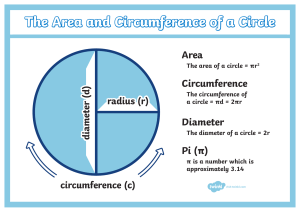
GEOMETRY Chapter:Circle Terminology 1) Radius A • The segment joining the center of a circle to a point on the circle. O • Example: OA 2) Diameter • A chord that passes through the center of a circle. A O • Example: AB B 3) Chord • A segment joining two points on a circle B • Example 01: AB A C B • Example 02: AB C A 4) Secant A • A line that intersects the circle at exactly two points. C O • Example 01: AB D B A C • Example 02: AB O D B 5)Tangent B C • A line that intersects a circle at exactly one point. A • Example: AB 6) Central Angle A • An angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle. B • Example: Angle ABC C 7)Inscribed Angle B A C • An angle whose vertex is on a circle and whose sides are determined by two chords. • Example: Angle ABC 8) Arc • A figure consisting of two points on a circle and all the points on the circle needed to connect them by a single path. • Example: arc AB B A . O The length of the circle or the distance around it is called circumference of the circle. Relation between radius and diameter RADIUS = DIAMETER 2 A OB = AB 2 . O B Ex : If diameter of the circle is 10 cm then find its radius? Sol. Radius =diameter / 2 radius=10 cm/ 2 radius =5 cm A . O Diameter = 10cm B Ex: If radius of the circle is 6 cm,then find the diameter of the circle? Sol. Diameter = 2 × Radius Diameter = 2 × 6cm Diameter = 12 cm A Radius = 6cm . O RELATION BETWEEN CIRCUMFERENCE AND DIAMETER CIRCUMFERENCE = 𝜋 × DIAMETER . DIAMETER O A B Ex. Find the circumference of the circle whose diameter is 10cm. Sol. Circumference = 𝜋 × diameter Circumference = 𝜋 × 10 cm Circumference = 10 𝜋 cm . O A DIAMETER=10 CM B