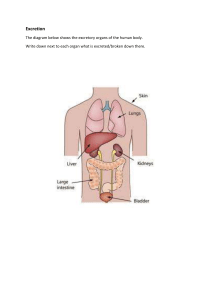
Could animal organs be transplanted into humans to save their lives Every year thousands of people die while waiting for an organ transplant. What if animal organs could save their lives? This idea, known as xenotransplantation, could be a ground-breaking solution to organ shortage. In the past couple years, there has been a tremendous organ shortage, as many people are being skeptical about donating organs. As a wider picture, there are multiple discussions about xenotransplantation about its benefits, the scientific and ethical concerns it raises and its broader implications for society. By analyzing both sides of the discussion, it aims to present a balanced perspective on whether this medical innovation is the right path forward. While some believe that transplanting organs from animals could be a feasible solution to organ shortage, others think that it's absolutely unethical. Firstly, the demand for organ transplants far exceeds the supply of available organs. According to World Health Organisation, over 130,000 people worldwide are waiting for organ donations with many patients dying before a suitable donor is found. Xenotransplantation can help bridge this gap by providing an alternative source of organs. Pigs, due to their physiological similarities to humans, are often considered ideal candidates for organ donation. Their organs such as kidneys and hearts are similar in size and function, potentially making them suitable for transplantation. Recent advances in xenotransplantation have shown promising results. In 2021, surgeons at the University of Maryland performed the first successful transplant of a genetically modified pig heart into a human patient. Although the patient later died, the procedure shows that it's possible for animal organs to function in the human body. This success paves the way for further research into refining the technique and overcoming the challenges that currently limits its use. If perfected. Xenotransplantation could provide a life-saving alternative for patients who would otherwise have no options. Despite the potential benefits, xenotransplantation raises significant ethical concerns, particularly regarding animal welfare. The process of genetically modifying animals to make their organs compatible with human biology involves potential harm and suffering. Pigs, for example, may undergo painful procedures that could lead to health complications. Many critics argue that using animals for organ harvesting, particularly when it involves genetic modification or suffering, raises serious moral concerns. The ethical debate centers around whether humans have the right to manipulate and harm animals for benefit of human health. Another major risk of xenotransplantation is the risk of disease transmission from animals to humans. Even with genetic modifications, animal organs may carry viruses or bacteria that could be harmful to humans. A major concern is for cross-species infections, which could lead to development of new diseases. In 2001, researchers observed that a transplanted pig heart in a baboon led to viral complications. Though scientists are working to reduce the risk of disease transmission, the possibility of unforeseen infections remains a significant barrier to widespread use of animal organs. However, advancements in genetic engineering & organ preservation may help address some of the challenges of xenotransplantation. In recent years scientists have developed genetically modified pigs whose organs are more likely to be accepted by the human immune system, reducing the risks of organ rejection. In addition, techniquesto improve organ preservation could make transplants safer and more successful. Researchers are also exploring ways to 'humanize' animal organs to better match human biological conditions, which could improve compatibility & long term outcomes for recipients. In conclusion, while xenotransplantation provides a potential solution to the organ shortage crisis, it is not without significant challenges. The promise of saving lives by using animal organs must be weighed against the ethical concerns regarding animal welfare & risk of disease transmission. Although recent advances in genetic engineering show promising breakthroughs, the long-term safety and effectiveness of xenotransplantation remains uncertain. Further research is needed so we can address such challenges and ensure that any use of animal organs for human transplants is safe, ethical, and beneficial for patients. All-in-all xenotransplantation can play a massive role in the future of medicine, but careful consideration of both scientific and ethical factors is extremely crucial before it becomes a global practice.