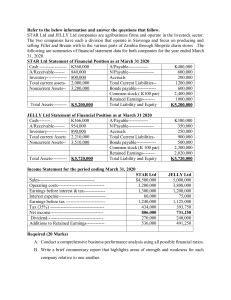
Location Strategies 8 PowerPoint presentation to accompany Heizer, Render, Munson Operations Management, Thirteen Edition, Global Edition Principles of Operations Management, Eleventh Edition PowerPoint slides by Jeff Heyl Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8-1 Outline ► Global Company Profile: FedEx The Strategic Importance of Location ► Factors That Affect Location Decisions ► Methods of Evaluating Location Alternatives ► Service Location Strategy ► Geographic Information Systems ► Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8-2 Location Provides Competitive Advantage for FedEx ▶ Central hub concept (superhub) ▶ Enables service to more locations with fewer aircraft ▶ Enables matching of aircraft flights with package loads ▶ Reduces mishandling and delay in transit because there is total control of packages from pickup to delivery Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8-3 Learning Objectives When you complete this chapter you should be able to: 8.1 Identify and explain seven major factors that effect location decisions 8.2 Compute labor productivity 8.3 Apply the factor-rating method 8.4 Complete a locational cost-volume analysis graphically and mathematically Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8-4 Learning Objectives When you complete this chapter you should be able to: 8.5 Use the center-of-gravity method 8.6 Understand the differences between service- and industrial-sector location analysis Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8-5 The Strategic Importance of Location ► One of the most important decisions a firm makes ► Increasingly global in nature ► Significant impact on fixed and variable costs ► Decisions made relatively infrequently Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8-6 The Strategic Importance of Location ► Long-term decisions ► Once committed to a location, many resource and cost issues are difficult to change Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8-7 The Strategic Importance of Location The objective of location strategy is to maximize the benefit of location to the firm Options include 1. Expanding existing facilities 2. Maintain existing and add sites 3. Closing existing and relocating Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8-8 Location and Costs ► Location decisions require careful consideration ► Once in place, location-related costs are fixed in place and difficult to reduce ► Effort spent determining optimal facility location is a good investment Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8-9 Factors That Affect Location Decisions ▶ Globalization adds to complexity ▶ Drivers of globalization ▶ Market economics ▶ Communication ▶ Rapid, reliable transportation ▶ Ease of capital flow ▶ Differing labor costs ▶ Identify key success factors (KSFs) Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 10 Location Decisions Country Decision Key Success Factors 1. Political risks, government rules, attitudes, incentives 2. Cultural and economic issues 3. Location of markets 4. Labor talent, attitudes, productivity, costs 5. Availability of supplies, communications, energy Figure 8.1 6. Exchange rates and currency risks Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 11 Location Decisions Region/ Community Decision Key Success Factors 1. Corporate desires 2. Attractiveness of region 3. Labor availability and costs MN 4. Costs and availability of utilities WI 5. Environmental regulations MI IL IN OH 6. Government incentives and fiscal policies 7. Proximity to raw materials and customers Figure 8.1 8. Land/construction costs Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 12 Location Decisions Site Decision Key Success Factors 1. Site size and cost 2. Air, rail, highway, and waterway systems 3. Zoning restrictions 4. Proximity of services/ supplies needed 5. Environmental impact issues Figure 8.1 6. Customer density and demographics Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 13 TABLE 8.1 Global Competitiveness Index of Countries Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Competitiveness of 137 Selected Countries COUNTRY 2018 RANKING Switzerland 1 U.S. 2 Singapore 3 Netherlands 4 Germany 5 Hong Kong 6 Canada 14 Israel 16 China 27 Russia 38 Mexico 51 Vietnam 55 Haiti 128 Mozambique 136 Yemen 137 8 - 14 Factors That Affect Location Decisions ► Labor productivity ► Wage rates are not the only cost ► Lower productivity may increase total cost Labor cost per day Productivity (units per day) = Labor cost per unit South Carolina $70 60 units = $1.17 per unit Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Mexico $25 20 units = $1.25 per unit 8 - 15 Factors That Affect Location Decisions ► Exchange rates and currency risks ► Can have a significant impact on costs ► Rates change over time ► ► Operational hedging – shift production as exchange rates change Costs ► ► Tangible – easily measured costs such as utilities, labor, materials, taxes Intangible – not as easy to quantify and include education, public transportation, community, quality-of-life Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 16 Factors That Affect Location Decisions ► Exchange rates and currency risks ► Can have a significant impact on costs ► Rates change over time ► Operational hedging – shift production as Location decisions exchange rates change based on costs ► Costs alone can create ► Tangible – easily measured costs such as difficult ethical utilities, labor, materials, taxessituations ► Intangible – not as easy to quantify and include education, public