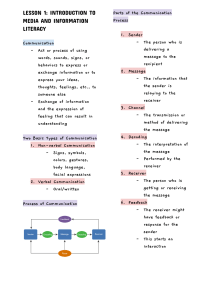
Tab 1 MEDIALIT REVIEWER Topic 1: What is Information and Communication MESSAGE - relayed as a piece of information. CHANNEL - the media that helps you reach your intended audience. RECEIVER - the people who read or listen to your information. INFORMATION - A processed, organized data presented in a given context and is useful to humans. A group of data that collectively carry a logical meaning.Plays a pivotal role in human development. COMMUNICATION - The act or process of using words, sounds, signs, or behaviors to express or exchange information or to express your ideas, thoughts, feelings, etc., to someone else. SHANNON-WEAVER MODEL OF COMMUNICATION (1948) BASIC TYPES OF COMMUNICATION NON-VERBAL COMMUNICATION • Signs • Symbols • Colors • Gestures • body language • facial expressions VERBAL COMMUNICATION • Oral • Written - Mother of all the communication model It requires channels that uses wires (ex. telephone) Circular LASSWELL’S MODEL OF COMMUNICATION (1948) —----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------THE COMMUNICATION PROCESS SENDER - the source of the message. - Linear By Harold Dwight Lasswell Ex. news, tv, radio, newspapers 5 Types of Analysis 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Control analysis (Communicator) Content analysis (Message) Media analysis (Medium) Audience analysis (Receiver) Effect analysis (Effect) OSGOOD-SCHRAMM’S MODEL OF COMMUNICATION (1954) - Like a cycle Model by Charles Eagerton Osgood and Wilbur Schramm WESTLEY AND MCLEAN’S MODEL OF COMMUNICATION • Event or Information (X1, X2, X3 and X4...Xn) • Feedback (f) • Advocate (A) • Channel (C) • Audience (B) BERLO’S SMCR MODEL OF COMMUNICATION (1960) SOURCE: The source is situated where the message originates . ● Communication skills – It is the skill of the individual to communicate. ● Attitudes – This includes attitudes towards the audience, subject and towards oneself. ● Knowledge– Communicating also means that the person needs to be knowledgeable about the subject or topic. ● Social system – The social system includes the various aspects of society like values, beliefs, culture, religion and a general understanding of society. ● Culture: Culture of a particular society also comes under the social system. Encoder: The sender of the message, from where the message originates, is referred to as the encoder. MESSAGE: ● ● ● ● ● Content – The body of a message, from the beginning to the end, comprises its content. Elements – It includes various things like language, gestures, body language, etc. They constitute all the elements of a particular message. Treatment – It refers to the packing of the message and the way in which the message is conveyed or the way in which it is passed on or delivered. Structure– The structure of the message refers to how it is arranged; the way people structure the message into various parts. Code– The code of the message refers to the means through which it is sent and in what form. ● ● Smelling: Smell also can be a channel to communicate. Tasting : The tongue is a muscular organ used in the act of eat and taste food. DECODER:: The person who receives the message and decodes it is referred to a decoder. RECEIVER: The receiver needs to think all the contents and elements of the source, so as to communicate/responds to sender effectively.; —-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------GRAPEVINE COMMUNICATION - Is an informal communication, unorganized and unofficial channel of communication in an organization. - Grapevine means a source of secret information. TYPES OF GRAPEVINE COMMUNICATION CHANNEL: ● ● ● Hearing: The use of ears to receive the message. For example, orally transmitted messages, interpersonal communication etc. Seeing: Visual channels, for example, Watching television so the message is conveyed through the scene/film. Touching: The sense of touch can be used as a channel to communicate. For example, we touch, buy food, hugging our loved ones,etc. The Wheel - one person is predominant. He transmits grapevine to different persons or group of persons. He is at the center and various lines of communication become the stokers of the wheel. Every person in the wheel becomes the causative factor for starting another wheel. The Cluster - The cluster like grapes, have several groups of people linked together by a cluster or chain of communication. The Chain - Chain is the most common pattern in which information passes through a series of people linked together in the organization. Free Flow - Most of the rumors or idle gossip is spread by random, free flow or haphazard network, which includes a number of people who are not necessarily linked by any organizational thread. Topic 2: What is Media and Information Literacy Media - Derived from the Latin word medius, which means “middle”. - It helps us spread information in different forms and devices. - It also helps improve the way we communicate with other people, especially those who are very far away from us. - Means of communication Media – as defined by UNESCO, refers to sources of credible and current information created through an editorial process determined by journalistic values, whereby editorial accountability can be attributed to a specific organization or a legal person. Information Literacy - The ability to recognize when information is needed and to locate, evaluate, effectively use and communicate information in its various formats. Media Literacy - The ability to read, analyze, evaluate and produce communication in a variety of media forms. A set of perspectives that people use actively to expose themselves to mass media and interpret the meaning of the messages they encounter. Technology (Digital) Literacy - The ability to use digital technology, communication tools or networks to locate, evaluate, use, and create information. environment around us. Like news, it is timely changing