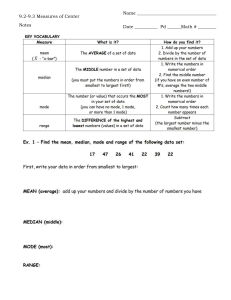
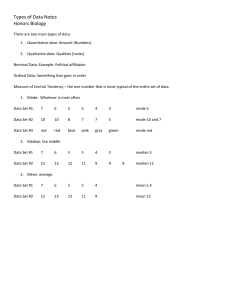
UNGROUPED DATA Introduction Fields of Statistics 1. Applied Statistics is concerned with the procedures and techniques used in collection, presentation, organization, analysis and interpretation of data. 2. Theoretical statistics is concerned with the development of the mathematical foundations of the methods used in applied statistics. Areas of interest in Applied Statistics 1. Descriptive statistics includes all the techniques used in organizing, summarizing and presenting the data on hand. 2. Inferential statistics includes all the techniques used in analysing the sample data that will lead to generalizations about a population from which the sample came from. Descriptive Statistics Measures of Central Tendency are descriptive measures that are used to describe the center of a set of data, arranged numerically. 1. The arithmetic mean is the most commonly used measure of central tendency. When we speak of average, we always refer to the mean. 2. The median is the value that divides the array into two equal parts. It is the midpoint of the data array. 3. The mode is the observed value that occurs with the greatest frequency in a data set. Measures of Central Tendency for Ungrouped Data Finding the mean To find the mean of ungrouped data use : 𝚺𝒙 x= 𝑵 Where : x = mean 𝚺𝒙 = sum of the given observations N = number of observations Measures of Central Tendency for Ungrouped Data Examples Six friends in a Mathematics class receives test grades of 92, 84, 65, 76, 88, and 90. Find the mean of these scores. 𝚺𝒙 x= 𝑵 𝟗𝟐 + 𝟖𝟒 +𝟔𝟓 + 𝟕𝟔 + 𝟖𝟖 + 𝟗𝟎 = 𝟔 495 = 6 x = 82. 5 Measures of Central Tendency for Ungrouped Data Examples The ages of five contestants in a Statistics Quiz Bee are the following: 18, 17, 18, 19, and 18. Find their average age. 𝚺𝒙 x= 𝑵 𝟏𝟖 +𝟏𝟕 +𝟏𝟖 +𝟏𝟗 +𝟏𝟖 = 𝟓 90 = 5 x = 18 Measures of Central Tendency for Ungrouped Data Finding the median Before finding the median, the data must be arranged in order, from least to greatest value. The median will be a specific value or will fall between two values. If the number of data is odd, the median is the middle value If the number of data is even, add the two middle values then divide the sum by 2. Therefore, the median is 𝒙𝟑 + 𝒙𝟒 = 𝟐 Measures of Central Tendency for Ungrouped Data Examples Seven mothers were selected and given a blood pressure check. Their systolic blood pressure were recorded as follows: 135 121 119 116 130 121 131. Find the median. Solution: arrange the data in order 116, 119, 121, 121, 130, 131, 135 There are seven observations in the data, and 7 is an odd number so the median is the middle value which is the fourth value. Therefore, the median , = 121 Measures of Central Tendency for Ungrouped Data Examples Find the median of the following: 5, 5, 2, 7, 9, 10, 7, 8, 6 , 14, 20, 25 Solution: arrange the data in order: 2, 5, 5, 6, 7, 7, 8, 9, 10, 14, 20, 25 There are twelve observations in the data, and 12 is an even number so the median are the two middle values which are the 6th and the 7th value. Therefore, the median , 𝒙𝟔 + 𝒙𝟕 𝟕 + 𝟖 𝟏𝟓 = = = = 𝟕. 𝟓 𝟐 𝟐 𝟐 Measures of Central Tendency for Ungrouped Data Finding the mode The mode is the value that occurs most often in a data set. If there is only one mode the set is unimodal; if there are 2 modes, then it is bimodal. More than 2 modes shows a data. Example: Find the mode of the given data: 15, 28, 25, 48, 22, 43, 39, 44, 43, 49, 22, 33, 27, 25, 22, and 30. The number that appeared most is 22. Therefore the mode is 22. The data is unimodal. Measures of Central Tendency for Ungrouped Data Example: Find the mode of the given data: 121, 110, 120, 119, 121, 118, 115, 107, 115, The numbers that appeared most are 115 and 121 . Thus, the data has two modes, and the data is said to be bimodal. Measures of Central Tendency for Ungrouped Data The Weighted Mean Weighted mean - is a type of mean that is calculated by multiplying the weight (or probability) associated with a particular event or outcome with its associated quantitative outcome and then summing all the products together. To find the mean of ungrouped data use : 𝚺 (𝒙∙𝒘) x= 𝚺𝒘 Where : x = weighted mean 𝚺 (𝒙 ∙ 𝒘)= sum of the products formed by multiplying each number by its assigned weight. 𝚺𝒘 = the sum of all the weights Measures of Central Tendency for Ungrouped Data What is the weighted mean of the ff: Subject Grade (x) Units (w) (𝒙 ∙ 𝒘) Mathematics 3.00 3 9.0 English 2.00 3 6.0 P.E. 1.25 2 2.5 𝜮𝒘=8 𝜮 (𝒙 ∙ 𝒘) = 17. 5 𝚺 𝒙∙𝒘 x= 𝚺𝒘 𝟏𝟕.𝟓 = = 𝟐. 𝟏𝟖𝟕𝟓 ≈ 𝟐. 𝟏𝟗 𝟖