transportation, community, quality-of-life Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 17 Factors That Affect Location Decisions ► Political risk, values, and culture ► National, state, local governments' attitudes toward private and intellectual property, zoning, pollution, employment stability may be in flux ► Worker attitudes toward turnover, unions, absenteeism ► Globally cultures have different attitudes toward punctuality, legal, and ethical issues Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 18 Ranking Corruption Least Corrupt Most Corrupt Rank Country 1 2 3 6 8 12 16 20 51 77 135 180 New Zealand Denmark Finland, Norway, Switzerland Singapore, Sweden Canada, UK Germany USA Japan South Korea China Mexico, Russia Somalia Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 2017 CPI Score (out of 100) 89 88 85 84 82 81 75 73 54 41 29 9 8 - 19 Factors That Affect Location Decisions ► ► Proximity to markets ► Very important to services ► JIT systems or high transportation costs may make it important to manufacturers Proximity to suppliers ► Perishable goods, high transportation costs, bulky products Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 20 Factors That Affect Location Decisions ► Proximity to competitors (clustering) ► Often driven by resources such as natural, information, capital, talent ► Found in both manufacturing and service industries Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 21 Clustering of Companies TABLE 8.3 Clustering of Companies REASON FOR CLUSTERING INDUSTRY LOCATIONS Wine making Napa Valley (U.S.) Bordeaux region (France) Natural resources of land and climate Software firms Silicon Valley, Boston, Bangalore, Israel Talent resources of bright graduates in scientific/technical areas, venture capitalists nearby Clean energy Colorado Critical mass of talent and information, with 1,000 companies Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 22 Clustering of Companies TABLE 8.3 Clustering of Companies REASON FOR CLUSTERING INDUSTRY LOCATIONS Theme parks (Disney World, Universal Studios, and Sea World) Orlando, Florida A hot spot for entertainment, warm weather, tourists, and inexpensive labor Electronics firms (Sony, IBM, HP, Motorola, and Panasonic) Northern Mexico NAFTA, duty free export to U.S. (24% of all TVs are built here) Computer hardware Singapore, Taiwan manufacturers Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. High technological penetration rate and per capita GDP, skilled/educated workforce with large pool of engineers 8 - 23 Clustering of Companies TABLE 8.3 Clustering of Companies INDUSTRY LOCATIONS REASON FOR CLUSTERING Fast food chains Sites within 1 mile of (Wendy’s, each other McDonald’s, Burger King, Pizza Hut) Stimulate food sales, high traffic flows General aviation aircraft (Cessna, Learjet, Boeing, Raytheon) Wichita, Kansas Mass of aviation skills (6070% of world's small planes/jets are built here) Athletic footwear, outdoor wear Portland, Oregon 300 companies, many owned by Nike, deep talent pool and outdoor culture Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 24 Factor-Rating Method ► Popular because a wide variety of factors can be included in the analysis ► Six steps in the method 1. Develop a list of relevant factors called key success factors 2. Assign a weight to each factor 3. Develop a scale for each factor 4. Score each location for each factor 5. Multiply score by weights for each factor and total the score for each location 6. Make a recommendation based on the highest point score Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 25 Factor-Rating Example TABLE 8.4 Weights, Scores, and Solution SCORES (OUT OF 100) KEY SUCCESS FACTOR WEIGHTED SCORES WEIGHT FRANCE DENMARK FRANCE DENMARK Labor availability and attitude .25 70 60 (.25)(70) = 17.50 (.25)(60) = 15.00 People-to-car ratio .05 50 60 (.05)(50) = 2.50 (.05)(60) = 3.00 Per capita income .10 85 80 (.10)(85) = 8.50 (.10)(80) = 8.00 Tax structure .39 75 70 (.39)(75) = 29.25 (.39)(70) = 27.30 Education and health .21 60 70 (.21)(60) = 12.60 (.21)(70) = 14.70 Totals 1.00 70.35 68.00 Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 26 Locational Cost-Volume Analysis ► An economic comparison of location alternatives ► Three steps in the method 1. Determine fixed and variable costs for each location 2. Plot the costs for each location 3. Select location with lowest total cost for expected production volume Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 27 Locational Cost-Volume Analysis Example Three locations: Selling price = $120 Expected volume = 2,000 units City Athens Brussels Lisbon Fixed Variable Total Cost Cost Cost $30,000 $75 $180,000 $60,000 $45 $150,000 $110,000 $25 $160,000 Total Cost = Fixed Cost + (Variable Cost x Volume) Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 28 Locational Cost-Volume Analysis Example Crossover point – Athens and Brussels 30,000 + 75(x) = 60,000 + 45(x) 30(x) = 30,000 x = 1,000 Crossover point – Brussels and Lisbon 60,000 + 45(x) = 110,000 + 25(x) 20(x) = 50,000 x = 2,500 Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 29 Locational Cost-Volume Analysis Example Annual cost Figure 8.2 – $180,000 – – $160,000 – $150,000 – – $130,000 – – $110,000 – – – $80,000 – – $60,000 – – – $30,000 – – $10,000 – | – 0 Athens lowest cost Lisbon lowest cost Brussels lowest cost | | | | | | 500 1,000 1,500 2,000 2,500 3,000 Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Volume 8 - 30 Center-of-Gravity Method ► Finds location of distribution center that minimizes distribution costs ► Considers ► Location of markets ► Volume of goods shipped to those markets ► Shipping cost (or