I(...,_
•
....,..-
(
I ..-
i
l.;
!
.·
0 ,. '
TEST CODE 02.112010
MAY/JUNE2013
CARIBBEAN
EXAMINATIONS
COUNCIL
CARIBBEAN ADVANCED PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION"'
CHEMISTRY - UNIT 1
Paper 01
1 hour 30 minutes
(
21 M~Y 2013 (a.m.) )
READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY.
1.
This test consists of 45 items. You will have I hour and 30 minutes to answer them.
2.
In addition to this test booklet, you should have an answer sheet'and a Data Booklet.
3.
Each item in this test has four suggested answers lettered (A), (B), (C), (D). Read each item
you are about to answer and decide which choi<;e is best.
4.
On your answer sheet, find the number which corresponds to your item and shade the space
having the same letter as.the answer you have cl10sen. Look at the sample item below.
Which of the followi11g transitions requires the HIGHEST energy in an organic compound?
(A)
n to er•
(B)
n to 7t•
(C)
7t to 7t•
cr to cr•
(D)
Sample Answer
..
@®©•
The best answer to this item is "cr to cr•", so answer space (D) has been shaded.
--=·--=
5.
If you want to change your answer, erase it completely before you fill in your new choice.
6.
When you are told to begin, turn the page and work as quickly and as carefully as you can. If
you cannot answer an item, go on to the next one. You may return to this item later. Your score
will be the total number of correct answers.
7.
You may do any.rough work in this booklet.
8.
Figures are 'not necessarily drawn to scale.
9.
You may use a silent, non-programmable calculator to answer items.
""""'
I
·
..
DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO.
Copyript C 2011 Caribbean Examin.tions Council
A II ri nht• -••'"'•A
~---~--------~
. .~
·"-'
-2l.
Which of the following statements is NOT
a part of Dalton's atomic theory?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Atoms are indivisible.
Atoms are characterised by their
atomic number.
The atoms of an element have
identical properties.
The atoms of an element differ from
those of other elements.
4.
Which of the following factors is important
in determining the stability of an isotope?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
5.
Which of the following statements is
TRUE about 5 dm 3 of hydrogen and 5 dm'
of oxygen at 0 °C and I OJ kPa?
Item 2 refers to the following diagram which
shows the energy levels for the hydrogen
atom and the electronic transitions which
produce lines in the visible region.
(B)
==========::::;==::i===n=S
(C)
(A)
=_-=i=_-==-~:1=_1::=~-<:!=~-= ::~
Size of atomic radius
Number of protons
Ratio of protons to electrons
Ratio of protons to neutrons
(D)
They react to produce 5 dm' of
water.
They possess the same amount of
kinetic energy.
They contain the same number of
molecules.
They react completely with each
other.
- - - - - - - - - - n=l
6.
2.
Which of the series below involves
transitions from higher energy levels to the
n = 2 level?
Which of the following solids has a giant
molecular lattice?
(A)
(B)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
3.
Balmer
Dalton
Lyman
Paschen
( C)
(D)
Carbon dioxide
Copper oxide
Magnesium oxide
Silicon dioxide
Which of the following ions has the
GREATEST polarizing power?
(A)
Be'+
(B)
Ca2•
(C)
Li+
(D)
Sr•
!
!
GO ON TO 11iE NEXT PAGE
-3Item 11 refers to the following information.
Item 7 refers to the following equation
which shows the production of ammonia.
N 2(g) + 3H2(g)
7.
A piece of copper metal is placed in silver
nitrate solution, as shown in the diagram
below.
.= 2NH,(g)
-
If I 0 cm' of nitrogen reacts with 30 cm' of
hydrogen at STP, what volume of NH, is
produced?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Cu metal
JO cm'
15 cm'
20cm'
40cm'
11.
8.
F9r complete reaction, 0.25 g ofa monobasic
acid requires IO cm' of0.2 mol dm·' sodium
hydroxide. What is the relative molecular
mass of the acid?
Which of the following observations is
correct?
(A)
(B)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
9.
10.
12.5
62.5
125
250
(C)
(D)
The simplest formula for a compound that
contains 50% S and 50% 0 by mass is
(A)
SO
(B)
(C)
so,
s,o
(D)
s,o.
