Storage Devices: Theory Notes - Types & Characteristics
advertisement

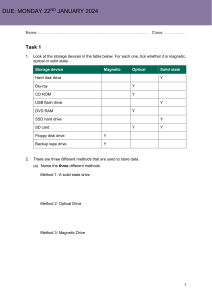
Ch.4: Storage Devices Theory Notes 4.1 Backing storage Definition and characteristics: • Non-volatile storage • Stores data permanently • Not directly accessed by the CPU, so it’s slower to access than the main memory Purpose: • • • For permanent storage of files and software To store data that is not currently required by the CPU To store data to transfer it to another computer The following table shows the differences between Main memory and backing storage: Main/Internal memory Backing storage Directly accessible by CPU Not directly accessible by CPU Faster access speed Slower access speed Tends to have greater storage RAM and ROM are fixed inside the computer Backing storage can either be fixed or it can be removable Can be volatile (RAM) and non-volatile (ROM) Non-volatile More expensive per unit storage Cheaper per unit storage Stores start-up instructions permanently (ROM) and stores data, instructions, software during processing (RAM) Stores files and software permanently Factors to consider when comparing backing storage devices: • Storage capacity • Data transfer rate • Data access time • Durability • Portability • Price per GB Data transfer rate: Rate at which data can be sent from a storage device to a computer (or vice versa). Data access time: Time it takes to locate specific data stored on a storage media. Eng. Omar El Safty 33 Eng. Mustafa El-Komy Ch.4: Storage Devices Theory Notes 4.2 Storage media vs. Storage device Storage Media definition: Hardware on which the data is stored (for example, CD and DVD). Storage Device definition: Hardware used to read from or write to the media (for example, a CD/DVD reader or writer). 4.3 Magnetic media and magnetic storage devices Fixed Hard Disk Drive (HDD) Advantages: • Large storage capacity • Fast data transfer rate • Fast data access times • Has great read/write longevity Disadvantages: • An incorrect shutdown procedure could lead to loss of data • They have many moving parts, which can affect their overall reliability • Quite noisy when compared to SSDs Uses: • To store the operating system • To store system software and working files • In real-time systems (systems that need fast retrieval and storage of data) • Used in file servers for computer networks Portable Hard Disk Drive Advantages: • Large storage capacity • Fast data transfer rate • Fast data access times • Portable, so it can be used in file transfer Disadvantage: • An incorrect shutdown procedure could lead to loss of data • They have many moving parts, which can affect their overall reliability • Data transfer rate is not as fast as for fixed hard drives Eng. Omar El Safty 34 Eng. Mustafa El-Komy Ch.4: Storage Devices Theory Notes Uses: • To store backups • To transfer data between computers Magnetic Tape Drive Advantages: • Huge storage capacity • It is a very robust technology (lasts for a long time) • Fast data transfer rate • Cheaper per unit memory than HDD Disadvantages: • Very slow data access times - Data is accessed serially; this means files are accessed one by one • They are affected by magnetic fields Uses: • To store backups • Used in long-term archiving of data Magnetic media example: Magnetic tape Magnetic devices examples: Hard disk drive, Portable hard disk drive, Magnetic tape drive 4.3.1 Optical media and optical storage devices Advantages of optical media: • • Cheaper to buy than other storage devices (as they tend to have small storage space) Portable Disadvantages of optical media: • • • • Tends to have lower storage space than other types of storage devices Slow data transfer rate Slow access times Not compatible with all computers Eng. Omar El Safty 35 Eng. Mustafa El-Komy Ch.4: Storage Devices Theory Notes CDs and DVDs CDs and DVDs can be categorized as follows: • ROM – can only be read • R – write only once • RW – can be written to or read from many times CD-ROM and DVD-ROM Advantage: • Prevents the deletion or overwriting of important data Disadvantages: • Data transfer rate is slower than for hard disks • Data access times are slower than for hard disks Uses: • Used in applications where there is a need to prevent the deletion or overwriting of important data • CD-ROMs are used to store music, software, and computer games • DVD-ROMs are used to store movies and more sophisticated computer games CD-R and DVD-R Advantages: • Cheaper to buy than RW disks for the same storage • Once burned, they behave like ROM, which protects against accidental overwriting of data Burning refers to adding data to an optical device. Disadvantages: • Can only be recorded once; if an error occurs, then the disk must be thrown away • Not all CD/DVD drives can read them Uses: • Archiving of data • File transfer between different computers Eng. Omar El Safty 36 Eng. Mustafa El-Komy Ch.4: Storage Devices Theory Notes CD-RW and DVD-RW Advantages: • Can be written over many times • Not as wasteful as R format as the files/data can be added at a later stage Disadvantages: • More expensive to buy than ROM and R formats for the same storage • It is possible to accidentally overwrite data Uses: • To store data and backups • File transfer between different computers • Used in CCTV systems DVD-RAM Main Advantage: • Can read and write data at the same time • Has greater storage capacity than CDs Main Disadvantage: • More expensive to buy than other CDs (and DVDs for the same storage) Uses: • To store backups • File transfer between different computers Blu-ray disc Advantages: • Greater storage capacity than other optical media • Faster data transfer rate than other optical