Plant Reproduction: Cross-Pollination, Self-Incompatibility, Seed Dispersal
advertisement

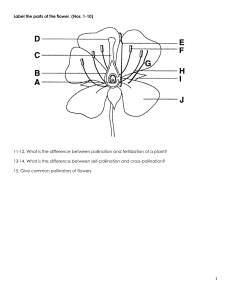
Methods of Promoting Cross-Pollination (D3.1.10) 1. Create a labelled diagram showing at least three adaptations in plants that promote cross-pollination (e.g., different maturation times, separate male and female flowers/plants). 2. Write a short explanation (100–150 words) describing how animals and wind assist in cross-pollination, giving specific examples of plants for each. Self-Incompatibility Mechanisms (D3.1.11) 1. Define self-pollination and explain why it can lead to inbreeding. 2. Research and write a short report (150–200 words) on how genetic mechanisms in plants prevent self-fertilisation. Use examples such as the S-gene system or other known incompatibility mechanisms. 3. Include a flow diagram showing the fusion of male and female gametes from different plants during fertilisation. Dispersal and Germination of Seeds (D3.1.12) 1. Create a comparison table showing at least three differences between pollination and seed dispersal. 2. Make a labelled diagram showing the stages of seed germination, including: ○ The development of the embryo ○ Mobilisation of food reserves 3. Write a short explanation (100–150 words) of how environmental conditions affect seed germination (e.g., water, temperature, oxygen). Extension Task: Choose a flowering plant and describe how it: Promotes cross-pollination Prevents self-fertilisation Disperses its seeds Include labelled diagrams and explanations.