: Let f(x) = x - 2 and g(x) = 3x2 -5x - 2. Find(f/g)(3). 3. Simplify (f/g)(x) = __ x – 2___ (x – 2)(3x + 1 ) (f/g)(x) = 1 _ 3x + 1 Example 3: Let f(x) = x - 2 and g(x) = 3x2 -5x - 2. Find(f/g)(3). 4. Substitute x = 3 to the resulting function. (f/g)(x) = 1 _ 3x + 1 (f/g)(x) = 1 _ Hence, (f/g)(3) = 1/10 3(3) + 1 (f/g)(x) = 1 _= 1 10 9+1