and requires the support of facts and information. - Social networks have become the central facilitator for daily communication with peers,family and acquaintances. Topic 3: Media and Information Literacy Media and Information Literacy - - - Refers to the essential competencies (knowledge, skills and attitude) that allow citizens to engage with media and other information providers effectively and develop critical thinking and life-long learning skills for socializing and becoming active citizens. Concerned with the use of the message, technology literacy focuses on the responsible and effective use of technology, tools, or networks in accessing, analyzing, evaluating, and creating the message. Promotes critical thinking to empower citizens to process and raise questions about the information they receive, the manner it was disseminated, and the purpose for which it was shared. How is communication affected by media and information? - Communication can be affected by external factors or from the Media - the media makes communicating a lot easier than before, there is an internet present today which enables chatting with friends and families through phone screens. Information - it is the , supply of communication it makes talking and sharing opinion with others much more meaningful and with sense. Lesson 2: The Evolution of Traditional to New Media, Internet of Things PRE-INDUSTRIAL AGE (BEFORE 1700) People discover fire, developed paper from plants, and forge weapon and tools with stone, bronze, copper, and iron. Cave paintings - are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. Clay tablets - were used as a writing medium, especially for writing in cuneiform, throughout the Bronze Age and well into the Iron Age. Cuneiform characters were imprinted on a wet clay tablet with a stylus often made of reed (reed pen). Papyrus - is first known to have been used in Egypt (at least as far back as the First Dynasty), as the papyrus plant was once abundant across the Nile Delta. It was also used throughout the Mediterranean region and in the Kingdom of Kush. Acta Diurna - also called Acta Populi, Acta Publica and simply Acta or Diurna, in ancient Rome a sort of daily government gazette, containing an officially authorized narrative of noteworthy events at Rome. Dibao - literally "reports from the official residences", were a type of publications issued by central and local governments in imperial China. Maya codices (singular codex) - are folding books written by the preColumbian Maya civilization in Maya hieroglyphic script on Mesoamerican bark paper. Woodblock printing (or block printing) - is a technique for printing text, images or patterns used widely throughout East Asia and originating in China in antiquity as a method of printing on textiles and later paper. INDUSTRIAL AGE (1700- 1930s) People used the power of steam developed machine tools, established iron production, and the manufacturing of various products (including books through the printing press) The London Gazette - the official journals of record of the British government, and the most important among such official journals in the United Kingdom, in which certain statutory notices are required to be published. Typewriter - a mechanical or electromechanical machine for writing characters similar to those produced by printer's movable type. Telephone or phone - is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be heard directly. Motion picture photography - When the still pictures are projected progressively and rapidly onto a screen, the eye perceives motion, hence they become a motion picture. This is termed persistence of vision. Printing press - a machine by which text and images are transferred to paper or other media by means of ink. Sound film - is a motion picture with synchronized sound, or sound technologically coupled to image, as opposed to a silent film. The Telegraph - is a national British daily broadsheet newspaper published in London by Telegraph Media Group and distributed across the United Kingdom and internationally. - introduced by IBM in 1954, is the first mass-produced computer with floatingpoint arithmetic hardware. Overhead Projector - is a variant of slide projector that is used to display images to an audience. The name is often abbreviated to OHP. ELECTRONIC AGE (1930s - 1980s) The invention of the transistor ushered in the electronic age. People harnessed the power of transistors that led to the transistor radio, electronic circuits, and the early computers. IN this age, long distance communication become more efficient. Transistor Radio - is a small portable radio receiver that uses transistor-based circuitry. Television (TV) - sometimes shortened to tele or telly, is a telecommunication medium used for transmitting moving images in monochrome (black and white), or in color, and in two or three dimensions and sound. ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) - was amongst the earliest electronic general-purpose computers made. It was Turing-complete, digital and able to solve "a large class of numerical problems" through reprogramming. NEW/ INFORMATION AGE (1900s 2000s) The internet paved the way for faster communication and the creation of the social network. People advanced the use of microelectronics with the invention of personal computers, mobile devices, and wearable technology. Moreover, voice, image, sound and data are digitalized. We are now living in the information age. Example Forms of Media: Web browsers: Mosaic (1993), Internet Explorer (1995) Blogs: Blogspot (1999), Wordpress (2003) Social networks: Friendster (2002), Multiply (2003) , FB (2004) Microblogs: Twitter (2006), Tublr (2007) Augmented Reality/Virtual Reality Video chat: Skype (2003) Search Engines: Google (1996), Yahoo (1995) IBM 704 Portable computers-laptops (1980), netbooks (2008), tablets (1993) Smart phones. Wearable technology. Cloud and Big data Tab 2