distance) Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 31 Center-of-Gravity Method ► ► Place existing locations on a coordinate grid ► Grid origin and scale are arbitrary ► Maintain relative distances Calculate x and y coordinates for 'center of gravity' ► Assumes cost is directly proportional to distance and volume shipped Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 32 Center-of-Gravity Method xi Qi x-coordinate of the i center of gravity Qi i yi Qi y-coordinate of the i center of gravity Q i where i xi = x-coordinate of location i yi = y-coordinate of location i Qi = Quantity of goods moved to or from location i Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 33 Center-of-Gravity Method TABLE 8.5 Demand for Quain's Discount Department Stores STORE LOCATION NUMBER OF CONTAINERS SHIPPED PER MONTH Chicago 2,000 Pittsburgh 1,000 New York 1,000 Atlanta 2,000 Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 34 Center-of-Gravity Method Figure 8.3 North-South New York (130, 130) Chicago (30, 120) 120 – Pittsburgh (90, 110) 90 – x1 = 30 y1 = 120 Q1 = 2,000 60 – 30 – | – Atlanta (60, 40) | | | | | 30 60 90 120 150 East-West Arbitrary origin Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 35 Center-of-Gravity Method x-coordinate = (30)(2000) + (90)(1000) + (130)(1000) + (60)(2000) 2000 + 1000 + 1000 + 2000 = 66.7 y-coordinate = (120)(2000) + (110)(1000) + (130)(1000) + (40)(2000) 2000 + 1000 + 1000 + 2000 = 93.3 Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 36 Center-of-Gravity Method Figure 8.3 North-South New York (130, 130) Chicago (30, 120) 120 – Pittsburgh (90, 110) + 90 – Center of gravity (66.7, 93.3) 60 – 30 – –| Atlanta (60, 40) | | | | | 30 60 90 120 150 East-West Arbitrary origin Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 37 Transportation Model ► Finds amount to be shipped from several points of supply to several points of demand ► Solution will minimize total production and shipping costs ► A special class of linear programming problems Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 38 Worldwide Distribution of Volkswagens and Parts Figure 8.4 Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 39 Service Location Strategy Major Determinants of Volume and Revenue 1. Purchasing power of customer-drawing area 2. Service and image compatibility with demographics of the customer-drawing area 3. Competition in the area 4. Quality of the competition 5. Uniqueness of the firm’s and competitors’ locations 6. Physical qualities of facilities and neighboring businesses 7. Operating policies of the firm 8. Quality of management Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 40 Location Strategies TABLE 8.6 Location Strategies – Service vs. Goods-Producing Organizations SERVICE/RETAIL/PROFESSIONAL GOODS-PRODUCING REVENUE FOCUS COST FOCUS Volume/revenue Drawing area; purchasing power Competition; advertising/pricing Physical quality Parking/access; security/lighting Appearance/image Cost determinants Rent Management caliber Operation policies (hours, wage rates) Tangible costs Transportation cost of raw material Shipment cost of finished goods Energy and utility cost; labor; raw material; taxes, and so on Intangible and future costs Attitude toward union Quality of life Education expenditures by state Quality of state and local government Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 41 Location Strategies TABLE 8.6 Location Strategies – Service vs. Goods-Producing Organizations SERVICE/RETAIL/PROFESSIONAL GOODS-PRODUCING TECHNIQUES TECHNIQUES Regression models to determine importance of various factors Factor-rating method Traffic counts Demographic analysis of drawing area Purchasing power analysis of area Center-of-gravity method Geographic information systems Transportation method Factor-rating method Locational cost–volume analysis Crossover charts ASSUMPTIONS ASSUMPTIONS Location is a major determinant of revenue High customer-contact issues are critical Costs are relatively constant for a given area; therefore, the revenue function is critical Location is a major determinant of cost Most major costs can be identified explicitly for each site Low customer contact allows focus on the identifiable costs Intangible costs can be evaluated Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 42 How Hotel Chains Select Sites ► Location is a strategically important decision in the hospitality industry ► La Quinta started with 35 independent variables and worked to refine a regression model to predict profitability ► The final model had only four variables ► Price of the inn ► Median income levels ► State population per inn ► Location of nearby colleges Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 43 How Hotel Chains Select Sites ► Location is a strategically important decision in the hospitality industry ► La Quinta started with 35 independent variables and worked to refine a regression model to predict profitability ► R2 = .51 The final model had only four variables ► Price of the inn ► Median income levels ► State population per inn ► Location of nearby colleges Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 51% of the profitability is predicted by just these four variables! 8 - 44 Geographic Information Systems (GIS) ► Important tool to help in location analysis ► Enables more complex demographic analysis ► Available databases include ► Detailed census data ► Detailed maps ► Utilities ► Geographic features ► Locations of major services Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 45 Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 46 Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 8 - 47