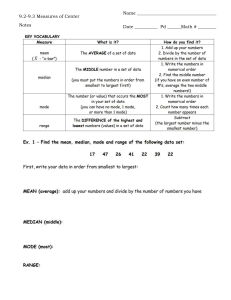
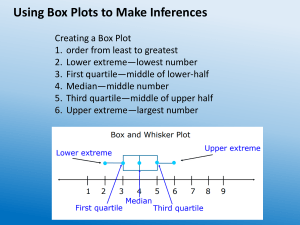
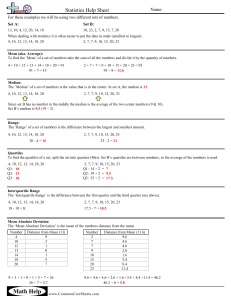
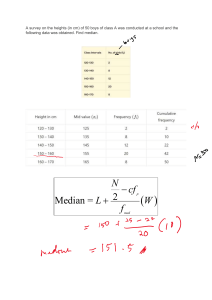
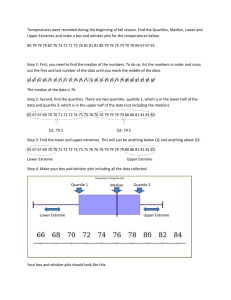
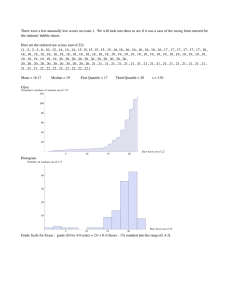
MEASURES OF POSITION: QUARTILE CLASSROOM OBSERVATION - FOURTH QUARTER FEBRUARY 13, 2025 Today you will learn: a. define and illustrate quartiles for ungrouped data, b. calculate a specified quartile position; and c. apply the concept of quartiles in interpreting data. ALL ABOUT MEDIAN HOW DO YOU DETERMINE THE MEDIAN OF A DATASET? A. Add all the numbers together and divide by the total count B. Identify the number that appears most often C. Arrange the numbers in order and find the middle value D. Select the largest number in the dataset IF A DATASET CONSISTS OF THE NUMBERS 2, 3, 3, 5, 7, 8, 8, 8, 9 WHAT IS THE MEDIAN? A. 2 B. 3 C. 5 D. 7 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING STATEMENTS IS TRUE ABOUT THE MEDIAN? A. The median is always the most frequently occurring number in a dataset. B. The median is the middle number when a dataset is arranged in order. C. The median is always equal to the mean in a dataset. D. The median is the sum of all numbers divided by the total count. NUMBER LINE SHUFFLE NUMBER LINE SHUFFLE 1. SET - UP 2. FIND YOUR SPOT 3. WHO IS STANDING IN THE MIDDLE? 4. LABEL IT! Ten of the Grade 10 Katmon Students obtained the following scores in a 10- item Mathematics Quiz: 8, 2, 5, 4, 8, 5, 7, 1, 3 and 6 1. Arrange the score in increasing or decreasing order. 2. Identify the lowest and highest score. 3. Find the middle score and label it as Q2. 4. Identify the value between the middle score and the lowest score. Label it as Q1. 5. Identify the value between the middle score and the highest score. Label it as Q3. Guide questions: • What are Q1, Q2, and Q3 of their scores? • Which scores fall under Q1, Q2, and Q3? • How many students belong to Q1, Q2, and Q3 in terms of their scores? MEASURES OF POSITION: QUARTILE MEASURE OF POSITION Measures of position are techniques that divide a set of data into equal parts. QUARTILES Quartiles are score points which divides a distribution into four equal parts. Illustration of quartiles • 25% of the data has a value ≤ Q1 or 75% of the data has a value ≥ Q1 • 50% of the data has a value ≤ Q2 or 50% of the data has a value ≥ Q2 • 75% of the data has a value ≤ Q3 or 25% of the data has a value ≥ Q3 EXAMPLE 3, 5, 5, 6, 2, 5, 4, 2, 4 ACTIVITY: ACTIVITY: ASSIGNMENT: There are a lot of examples that show how the measures of position are applied in real-life situations. Give utmost 5 examples of real-life situations that use the measures of position. Make sure to briefly explain how these situations use quartiles. THANK YOU!