•
Which of the following gases is MOST
likely to have the characteristics of an ideal
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(A)
Mn02 --+ Mn2 +
(B),
Mno.---+ Mno 2-
(C)
Mno.---+ MnO,
(D)
Mn02 --+ Mno.-
•
·-. -- .... -
12.
Copper metal dissolves and the
solution remains colourless.
Copper metal is deposited and the
solution turns blue.
Silver metal forms and the solution
turns blue.
Silver metal forms and the solution
remains colourless.
gas?
Which ofthe following processes represents
an oxidation?
""""··~"·"'
.I
"
13.
Ammonia
Helium
Methane
Oxygen
A gas in a syringe occupies a volume of
50 cm' and has a pressure of 0.49346
atmospheres. What is the pressure of the
gas if the plunger of the syringe is pushed in,
reducing the volume of the gas to 20 cm'?
(I atmosphere= IOI 325 Pa)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
20kPa
125 kPa
20 OOOkPa
125 000 kPa
00 ONro nm NEXT PAGE
-414.
The second ionisation energy of calcium is 1150 kJ mo1-1 •
Which of the following equations represents this statement?
kJmot 1
(A)
ca• (g) -+ Ca2• (g) + e-
L\H = +1150
(B)
Ca(g) -+ Ca2+ (g) + 2e-
L\H =+1150
(C)
ca• (g) -+ Ca2• (g) + e-
L\H =-1150
(D)
Ca (g) -+ Ca,. (g) + 2e-
L\H =-1150
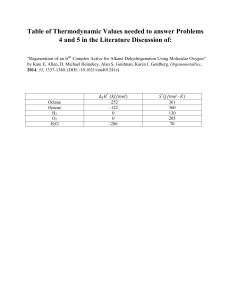
Item 15 refers to the following standard enthalpies of combustion for carbon, hydrogen and octane.
kJmot 1
Carbon
Hydrogen
Octane
15.
The standard enthalpy of formation of octane,
-394
-286
-5476
MJ , is calculated using
(C)
MIJ (octane)= -8 (-394}-9(-286)-5476 kJ rnoJMIJ (octane)= -8 (-394}-9(-286)-{-5476) kJ mo1MIJ (octane)= 8 (-394) + 9(-286)-{-5476) kJ mo1-
(D)
L\H1 (octane)= 8 (-394)-9(-286)-{-5476) kJ mo1- 1
(A)
(B)
1
1
8
•
1
•
•
00 ON TO T1IE NEXTPAOE
-5Item 16 refers to the following reaction which occurs in the presence of dilute acid.
CH,COCH, (aq) + 12 (aq)--+ CH) COCH, (aq) + H• (aq) + 1- (aq)
16.
The rate equation for the reaction is
Rate = k[CH,COCH, (aq)] [H'{aq)). Which of the following equations BEST illustrates the SLOW
step?
(A)
(Il)
(C)
(D)
0
OH
II
I
CH,-C-CH, + H• -+CH,-C-CH,
Ea
0
l
II
I
CH,- C-CH, + 12 --+ CH,-C-CH, + 1Ea
0
l
II
I
CH,- C - CH, + 1- --+CH,- C - CH,
Ea
0
OH
II
I
CH-C-CH
,
, +I, +H• -+CH-C
, I -CH,
l
i
I
r
I
•
17.
The rate Jaw for a given reaction is Rate= k[A) 2 [B] . What are the units fork?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
moJ-2 dm-2 s- 1
mo) dm-3 s- 1
moJ- 1 dm' s- 1
mo1-2 dm' s- 1
•
GO ON TO 1liE NEXT PAGE
-618.
Which of the following phrases BEST
describes the relationship between the
half-life of a second order reaction and the
reactants?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
20.
(A)
(B)
Dependent on the initial
concentration of the reactants
Independent of the initial
concentration of the reactants
Dependent on the state of the
reactants
Dependent on the final concentration
of the reactants
Item 19 refers to the following equilibrium.
N, (g) + 0 2 (g)
Which of the following statements
·does NOT refer to a system in dynamic
equilibrium?