media • Faster data access times than other optical media • Automatically comes with a secure encryption system that helps to prevent piracy and copyright infringement Disadvantage: • The most expensive optical media to buy Uses: • To store HD movies and games • To store backups • File transfer between different computers Eng. Omar El Safty 37 Eng. Mustafa El-Komy Ch.4: Storage Devices Theory Notes We can summarize the differences between different optical media in the following diagram: CD DVD DVD-RAM Blu-ray disc Greater storage capacity Faster data transfer rate Faster data access times More expensive to buy Optical media examples: CD, DVD, Blu-ray disc Optical devices examples: CD drive, DVD drive, Blu-ray drive 4.3.2 Solid-state media and solid-state storage devices Solid State Drives (SSDs) Advantages of SSDs over HDDs: • • • • • • • • Faster access times Faster data transfer rate No moving parts, so more reliable Less power consumption They run much cooler They occupy less physical space They run quieter They are lighter Disadvantages of SSDs over HDDs: • More expensive per unit memory • HDDs have greater longevity than SSDs Uses: • To store the operating system • To store system software and working files • In real-time systems (systems that need fast retrieval and storage of data) • Used in smartphones and tablets as the main backing storage device Any device that uses solid-state technology can be referred to as a flash drive. Eng. Omar El Safty 38 Eng. Mustafa El-Komy Ch.4: Storage Devices Theory Notes Pen drive/Memory stick Advantages: • Very portable and compact • Very robust • Not affected by magnetic fields Disadvantages: • Easy to lose • Lower storage capacity compared to HDDs • More expensive per unit memory than HDDs Uses: • To store backups • File transfer between different computers Memory cards Examples: • SD cards (secure digital card) - Used in digital cameras, audio players, smartphones and tablets • XD cards (extreme digital card) - Used in digital cameras • CFast card (compact-fast card) - Used in expensive digital and video cameras Advantages: • Small and can be easily removed and used in another device • Very durable Disadvantages: • More expensive per unit memory than HDDs • Have a lower storage capacity than HDDs • Not all computers come with memory card readers built-in Uses: • To store photos on a digital camera • Used as mobile phone memory cards • To store backups in hand-held devices Eng. Omar El Safty 39 Eng. Mustafa El-Komy Ch.4: Storage Devices Theory Notes Error messages that may appear when attempting to save the work on memory cards: • Device not recognized • Corrupt card • Medium is full • Write error • Virus found on the card Solid-state media example: Memory cards (SD card, XD card, CFast card) Solid-state devices examples: SSD, Flash drive, Pen drive, Memory card reader The following table summarizes the comparison between different types of storage: Magnetic Storage Optical Storage Solid-State Storage Highest Low High Data Access Speed Fast (Except for Magnetic Tape Drive) Slow Fastest Data Transfer Rate Fast Slow Fastest Durability Vulnerable to shocks and magnetic fields More durable/robust than magnetic storage More durable/robust than optical and magnetic storage Price Per GB Low Low High Special Characteristics Great longevity Not compatible with all devices Storage Capacity Eng. Omar El Safty 40 • • • Runs cool Low power consumption Runs quietly Eng. Mustafa El-Komy Ch.4: Storage Devices Theory Notes 4.4 Cloud storage (Cloud computing) Definition: • Online storage platform • Data is stored in a remote physical location .. • .. using hundreds of interlinked data servers A server is a computer. Data servers used to store data are referred to as Cloud. How data is stored using cloud storage: • User accesses the cloud storage using the internet .. • .. from any device • User uploads files to a data server • Users pay a monthly/annual fee for storage used How data is managed using cloud storage: • The server is managed by a cloud provider • Data is automatically backed up • If one server fails, there are others used as backup Steps to transfer files from a computer at home to another computer at university using cloud storage: 1 User logs into the cloud from any device at home using the internet 2 User ensures sufficient storage in the cloud account 3 User uploads the files from his home computer to the data server 4 User then logs into the cloud storage account from the university’s computer using the internet 5 Finally, the user downloads the files on the university’s computer Advantages compared to storing data locally: • Data is accessible at any time, from any device, anywhere in the world, provided internet access is available • More available storage space • Storage capacity can be increased without adding additional physical devices • Automatic backups can be made • Users only pay for the storage they use • No need to carry any storage device, so data will not be lost if the storage device is lost/stolen Eng. Omar El Safty 41 Eng. Mustafa El-Komy Ch.4: Storage Devices Theory Notes Disadvantages compared to storing data locally: • May lose access to data if internet connection is lost/not available • Users must have a reliable internet connection to store data • Could incur an ongoing cost • Reliant on the cloud provider to maintain the hardware • Loss of control over the storage of data (storage is controlled by the cloud provider) • May be less secure as multiple copies of the data are stored for a long period of time Last two disadvantages are issues related to the security of data in the cloud. Eng. Omar El Safty 42 Eng. Mustafa El-Komy