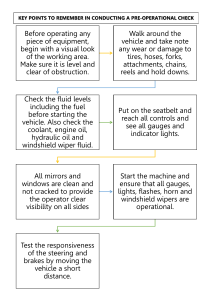
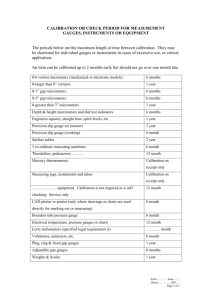
What is Tolerance ? Permissible variation in the size (dimension) of a component to suit Functional Requirements How to choose Tolerance? •Cost of Production •Productivity (Time) •Availability of Manufacturing Resources Tolerance Callout Hole : 25 H7 Shaft : 25 g6 Assembly : 25H7g6 Tolerance Zones – Shaft and Hole GAUGES Gauging, done in manufacturing processes, refers to the method by which it is determined quickly whether or not the dimensions of the checking parts in production, are within their specified limits. It is done with the help of some tools called gauges. Gauges are the tools which are used for checking the size, shape and relative positions of various parts but not provided with graduated adjustable members. Gauges are, therefore, understood to be single-size fixed-type measuring tools. Classifications of Gauges (a) Based on the standard and limit • Standard gauges • Limit gauges or “go” and “not go” gauges (b) Based on the consistency in manufacturing and inspection • Working gauges --Working gauges are those used at the bench or machine in gauging the work as it being made. • Inspection gauges --These gauges are used by the inspection personnel to inspect manufactured parts when finished. • Reference or master gauges --These are also called master gauges. These are used only for checking the size or condition of other gauges and represent as exactly as possible the physical dimensions of the product. (c) Depending on the elements to be checked • Gauges for checking holes • Gauges for checking shafts • Gauges for checking tapers • Gauges for checking threads • Gauges for checking forms (d) According to the shape or purpose for which each is used • Plug • Ring • Snap • Taper • Thread • Form • Thickness Go-NoGo Limit Gages Objective •Check if the part size is within the Upper and Lower size Limits •Go gage should always go (into the part). •NoGo gage should NOT go. •Go gage should check both part Form and Dimension. Taylor’s Principle for Gage Design Go gage size corresponds to the Maximum Material Condition (MMC) of the Part. • Upper size limit for Shaft • Lower size limit for Hole