(C)
(D)
21.
Which of the following statements about a
catalyst would be true?
~ 2NO(g), LlH =+I 80 kJ moJ· 1
I.
19.
The reaction is reversible.
The amounts of all the species in the
system remain constant.
The concentrations of all reactants
and products are equal.
The rate of the forward reaction is
equal to the rate of the backward
reaction.
Which of the curves in the diagram below
shows how increasing temperature affects
the yield of the product?
II.
Ill.
(D)
(A)
(B)
(C)
.CD)
22.
-----,(A)
Temperature (UC)
It increases the equilibrium constant
for the forward reaction only.
It increases the equilibrium constant for both the forward and
backward reactions.
It has no effect on the position of
equilibrium.
I only
III only
I and III only
II and III only
The value of Kp for the equilibrium reaction
H2 (g) + 12 (g) ~ 2HJ (g) at 444 'C at I atm
pressure is 50.
What is the value of KP if the pressure
is changed to 2 atm and the temperature
remains the same?
(A)
25
(B)
50
(C)
(D)
100
200
•
00 ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
-723.
In pure ethanol, (C,H,OH), the following
equilibrium can exist with ammonium ions.
NH; + C2H50H ~NH,+ C,H,OH,+
Which of the following combinations
describes the functions of NH; and C,H,OH
according to the Bronsted-Lowry theory?
NH•
'
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Acid
Base
Conjugate acid
Acid
24.
The results for four experiments which
. investigated
the
reaction
between
propanaone and iodine (ca~lysed by acid)
are given in the table below.
Expt
(H•]
[Propanone]
[Iodine]
Rate
I
I
0.5
I
10.8
2
0.5
I
3
4
0
0.5
0.25
I
5.3
5.4
0
0.5
0.5
10.6
C2H 50H
Base
Acid
Base
Conjugate base
Which ofthe following graphs represents the
order of reaction with respect to propanone?
(A)
Rate
[Propanone)
(B)
•
Rate
[Propanone)
(C)
Rate
[Propanone)
(D)
Rate
lPs »
I
•
M1, ..,~,,.,,..A~"'"'..,
00ONTO1llE NEXT PAGE
l
r
- 8-
25.
Which of the following expressions
represents the solubility product of
iron(lll) hydroxide?
(A)
(B)
27.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(0)
[Fe>+] [JOH-]
[Fe 3+] [OH-]3
[Fe(OH) 3 ]
(C)
[Fe1 •] [30H-]3
(D)
[Fe1 •] [OH-] 3
mol dm-'
mol' dm-6
moP dm_.
mol 4 dm-12
Which·ofthe following indicators is MOST suitable for use when titrating a weak acid against a
strong base?·
Indicator
(A)
(B)
(C)
(0)
28.
26. · Silver chromate(VI), Ag,Cr04 , is sparingly
soluble in water. The units. for the solubility
product (K,,,) for silver chromate(VI) are
pH of Change
Colour Change
Acid ~Alkali
3.5
red -+ yellow
red-+ blue
yenow -+ blue
colourless -+ pink
Methyl orange
Litmus
Bromothymol blue
Phenolphthalein
6.0
7.0
9.5
A weak acid, HX, dissociates as follows:
HX(aq) .= x-(aq) + H'(aq)
-The -dissocfation ·coiitint, K-; for the above reaction Is 1.0 x llf1,-mol am-3 .-w!tafwill oo the-•
approximate pH of 1.0 x 10-2 mol dm-1 HX?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
29.
S
6
7
8
Using standard electrode potentials, which of the following reactions would be MOST feasible?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Zn(s) + Cu''(aq)-+ Zn'+ (aq) + Cu(s)
Zn(s) + Pb2•(aq) -+ Zn 2+(aq) + Pb(s)
Pb(s) + Zn2•(aq) -+ Pb2• (aq) + Zn(s)
Ca(a) + Zn2+(aq)- Cu,. (aq) + Zn(•)
•
00ONTO11fE NEXT PAOE
...
-9-
Item 30 refers to the electrochemical cell
below.
Zn(s) I Zn 2• (aq) II Ag+ (aq) IAg(s)
30.
In the cell shown above, electrons originate
from
(A)
31.
