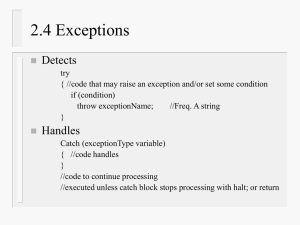
Introduction to Data Structures Dr. Partha Pratim Sarangi July 26, 2021 KIIT Deemed to be University Presentation Outline Introduction Fundamentals Data Types Abstract Data Type (ADT) Data Structure Comparison of Abstract Data Type and Data Structure Dr. Partha Pratim Sarangi Introduction to Data Structures 1/7 Introduction Prerequisite Knowledge I. Basic ’C’ programming constructs including primitive data types, operators, decision control, loops, and string. II. Derived data types: Arrays, pointers and functions III. User defined data types: Structures and unions IV. Dynamic memory allocation Note that, you have to practice some programs based on above topics using ’C’ programming language. Dr. Partha Pratim Sarangi Introduction to Data Structures 2/7 Fundamentals Basic Terminologies and Concepts • Data: Data means value or set of values. Values are raw facts including numerial values, text, graphs, sounds, images, video etc. • Entity : An entity is one that has certain attributes and each attribute holds value. It has existence. • For example, an employee in an organization is an entity. The possible attributes and the corresponding values for an entity as follows. Entity: EMPLOYEE Attributes: NAME DOB SEX DESIGNATION Values: Ravi Sankar 19/06/74 M Director • Note that, an entity after assigning its values results a composite data. • Information: It is defined as meaningful data or processed data. Given set of data are processed to retrieve information. • The terms data, entity, and information are quite useful in computer science. Dr. Partha Pratim Sarangi Introduction to Data Structures 3/7 Data Types Basic Terminologies and Concepts Continued... • Data Type: A data type is a term in computer programming which refers to the kind of data that is used in computation. • A data type defines a domain of allowed values and the set of operations that can be performed on those values. • For example, Numetric, Real, Boolean, Character, String, Alphanumeric, Date, Array of integer, Graphics, Image, etc. • Built-in Data Type or Primitive Data Type: Every programming language contains a predefined set of data types. • For example, ’C’ language contains seven built-in data types such as: char, short, int, long, float, double, long double. • Java language contains eight built-in data types as follows: boolean, char, byte, short, long, float, and double. • If an application needs to use a data type other than the primitive data types of a language, then the concept of Abstract Data Type (ADT) and Data Structure come into picture. Dr. Partha Pratim Sarangi Introduction to Data Structures 4/7 Abstract Data Type (ADT) Basic Terminologies and Concepts Continued... • An abstract data type (ADT): It is a mathematical model or concept that logically defines a user-defined data type. • It contains a set of data and the set of valid operations on it. • The specification of a set of data is independent of the actual implementation and so is abstract. • An Abstract data type consists of two parts: • Declaration of set of data • Declaration of operations • Think of ADT as a black box which hides the inner structure and design of the data type. • Commonly used ADTs include: Linked Lists, Stacks, Queues, Binary Trees, Dictionaries, Disjoint Sets, Hash Tables, Graphs, and many others. Dr. Partha Pratim Sarangi Introduction to Data Structures 5/7 Data Structure Basic Terminologies and Concepts Continued... • Data Structures: It is a programming construct used to implement an ADT. • Data structure is a physical approach of arranging and storing data in the computer memeory so that it can be used efficiently. • It is physical implementation of ADT. • ADT is the logical view of data and the set of operations which are perfromed on data. • While, Data structure is the physical representation of data and the algorithms to perform operation on data. • ADT is a logical description of operations while Data structure is concrete i.e., ADT tells us what is to be done and Data structure tells us how to do it. Dr. Partha Pratim Sarangi Introduction to Data Structures 6/7 Comparison of Abstract Data Type and Data Structure Abstract Data Type and Data Structure Figure 1: Illustrates difference between ADTs and Data Structures Dr. Partha Pratim Sarangi Introduction to Data Structures 7/7 Thank You! Dr. Partha Pratim Sarangi Introduction to Data Structures 8/7