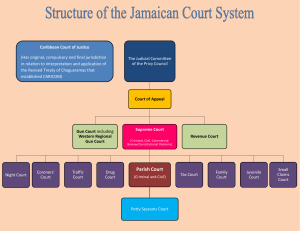
THE INTEGRATION MOVEMENT Explain the goals, motives Assess the achievement of each integration movement and their failures Why Integrate? Integration creates a greater weight as Caribbean region, in the diplomatic arena there would be a larger voice When it comes to trade it would mean pooling resources, creating trading bloc Helping each other out, less developed economies helping out other economies There could be uniformity, standardization Gain some advantage, make us more competitive More self sufficient Factors in Support of Caribbean integration Common historical experience (exploitation), that means modern day we continue to experience the effects of it and the challenges Cultural similarities, integration easy Geographical proximity Common economic, political, social issues Challenges to Integration Lack of regionalism Currency differences Different stages of development Language barriers Political differences, statuses, different stages of de-colonisation Immigration barriers (freedom of movement) West Indies Federation (1958-1962) Prior- Lee ward island federation (1671 ), then the West Indies Confederation (1876), Montego Bay Jamaica (1958), All of the British west Indies territories except Bahamas and Guyana. It contributed to individual independence. It determined future attitudes towards economic partnerships and interactions. Economic integration. Goal- to hand the Caribbean independence, through the Federation, achieve economic integration CARIFTA 1963 (after independence) Trade association, it included all the poorer regions, stimulate trade among member states by removing tariffs and trade barriers (goods produced within the region), mobilise labour in the region. Only integrates the economic aspect. Assessment It failed to increase production and trade CARIFTA games, Caribbean Development Plan CARICOM (replaced CARIFTA, 1973 (Treaty of Chaguaramas) Members include, Belize and Bahamas, Suriname, Haiti & Cuba (provisional members) Motives of CARICOM Create deeper economic union through common interests (facilitate free trade and a common market) Integrate economic policies Human resource (achieve functional corporation to things like education and health) To coordinate foreign policy to establish a free movement of capital services and labour in the Caribbean To establish regional security (RSS) Regional Secretariat- coordinate and organise Has both a political and economic goals Improve standards of living Provide full employment of labour and other factors of production Increased production and productivity Advance social and technological developments Problems of CARICOM Countries continue to trade with the US, Europe Remain as distinct economic policies Funding for Caricom 1976-1982 (government did not meet) 1980s boom (Trinidad), Jamaica (economic debt) 1989- economic integration the CSME (2006) is proposed as a separate entity under CARICOM, revised Treaty of Chaguaramas The Bahamas is not part of the CSME (economy is based of the offshore banking) Motives in 2015-2019 (be completed by 2024) Sustainable economic growth and development Sound environment policy (energy sources, st.lucia coral reef management) Technical and technological advancement Strengthening governance (preferential tariffs and duties) Extending free trade, Establishment of the Caribbean Court of Justice Common foreign policy towards non-member states Have these goals been met? Factor in the Covid 19. CCJ- Barbados, Belize, Dominica, Guyana Launched Vision 25 by 2025, locally produced food using Sargasso weed for fertilizer *Politics- the management of economic resources *Government -The body of people you elect to manage economic resources. OECS (Formed through the lesser Antilles) 1978 Susceptible so similar disasters, volcanic eruptions Their survival depended on integration Motives Promote the development of the sub region Pool resources together Rationalise development projects Free trade and movements in that region Economic integration Achievements A single currency (EC Dollar) Single judicial system Joint civil aviation authority Central bank ACS (Association of Caribbean States) 1984 Fourth largest trading bloc in the world, members are the wider Caribbean (geographic definition) Promote economic cooperation Disaster risk reduction Language trading Caribbean Sea initiative- recognise that all the territories share the Caribbean coast hence it will affect the other country, marine life, tourism Updating building codes Wider platform than just CARICOM