Zn( s) I Zn''( aq)
(C)
Ag•(aq) I Ag(s) II Zn(s) I Zn2'(aq)
(D)
Zn(s) I Zn''(aq) II Ag• (aq) IAg(s)
Which of the following sets of oxides is
classified rorrectly?
(D)
Acidic Amphoteric
Basic
co,
CuO
MgO
so,
so,
Al,03
so,
co
P,0 10
Feature
(A)
(B)
(C)
State at 25 °C
Solid
Solid
Liquid
Barium
Beryllium
Magnesium
Strontium
Gas
10
7
0
I
Match EACH oxide below with one of the
options (A, B, C, or D) above. Each option
may be used once, more than once or not at
all.
33.
Oxide of silicon
34.
Oxide of sulphur
35.
Group II elements of the periodic table have
Cao
(A)
Na,O
so,
(B)
(€)
Which of the following elements reacts very
slowly with cold water and burns with a
bright white flame?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(D)
Bonding and
Ionic Giant
Covalent Covalent
Structure in Oxide lattice covalent molecular molecular
pH of Aqueous
Solution
(B)
(A)
(B)
(C)
32.
Ag'(aq) I Ag(s)
Items 33-34 refer to the information in the
following table.
(D)
36.
high melting points and low
dens4ties
high electrical conductivities and
low densities
high melting points and high
electrical conductivities
low melting points and poor
electrical conductivities
The high meli:ing point of graphite ~an be
attributed to the
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
delocalised electrons
hexagonal arrangement of the
carbon atoms
van der Waals' forces between the
layers
strong covalent bonds within the
layers
,..,.., _...,
____ . ____ _
•
- I0 -
37.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
38.
(D)
40.
Aluminium
Chlorine
Sulphur
Phosphorus
1000
900
800
700
0
s 600
g 500
400
11-1
300
200
100
0
~
-
When AgNO,(aq) is added to fluoride ions
followed by NH3(aq) the result is
(A)
(B)
(C),
39.
Item 41 refers to the graph below showing
the first ionisation energy (IE) of some
elements.
Which of the following elements in the
third period has the same oxidation number in ALL of its known compounds?
no precipitate
white silver fluoride
yellow silver fluoride
cream-coloured ammonium fluoride
Elements
41.
In which of the following options are the
halide ions placed in order of INCREASING
reducing power?
(A)
Br-, Cl -, 1-
(B)
Cl-, 1-, Br·
Ca Sc Ti V Cr MnFe Co Ni Cu Zn
The sharp increase from copper (Cu) to zinc
(Zn) is caused by filled
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
4s-orbitals
d-orbitals
4s and d-orbitals
4s-orbitals and half-filled d-orbitals
(C)
c1-, Br·,1-
Item 42 refers to the information in the table
below.
(D)
I-, Br-, Cl -
Element
On heating CaSO• strongly, it decomposes
into CaO and SO,(g). CaCO, decomposes
ani mucfi lower temperature than CaSO,.
Which of the following factors BEST
explains the greater thermal stability of
CaSO,?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
CaC03 has a higher lattice energy
than Caso,.
CO, is a smaller molecule than SO,.
The co, 2 - ion is more easily
polarised than the SO,'-ion.
The co,>- ion has a higher charge
density than the so,>- ion.
42.
I
Melting
Point (°C)
1538
Density
II
660
2.70
III
328
11.34
(g cm-l)
7.86
Which of the elements in the table can be
classified as transition?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
I only
II only
I and II only
II and Ill only
•
00ONTO11fE NEXT PAOE
- 11 -
43.
Items 44-45 refer to the following options.
Which of the following metals gives a green
flame when heated?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Calcium
Copper
Magnesium
Sodium
A central ion in a complex
A ligand
An octahedral complex
A tetrahedral complex
Match EACH formula below with one of the
options (A, B, C or D) above. Each option
may be used once, more than once, or not at
all.
44.
[Co(H,O)J>+
45.
CH,NH 2
•
END OF TEST.
IF YOU FINISH BEFORE TIME IS CALLED, CHECK YOUR WORK ON THIS TEST.
•
02112010/CAPE 2013