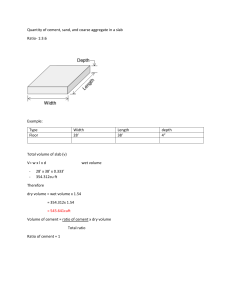
QUARRY CRUSHER STOCKPILE COAL COAL CRUSHER RAW COAL HOPPER RAW MILLER COOLER COAL MILLER CEMENT MARKET NAME: DESALES, SHAIRA MAE G. PACKING ROTARY KILN GYPSUM CEMENT SILO TITLE: PROCESS FLOW DIAGRAM OF CEMENT PROCESSING PLANT CEMENT MILLER FLYASH SUBJECT: MEC132: MANUFACTURING AND INDUSTRIAL PROCESSES WITH PLANT VISIT 1. Belt Conveyors - transported quarried raw material to the cement plant. 2. Impact Crusher - a machine that uses high-speed impacts to break down materials into smaller pieces. 3. Limestone Stockpile - used to store the material. 4. Additives Storage Hooper - storage for a certain additive such as iron ore, bauxite, laterite, quartzite, and fluorspar. 5. Raw Mill - raw material is finished ground before being fed into the kiln for clinker. This grinding is done by using vertical roller mills. 6. Blending and Storage Silo - to blend and homogenize the raw materials properly. 7. Preheater - offer heat transfer from the hot kiln gases. 8. Gas Conditioning Tower - used to reduce the temperature and increase the moisture level of the dusty exhaust gas from the kiln, before it passes through the bag house and ESP. 9. ESP - Electrostatic Precipitators are used in cement plants, particularly for the removal of dust from the exit gases of cement kilns and from the exhaust air discharged by dryers. 10. Kiln - a long cylindrical pipe, that rotates in a horizontal position. Its internal surface is lined by refractory bricks. 11. Cooler - cold air is blown to affect the heat exchanger between hot clinker and cold air. 12. Deep Bucket Conveyor - equipment to lift material vertically. 13. Clinker Storage - the output of the kiln is stored before it is fed to the cement mill for conversion to cement. 14. Gypsum Storage - storage space used for gypsum storage. 15. Coal Mill - houses the mill for grinding lumpy coals. 16. Cement Mill and Bag House - clinker along with additives is ground in a cement mill and bag house, and applied to large filters containing a number of tubular bags. 17. Cement Storage Silo - used for storing the finished product. 18. Packing and Dispatch - the cement is packed with the help of a rotary pacher and finally dispatched to the market. NAME: DESALES, SHAIRA MAE G. TITLE: PROCESS FLOW DIAGRAM OF CEMENT PROCESSING PLANT SUBJECT: MEC132: MANUFACTURING AND INDUSTRIAL PROCESSES WITH PLANT VISIT H20 HOPS BARLEY SILO MILLING MASHING LAUTERING BOILING WHIRLPOOLING COOLING YEAST DELIVERY PACKAGING NAME: DESALES, SHAIRA MAE G. BOTTLING FILTERING TITLE: PROCESS FLOW DIAGRAM OF BREWERY PROCESSING PLANT CONDITIONING FERMENTATION SUBJECT: MEC132: MANUFACTURING AND INDUSTRIAL PROCESSES WITH PLANT VISIT 1. Malting - here, carbohydrates turn into dextrin and maltose. The grain commonly used is barley, which can last long after being harvested. The malted barley is responsible for the special color and flavor of beer. 2. Milling - the malt is mixed with water to complete the conversion of starches in the grain to sugar. After that, the grain is milled to create the proper consistency to the malt. 3. Mashing - converts the starches released during the malting stage, into sugars that can be fermented. 4. Lautering - the liquid containing the sugar extracted during mashing is now separated from the grains. It is then generally termed as wort. 5. Wort Boiling - Boiling the wort, ensures its sterility and thus prevents a lot of infections. Hops are added during this stage of boiling. Hops are used to add flavor and aroma to balance the sweetness of the malt. 6. Cooling - the wort is hot after the boil and in need of cooling so, yeast can be pitched. 7. Fermentation - the yeast is now added, and the beer is fermented. The yeast breaks down the sugars extracted from the malt to form alcohol and CO2. 8. Conditioning - reduces the levels of these undesirable compounds to produce a more finished product. 9. Filtering - helps to remove excess of the yeast and any solids, like hops or grain particles that remains in the beer. This process which produces the clear, bright and stable beer. 10. Packaging - putting the beer into the bottles, cans or some other high-volume vessels. One of the most important things in packaging is to exclude oxygen away from the beer. NAME: DESALES, SHAIRA MAE G. TITLE: PROCESS FLOW DIAGRAM OF BREWERY PROCESSING PLANT SUBJECT: MEC132: MANUFACTURING AND INDUSTRIAL PROCESSES WITH PLANT VISIT ACTIVATION HOPPER LITTER STORAGE DRYER MILLING RINSE TREATMENT PELLETIZER PYROLSIS ASH TO DISPOSAL HCL WATER TO SEWER COOLING HCL STORE AND MIX CARBON WASHING DEWATERING PRODUCT DRYING SCREENING PRODUCT STORAGE PACKAGING NAME: TITLE: DESALES, SHAIRA MAE G. PROCESS FLOW DIAGRAM OF GRANULAR ACTIVATED-CARBON PROCESSING PLANT DELIVERY SUBJECT: MEC132: MANUFACTURING AND INDUSTRIAL PROCESSES WITH PLANT VISIT 1. Dryer - uses the waste heat of the carbonization furnace and activation to dry materials. 2. Mill - break down solid materials into smaller fragments. 3. Pelletizer - a mixture of raw materials and binder is molded into a cylindrical shape. 4. Pyrolysis - thermal decomposition process where raw material of high molecular weight is decomposed or cracked to produce primary volatiles. 5. Activator - the carbonized char is heated to high temperature and treated with gases like steam and carbon dioxide. This process created pores by causing the carbonized char to shrink and develop cracks. 6. Cooler- to reduce high-temperature material and directly enter the packaging. 7. Acid Washer Tank - maintains the activity of activated carbon. Throughout the operation, carbon will typically become begrime due to an accumulation of precipitated mineral salts. 8. Product Dryer - dries the activated carbon to remove excess moisture. NAME: TITLE: DESALES, SHAIRA MAE G. PROCESS FLOW DIAGRAM OF GRANULAR ACTIVATED-CARBON PROCESSING PLANT SUBJECT: MEC132: MANUFACTURING AND INDUSTRIAL PROCESSES WITH PLANT VISIT