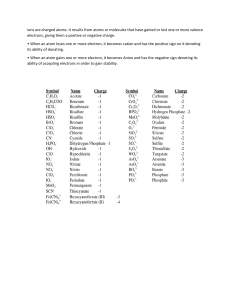
CHEMISTRY the ionicbond ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond that occurs between two atoms when one atom transfers electrons to another usually happens between metals and non-metals · how does ionic · bonding work ? O atoms and electrons each atom has electrons that orbit the nucleus arranged in · , shells atoms want to fill their outer/valence shell with electrons to reach the most stable / lowest-energy state they can (by satisfying the · octet rule ① formation ot ions metals (like sodium) tend to have fewer electrons in their outer shell and tend to lose them. When they lose · an electron. they become a positively charged ion / cation . non-metals (like chlorine) tend to have more · electron they become , a electrons in their outer shell and tend to gain electrons When they gain . negatively charged ion/anion. * sodium chloride (Nack) eg * Na a) sodium atom · b) * + : :: 11 · in its outer shell xxH Chlorine atom · · *** sodium (Na) has one electron an * Chlorine (C1) has seven electrons in its outer shell N X c) ionic bond formation XX :: · * & · · when sodium loses its electron , and chlorine gains that electron , they become ions the positively charged sodium ion (Nat) and negatively charged chlorine ion attract each other forming an ionic , bond (Nack) the covalent bond · · covalent bonding involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms typically occurs between non-metals and allows atoms to achieve full outer shells how does covalent bonding work ? ① atoms and electron configuration · atoms aim to have a full valence shell which usually means 8 electrons (according to the octet , for rule) , except for hydrogen and helium which aim 2 ① single/double/triple bonds · · single bond = double bond : one pair of electrons is shared leg #2 two pairs of electrons are shared - . H leg O . - H) = 0 = 0 triple bond · = three pairs of electrons shared leg (1 - N = N . eg water (H2O) a) hydrogen atom each hydrogen atom has · I electron and needs one more for afull outer shell b) oxygen atom oxygen has 6 electrons and needs [more: · it can share 1 electron with each hydrogen atom ⑧ D c) overall structure consists of two single covalent · gas tests O glowing splint test a · H H HO · : 0 % H bonds" test for oxygen (0 ) . a - % glowing splint (a wooden stick that has been burned and is still glowing) is inserted into a test tube containing the gas if oxygen is present the splint will reignite · , ② pop test · · test for hydrogen (H) a - a lit splint is brought near the gas if hydrogen is present it will produce a characteristic "pop" sound , ③ limewater test - a test for carbon dioxide (CO) bubble the gas through lime water (a dilute solution of calcium hydroxide) (Ca[OH]e) · (CaCOs) if carbon dioxide is present the limewater will turn cloudy due to the formation of calcium carbonate · , ① blue litmus paper test use · - a test for chlorine (((2) damp blue litmus paper and place it in a container with the gas if chlorine is present the blue litmus paper will turn red and may eventually bleach white · , ⑤ red litmus paper test · · - a test for ammonia (NHs) bring damp red litmus paper close to the gas if ammonia is present the red litmus paper will turn blue , metal ion solutions O test for Calcium · · · reagent = (Ca2t) Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) add a few drops of sodium hydroxide to the solution hydroxide to the solution containing calcium ions a white precipitate of calcium hydroxide Cal + 2NaOH - (Ca[OH],) may form CaCOH)c + I Nat